Chapter 8 Sections 1-4
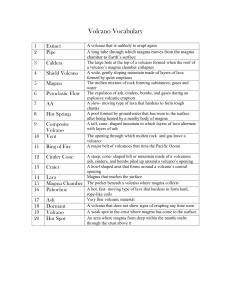
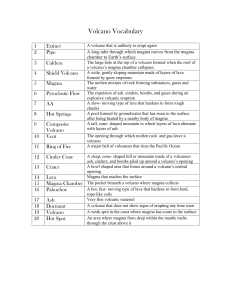
... • Thon The earTh’s e poinT surface directly above an earthquakes starting point. • The most common method by which seismologisTs find an earThquake’s epicenter is the ...
... • Thon The earTh’s e poinT surface directly above an earthquakes starting point. • The most common method by which seismologisTs find an earThquake’s epicenter is the ...
Plate Tectonics Lecture Notes
... Observations: Where very old mountain ranges or mineral deposits like coal and diamonds are found along the coast of one continent, they are also found on the coast of the another continent at the place where the continents “fit together.” Observations: Identical fossils of plants and animals have b ...
... Observations: Where very old mountain ranges or mineral deposits like coal and diamonds are found along the coast of one continent, they are also found on the coast of the another continent at the place where the continents “fit together.” Observations: Identical fossils of plants and animals have b ...
Mountain Belts and Continental Crust
... Size of an area that needs to stay in isostatic equilibrium increases with time as the planet has cooled and the lithosphere has thickened. Early on, 'isostatic size' was very small, now it is around 100km. (Think of ice thickening on a pond: with thin ice, any weight causes warping, as the ice get ...
... Size of an area that needs to stay in isostatic equilibrium increases with time as the planet has cooled and the lithosphere has thickened. Early on, 'isostatic size' was very small, now it is around 100km. (Think of ice thickening on a pond: with thin ice, any weight causes warping, as the ice get ...
18.2-notes-eruptions
... The composition of magma is what decides if the volcanic eruption is going to be explosive or quiet. Lava can be thin and runny or thick and lumpy. Temperature, pressure and the presence of water affect the formation of magma. TEMPERATURE: Rocks melt at temperatures between 800oC (1,472oF) and 1200o ...
... The composition of magma is what decides if the volcanic eruption is going to be explosive or quiet. Lava can be thin and runny or thick and lumpy. Temperature, pressure and the presence of water affect the formation of magma. TEMPERATURE: Rocks melt at temperatures between 800oC (1,472oF) and 1200o ...
Wednesday, February 18, 2015
... Susanne Buiter & Joya Tetreault: Geodynamic models of continental extension and subduction dynamics: insights into microcontinent formation and terrane subduction, accretion and collision ...
... Susanne Buiter & Joya Tetreault: Geodynamic models of continental extension and subduction dynamics: insights into microcontinent formation and terrane subduction, accretion and collision ...
• How do volcanoes influence climate? • How do volcanoes and
... Explain 3 ways can volcanoes form? (Divergent plate boundaries.; Convergent plate boundaries; hot spots) What is a hot spot? Why are eruptions quiet at hot spot volcanoes? How were the Hawaiian islands formed? Quiet vs. Explosive eruptions (silica; water; temps.; & viscosity) Volcano types ...
... Explain 3 ways can volcanoes form? (Divergent plate boundaries.; Convergent plate boundaries; hot spots) What is a hot spot? Why are eruptions quiet at hot spot volcanoes? How were the Hawaiian islands formed? Quiet vs. Explosive eruptions (silica; water; temps.; & viscosity) Volcano types ...
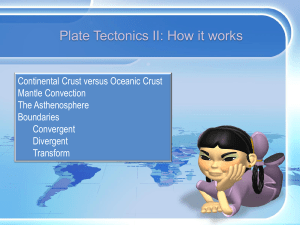
tectonics2
... convection. Hot mantle material rises at ridges and cooler mantle material sinks at subduction zones. ...
... convection. Hot mantle material rises at ridges and cooler mantle material sinks at subduction zones. ...
Slide 1
... Italian peninsula is almost parallel to the convergence direction between Africa and Eurasia. There is considerable earthquake activity along the Apennines BUT Earthquakes are concentrated beneath the mountains and descend to the depth of ~ 100 km. ...
... Italian peninsula is almost parallel to the convergence direction between Africa and Eurasia. There is considerable earthquake activity along the Apennines BUT Earthquakes are concentrated beneath the mountains and descend to the depth of ~ 100 km. ...
Lab: Plate Tectonic and Earthquake Extravaganza
... This motion is a very slow process and the upper portion of the earth is not especially capable of moving in slow continuous motion, so the movement of the plates is done in jerky motions that result in earthquakes. As these pieces of crust slide past one another they create waves that shake the gro ...
... This motion is a very slow process and the upper portion of the earth is not especially capable of moving in slow continuous motion, so the movement of the plates is done in jerky motions that result in earthquakes. As these pieces of crust slide past one another they create waves that shake the gro ...
Classifying Rocks
... metamorphic rock. These formation processes result in characteristic appearances and properties that enable classification of rocks into one of the three categories. 3 Deep under Earth's crust, the temperature is so high that it is hot enough to melt rocks. This molten rock called magma will eventua ...
... metamorphic rock. These formation processes result in characteristic appearances and properties that enable classification of rocks into one of the three categories. 3 Deep under Earth's crust, the temperature is so high that it is hot enough to melt rocks. This molten rock called magma will eventua ...
Lesson 4: Volcanoes Lesson Plan
... magma then forces its way back to the surface to form a volcano. The eruptions that happen at destructive boundaries tend to be violent because the converging plates do not simply glide under one another but undergo tremendous pressure, which can also cause earthquakes. Chile, in South America, has ...
... magma then forces its way back to the surface to form a volcano. The eruptions that happen at destructive boundaries tend to be violent because the converging plates do not simply glide under one another but undergo tremendous pressure, which can also cause earthquakes. Chile, in South America, has ...
Stephen D. Malone - Earth and Space Sciences at the University of
... After studying glacier-quakes on Mount Rainier and Mount St. Helens and a thermal transient on Mount Baker his topic really heated up in 1980 with the explosive eruptions of Mount St. Helens. Dr. Malone was in charge of the seismic monitoring during and since the beginning of this activity and pione ...
... After studying glacier-quakes on Mount Rainier and Mount St. Helens and a thermal transient on Mount Baker his topic really heated up in 1980 with the explosive eruptions of Mount St. Helens. Dr. Malone was in charge of the seismic monitoring during and since the beginning of this activity and pione ...
Clogher Head Formation - Geological Survey of Ireland
... a near-vertical cleavage that is refracted where it transects beds of differing competence. Some surfaces show tectonic rippling, an effect produced by intersection of cleavage and bedding. Lamprophyres are relatively uncommon basic or ultrabasic igneous rocks typically found as small intrusions and ...
... a near-vertical cleavage that is refracted where it transects beds of differing competence. Some surfaces show tectonic rippling, an effect produced by intersection of cleavage and bedding. Lamprophyres are relatively uncommon basic or ultrabasic igneous rocks typically found as small intrusions and ...
Day Six Lesson - Russell County Schools
... Igneous rocks form from the cooling and hardening of molten magma in many different environments. The chemical composition of the magma and the rate at which it cools determine what rock forms. Igneous rocks can cool slowly beneath the surface or rapidly at the surface. These rocks are identified by ...
... Igneous rocks form from the cooling and hardening of molten magma in many different environments. The chemical composition of the magma and the rate at which it cools determine what rock forms. Igneous rocks can cool slowly beneath the surface or rapidly at the surface. These rocks are identified by ...
Rocks pupil notes - Lesmahagow High School
... 1. Describe some of the properties of different types of rocks. 2. What test could you use to rate the hardness of a rock? 3. Which type of rock do YOU think would be best for buildings? ...
... 1. Describe some of the properties of different types of rocks. 2. What test could you use to rate the hardness of a rock? 3. Which type of rock do YOU think would be best for buildings? ...
Chapter 7:2 pages 198-201
... system of mid-ocean ridges that are underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins. 2. Mid-ocean ridges are places where sea-floor spreading takes place. Sea-floor spreading is the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies. ...
... system of mid-ocean ridges that are underwater mountain chains that run through Earth’s ocean basins. 2. Mid-ocean ridges are places where sea-floor spreading takes place. Sea-floor spreading is the process by which new oceanic lithosphere forms as magma rises toward the surface and solidifies. ...
Philippine Fault System
... In the west, more steeply eastdipping subduction of the Eurasian Plate (South China Sea basin and the transitional oceaniccontinental crust of the Palawan block) along the 560 mile (900 km) length of the Manila and Sulu trenches produces a discontinuous line of active volcanoes from Taal in the sou ...
... In the west, more steeply eastdipping subduction of the Eurasian Plate (South China Sea basin and the transitional oceaniccontinental crust of the Palawan block) along the 560 mile (900 km) length of the Manila and Sulu trenches produces a discontinuous line of active volcanoes from Taal in the sou ...
Appalachian Mountains
... The Appalachian Mountains—A Case Study Geologists have divided the Appalachians into several distinct regions. Each region is characterized by rocks that show different degrees of deformation. ...
... The Appalachian Mountains—A Case Study Geologists have divided the Appalachians into several distinct regions. Each region is characterized by rocks that show different degrees of deformation. ...
The Oldest Crust in Ocean Basins
... The oldest crust in the ocean basins is the Mesozoic crust located in the Pacific Ocean Basin (Figure 1). Scientists have been studying this area, in water depths of more than 6000m, through ocean drilling for more than three decades. The most recent penetration of the approximately 170 million-year ...
... The oldest crust in the ocean basins is the Mesozoic crust located in the Pacific Ocean Basin (Figure 1). Scientists have been studying this area, in water depths of more than 6000m, through ocean drilling for more than three decades. The most recent penetration of the approximately 170 million-year ...
PPT link ch 14
... Mantle = malleable layer on which the crust floats Core = molten heavy center of Earth made mostly of iron ...
... Mantle = malleable layer on which the crust floats Core = molten heavy center of Earth made mostly of iron ...
platetect
... specify both texture and composition. Thus, an arkose sandstone is a rock of sand sized particles, with a high percentage of those particles being feldspar. It might seem that an unlimited variety of particles could end up in a sedimentary rock. After all, there are over 6000 known minerals. In addi ...
... specify both texture and composition. Thus, an arkose sandstone is a rock of sand sized particles, with a high percentage of those particles being feldspar. It might seem that an unlimited variety of particles could end up in a sedimentary rock. After all, there are over 6000 known minerals. In addi ...
Plate Tectonics
... History of Events Leading up to the Formulation of the Theory of Plate Tectonics *Note that plate tectonics is a theory. It is not something that we can directly sample or touch, or for that matter prove. That is why we will refer to it as a theory. *In 1915, a Bavarian scientist named Alfred Wegen ...
... History of Events Leading up to the Formulation of the Theory of Plate Tectonics *Note that plate tectonics is a theory. It is not something that we can directly sample or touch, or for that matter prove. That is why we will refer to it as a theory. *In 1915, a Bavarian scientist named Alfred Wegen ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.