Plate Tectonics PowerPoint
... means “all of the earth”. Pangaea occurred during the Carboniferous period which happened about 3 million years ago. He originally came up with this theory in 1912 but it was not accepted by other scientists. It was not until 1950 (20 years after Wegener died) that they finally began accepting it. H ...
... means “all of the earth”. Pangaea occurred during the Carboniferous period which happened about 3 million years ago. He originally came up with this theory in 1912 but it was not accepted by other scientists. It was not until 1950 (20 years after Wegener died) that they finally began accepting it. H ...
The Restless Earth
... • You have 10 seconds… to draw the 4 layers of the earth • You have 20 seconds… to give two differences between oceanic and continental crust • You have 30 seconds… to draw and label a destructive subduction margin ...
... • You have 10 seconds… to draw the 4 layers of the earth • You have 20 seconds… to give two differences between oceanic and continental crust • You have 30 seconds… to draw and label a destructive subduction margin ...
Sample Chapter 3 - Plate Tectonics
... 3. Along the rift, magma erupts onto the seafloor as submarine lava flows, while other magma solidifies at depth. These magmatic additions create new oceanic crust along the spreading center and add to the oceanic plates as they move away. This entire process is called seafloor spreading. ...
... 3. Along the rift, magma erupts onto the seafloor as submarine lava flows, while other magma solidifies at depth. These magmatic additions create new oceanic crust along the spreading center and add to the oceanic plates as they move away. This entire process is called seafloor spreading. ...
Jeopardy_review
... If you know the difference in arrival time of p and s waves , you can figure out….. ...
... If you know the difference in arrival time of p and s waves , you can figure out….. ...
EGU2017
... of a typical accommodation zone trough the Ruzizi depression. However, this structure appeared only late in the development of the Western branch of the East African Rift System and is the result of a strong control by pre-existing structures of Precambrian to early Palaeozoic origin. In the frame o ...
... of a typical accommodation zone trough the Ruzizi depression. However, this structure appeared only late in the development of the Western branch of the East African Rift System and is the result of a strong control by pre-existing structures of Precambrian to early Palaeozoic origin. In the frame o ...
Author`s personal copy - Laboratoire de Planétologie et
... unconformably the Paleozoic Eastern Andean Metamorphic Complex (Bell and Suárez, 2000). Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous marine sedimentary rocks overlies unconformably the Ibañez Group (Suárez et al., 1996). The last major compressive phase which affected the Patagonian fold and thrust belt occurr ...
... unconformably the Paleozoic Eastern Andean Metamorphic Complex (Bell and Suárez, 2000). Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous marine sedimentary rocks overlies unconformably the Ibañez Group (Suárez et al., 1996). The last major compressive phase which affected the Patagonian fold and thrust belt occurr ...
Unit 5 Test - Ms. Williams
... 42. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of S waves? a. they travel more slowly than P waves b. they temporarily change the volume of material they pass through by compression and expansion c. they shake particles at right angles to their direction of travel – side to side, like a snake d. ...
... 42. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of S waves? a. they travel more slowly than P waves b. they temporarily change the volume of material they pass through by compression and expansion c. they shake particles at right angles to their direction of travel – side to side, like a snake d. ...
MT1_mtmeth
... • Underthrust sediments • Regions of metamorphism and partial melting • Fault zones (fractured, fluid-filled rock) *At crustal temperatures! ...
... • Underthrust sediments • Regions of metamorphism and partial melting • Fault zones (fractured, fluid-filled rock) *At crustal temperatures! ...
view PDF
... current regional geological setting of Namibia as well as the local geology of all the settlements including Windhoek. If we consider the whole earth, it has long been recognised that the earth is divided into several plates which move against or away from one another. Today there is evidence which ...
... current regional geological setting of Namibia as well as the local geology of all the settlements including Windhoek. If we consider the whole earth, it has long been recognised that the earth is divided into several plates which move against or away from one another. Today there is evidence which ...
volcano - from wikipedia
... flows and other ejecta in alternate layers, the strata that give rise to the name. Stratovolcanoes are also known as composite volcanoes, created from several structures during different kinds of eruptions. Strato/composite volcanoes are made of cinders, ash and lava. Cinders and ash pile on top of ...
... flows and other ejecta in alternate layers, the strata that give rise to the name. Stratovolcanoes are also known as composite volcanoes, created from several structures during different kinds of eruptions. Strato/composite volcanoes are made of cinders, ash and lava. Cinders and ash pile on top of ...
Convection and the Mantle
... The transfer of heat by the movement of a heated fluid is called convection. Fluids include liquids and gases. During convection, heated particles of a fluid begin to flow, transferring heat energy from one part of the fluid to another. Heat transfer by convection is caused by differences in tempera ...
... The transfer of heat by the movement of a heated fluid is called convection. Fluids include liquids and gases. During convection, heated particles of a fluid begin to flow, transferring heat energy from one part of the fluid to another. Heat transfer by convection is caused by differences in tempera ...
Historical Geology and the history of the continents
... Plate tectonics was ongoing through all of this time, bringing continents together to form mountain belts and tearing them apart to form ocean basins. Over all this time there were other changes taking place: ...
... Plate tectonics was ongoing through all of this time, bringing continents together to form mountain belts and tearing them apart to form ocean basins. Over all this time there were other changes taking place: ...
Volcanoes
... steep heap of loose rock held together by the force of gravity and a cubic mile of glacier ice that could be melted or shaken loose • Lahar flows average every 500 years and have gone as far as the Puget Sound lowlands (1 in 7 chance of it happening during your lifetime) • Mount Rainier has erupted ...
... steep heap of loose rock held together by the force of gravity and a cubic mile of glacier ice that could be melted or shaken loose • Lahar flows average every 500 years and have gone as far as the Puget Sound lowlands (1 in 7 chance of it happening during your lifetime) • Mount Rainier has erupted ...
Chapter 10: Plate Tectonics
... How could continents drift? Although Wegener provided evidence to support his hypothesis of continental drift, he couldn’t explain how, when, or why these changes, shown in Figure 4, took place. The idea suggested that lower-density, continental material somehow had to plow through higher-density, ...
... How could continents drift? Although Wegener provided evidence to support his hypothesis of continental drift, he couldn’t explain how, when, or why these changes, shown in Figure 4, took place. The idea suggested that lower-density, continental material somehow had to plow through higher-density, ...
Standards
... As early as the 1920’s scientists recognized that earthquakes lined up along fault zones and were not randomly scattered across the globe. The technology improved dramatically in the 1960’s when standardized seismic monitoring stations were established around the globe to police the ban on above-gro ...
... As early as the 1920’s scientists recognized that earthquakes lined up along fault zones and were not randomly scattered across the globe. The technology improved dramatically in the 1960’s when standardized seismic monitoring stations were established around the globe to police the ban on above-gro ...
Forest River – Field Trip
... Brief Geologic History of the North Shore The rocks exposed at Forest River Park are just a piece of the puzzle. Rarely is the geologic history of an area interpreted from a single location, but from data obtained regionally. The senario below describes the prevailing tectonic hypothesis interprete ...
... Brief Geologic History of the North Shore The rocks exposed at Forest River Park are just a piece of the puzzle. Rarely is the geologic history of an area interpreted from a single location, but from data obtained regionally. The senario below describes the prevailing tectonic hypothesis interprete ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... Igneous Rocks Form as magma cools and crystallizes Rocks formed inside Earth are called plutonic or intrusive rocks Rocks formed on the surface Formed from lava (a material similar to magma, but without gas) Called volcanic or extrusive rocks ...
... Igneous Rocks Form as magma cools and crystallizes Rocks formed inside Earth are called plutonic or intrusive rocks Rocks formed on the surface Formed from lava (a material similar to magma, but without gas) Called volcanic or extrusive rocks ...
ES 106 Laboratory # 4 - Western Oregon University
... basins are geologically young, ephemeral features. Based upon this discovery, a revolutionary theory called plate tectonics has been developed that helps to explain and interrelate earthquakes, mountain building, and other geologic events and processes. The theory of plate tectonics is the foundatio ...
... basins are geologically young, ephemeral features. Based upon this discovery, a revolutionary theory called plate tectonics has been developed that helps to explain and interrelate earthquakes, mountain building, and other geologic events and processes. The theory of plate tectonics is the foundatio ...
Candy Bar Tectonics
... Part A: Getting Ready 1. Use your fingernail to make small cracks in the surface of your “Earth” or candy bar. Place on a paper towel. What do we call the cracks in the Earth’s surface? ________________ What do we call the large pieces of Earth’s crust? ________________ 2. Compare the candy bar to t ...
... Part A: Getting Ready 1. Use your fingernail to make small cracks in the surface of your “Earth” or candy bar. Place on a paper towel. What do we call the cracks in the Earth’s surface? ________________ What do we call the large pieces of Earth’s crust? ________________ 2. Compare the candy bar to t ...
Rocks and minerals Minerals
... The size of the crystals is a basis for classification and relates to the mode of cooling of the original magma. Thus igneous rocks vary from fine grained to coarse grained with crystals ranging from as small as 1 mm across on the former to 3 mm or more across in the later. Igneous rocks are divisib ...
... The size of the crystals is a basis for classification and relates to the mode of cooling of the original magma. Thus igneous rocks vary from fine grained to coarse grained with crystals ranging from as small as 1 mm across on the former to 3 mm or more across in the later. Igneous rocks are divisib ...
Name
... 2. Similar animal and plant fossils were discovered in places that were far apart a. In matching coastlines of different continents 3. Age and kinds of rocks along the edge of one coastline are similar to those on another continent 4. Some mountain ranges on different continents seem to match ...
... 2. Similar animal and plant fossils were discovered in places that were far apart a. In matching coastlines of different continents 3. Age and kinds of rocks along the edge of one coastline are similar to those on another continent 4. Some mountain ranges on different continents seem to match ...
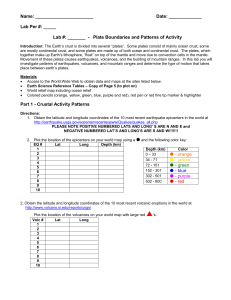
Crustal Boundaries and Patterns of Activity
... 3. Observe the World Seismicity Map at http://wwwneic.cr.usgs.gov/neis/general/seismicity/world.html. Plot the general locations of past earthquakes shown on this map by shading in those areas on your world map using the same color key for earthquake depth as in step 1. (Make sure the individual ea ...
... 3. Observe the World Seismicity Map at http://wwwneic.cr.usgs.gov/neis/general/seismicity/world.html. Plot the general locations of past earthquakes shown on this map by shading in those areas on your world map using the same color key for earthquake depth as in step 1. (Make sure the individual ea ...
GEOLOGY FOR MINING ENGINEERS
... Chances are small that the river flowing through your city will flood this spring, but if you lived to be 100 years old, you would probably see a catastrophic flood. When we study the 4.6 billion years of Earth history, they find abundant evidence of catastrophic events that are highly improbable in ...
... Chances are small that the river flowing through your city will flood this spring, but if you lived to be 100 years old, you would probably see a catastrophic flood. When we study the 4.6 billion years of Earth history, they find abundant evidence of catastrophic events that are highly improbable in ...
Who Wants to Be a Millionaire?
... Which of the following is a correct cause and effect relationship? A. Volcano-Sand Dune ...
... Which of the following is a correct cause and effect relationship? A. Volcano-Sand Dune ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.