Document
... continental rifts (orange): crustal extension via normal faulting leads to transport of heat to shallow levels, followed by cooling to a normal thermal gradient. ...
... continental rifts (orange): crustal extension via normal faulting leads to transport of heat to shallow levels, followed by cooling to a normal thermal gradient. ...
Instructor`s Manual to accompany
... 7. Earth processes are driven by two heat engines: one that is internal powered by heat from the earth's core; one that is external powered by the sun. 8. The earth's interior comprises three concentric zones: crust (thin, oceanic crust and thicker, continental crust), mantle (solid and thickest zon ...
... 7. Earth processes are driven by two heat engines: one that is internal powered by heat from the earth's core; one that is external powered by the sun. 8. The earth's interior comprises three concentric zones: crust (thin, oceanic crust and thicker, continental crust), mantle (solid and thickest zon ...
earthquake
... Long-Range Forecasts • Scientists don’t yet understand enough about how and where earthquakes will occur to make accurate long-term predictions. • A seismic gap is an area along a fault where there has not been any earthquake activity for a long period of time. ...
... Long-Range Forecasts • Scientists don’t yet understand enough about how and where earthquakes will occur to make accurate long-term predictions. • A seismic gap is an area along a fault where there has not been any earthquake activity for a long period of time. ...
Basic Geology and Groundwater - well drilling school
... And then just a minute before midnight, at 11.59 P.M., humankind makes its appearance on earth, or less than two million years ago. During this entire time, 4.6 billions years, geologic processes have been continually shaping the world. As an example, the basement rocks beneath Florida were once par ...
... And then just a minute before midnight, at 11.59 P.M., humankind makes its appearance on earth, or less than two million years ago. During this entire time, 4.6 billions years, geologic processes have been continually shaping the world. As an example, the basement rocks beneath Florida were once par ...
Timing and magma evolution of the Chelopech volcanic complex
... images and Laser Ablation (LA) ICP-MS analyses of the zircons help the proper interpretation of the geochronological data and give evidence for changes in the geochemistry and oxidation state of the magma. Isotope Sm–Nd and Rb–Sr whole rock and Hf-zircon analyses provide additional information about ...
... images and Laser Ablation (LA) ICP-MS analyses of the zircons help the proper interpretation of the geochronological data and give evidence for changes in the geochemistry and oxidation state of the magma. Isotope Sm–Nd and Rb–Sr whole rock and Hf-zircon analyses provide additional information about ...
Chapter 13 - MiraCosta College
... • Subducting plates—the demise of an ocean basin • The Farallon plate once occupied much of the eastern Pacific basin. – Beginning 180 million years ago, the Farallon plate was subducting beneath the Americas faster than it was being generated. – The plate got continually smaller and now only fragme ...
... • Subducting plates—the demise of an ocean basin • The Farallon plate once occupied much of the eastern Pacific basin. – Beginning 180 million years ago, the Farallon plate was subducting beneath the Americas faster than it was being generated. – The plate got continually smaller and now only fragme ...
Suggested Content SC 33 Earth and Space Science
... subduction zone, 19. Seafloor deep ocean trench, Spreading volcanic island arc 20. Shear Force (Japan or Allusions ...
... subduction zone, 19. Seafloor deep ocean trench, Spreading volcanic island arc 20. Shear Force (Japan or Allusions ...
Earthquakes: fault classification, terminology, stress
... • Plate movement concentrates energy in crust • When the stored energy exceeds the strength of the crust, the crust ruptures • The rupture generally occurs along faults because this is the weakest point • Japan’s earthquake was produced on a plate boundary ...
... • Plate movement concentrates energy in crust • When the stored energy exceeds the strength of the crust, the crust ruptures • The rupture generally occurs along faults because this is the weakest point • Japan’s earthquake was produced on a plate boundary ...
geology of the ahuachapan-chipilapa, el salvador ca geothermal zone
... According to its characteristics of lithology, grain size and texture. the pyroclastic materials can be classified as proximal, distal and fall deposits The material accumulated towards the roof of the chamber The must have been within a temperature range of 650 50 evacuation followed the "Zebra" ev ...
... According to its characteristics of lithology, grain size and texture. the pyroclastic materials can be classified as proximal, distal and fall deposits The material accumulated towards the roof of the chamber The must have been within a temperature range of 650 50 evacuation followed the "Zebra" ev ...
On the enigmatic birth of the Pacific Plate within the
... of the North American margin have previously been linked to the fringing subduction system (29, 30), whereas the remnants of the northwest Pacific appear to have traveled farther and are related to the Telkhinia subduction system (29). Our reconstruction links the birth of the Pacific Plate to the t ...
... of the North American margin have previously been linked to the fringing subduction system (29, 30), whereas the remnants of the northwest Pacific appear to have traveled farther and are related to the Telkhinia subduction system (29). Our reconstruction links the birth of the Pacific Plate to the t ...
Earthquakes T. Perron – 12.001 – March 17, 2010 In our lab on
... What happens during an EQ? Fault rupture nucleates at a point (focus or hypocenter). These are the first seismic waves emitted. Rupture propagates outward along the fault surface at a few km/s (~ speed of sound in rock), continuing to emit seismic waves. (Note, though, that much of the energy re ...
... What happens during an EQ? Fault rupture nucleates at a point (focus or hypocenter). These are the first seismic waves emitted. Rupture propagates outward along the fault surface at a few km/s (~ speed of sound in rock), continuing to emit seismic waves. (Note, though, that much of the energy re ...
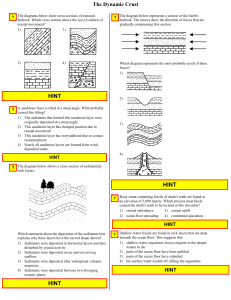
The Dynamic Crust
... ? To get sample material from the mantle, drilling will be done through the oceanic crust rather than through the continental crust because oceanic crust is 1) more dense than continental crust 2) softer than continental crust 3) thinner than continental crust 4) younger than continental crust ...
... ? To get sample material from the mantle, drilling will be done through the oceanic crust rather than through the continental crust because oceanic crust is 1) more dense than continental crust 2) softer than continental crust 3) thinner than continental crust 4) younger than continental crust ...
orogenesis and ore deposits
... Observations of sediments in the Precambrian shields indicate that break-down of rocks under weathering was less complete than in later times. Deformation and igneousactivity within orogenicbelts developed along the samegenerallines in the Precambrianas in subsequentgeologic time. Differences betwee ...
... Observations of sediments in the Precambrian shields indicate that break-down of rocks under weathering was less complete than in later times. Deformation and igneousactivity within orogenicbelts developed along the samegenerallines in the Precambrianas in subsequentgeologic time. Differences betwee ...
Quiz 2 Fall 2007 Handout Page
... a. 9.6 – 33.0 million years b. older than 141.9 million years c. younger than 9.6 million years d. 33.0 – 83.0 million years e. 83.0 – 141.9 million years ...
... a. 9.6 – 33.0 million years b. older than 141.9 million years c. younger than 9.6 million years d. 33.0 – 83.0 million years e. 83.0 – 141.9 million years ...
- UWI Seismic Research Centre
... the south-eastern margin of the Caribbean Plate. The Caribbean plate is bounded on its eastern margin by a portion of the North American (NA) Plate. At about 200 kilometres east of the chain of volcanic islands in the eastern Caribbean the NA Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean plate. Alo ...
... the south-eastern margin of the Caribbean Plate. The Caribbean plate is bounded on its eastern margin by a portion of the North American (NA) Plate. At about 200 kilometres east of the chain of volcanic islands in the eastern Caribbean the NA Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean plate. Alo ...
Rocks and Minerals Interactive Student Notebook
... 3. Purchase your land from the owner and enter the cost on your Birdseed Spreadsheet. Purchase Equipment and Pay Workers: 4. Do not touch the seed/bead mixture with your hands. You will only use your mining equipment (toothpick @ $5 and/or paper clip @ $10) to mine. Purchase your equipment from the ...
... 3. Purchase your land from the owner and enter the cost on your Birdseed Spreadsheet. Purchase Equipment and Pay Workers: 4. Do not touch the seed/bead mixture with your hands. You will only use your mining equipment (toothpick @ $5 and/or paper clip @ $10) to mine. Purchase your equipment from the ...
paper 2 revision booklet
... At a divergent plate boundary the plates are moving away from each other as a result of convection currents which operate in the mantle. Here hot magma rises to the surface and spreads out pulling the plates apart, forming a ridge. Magma fills the gap in the ridge, creating new crust and causes volc ...
... At a divergent plate boundary the plates are moving away from each other as a result of convection currents which operate in the mantle. Here hot magma rises to the surface and spreads out pulling the plates apart, forming a ridge. Magma fills the gap in the ridge, creating new crust and causes volc ...
The Rock Cycle - Salt Lake City School District
... sedimentary - can be subjected to enough heat and or pressure causing it to melt. Molten rock is called magma. When magma cools to a solid it becomes an igneous rock. The kind of igneous rock formed depends on what was melted and how it cooled. ...
... sedimentary - can be subjected to enough heat and or pressure causing it to melt. Molten rock is called magma. When magma cools to a solid it becomes an igneous rock. The kind of igneous rock formed depends on what was melted and how it cooled. ...
Dynamic Earth Unit 3 Study Guide Ans. key
... What change of state happens when magma turns into igneous rock? A change of state from liquid to solid Which cause more weathering acid rain or normal rain? Acid rain What causes rocks in a river to erode? Flowing water What is a rift zone? Area where a deep set of cracks form when two tectonic pla ...
... What change of state happens when magma turns into igneous rock? A change of state from liquid to solid Which cause more weathering acid rain or normal rain? Acid rain What causes rocks in a river to erode? Flowing water What is a rift zone? Area where a deep set of cracks form when two tectonic pla ...
CV OJagoutz_May_2014 - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... I have extensive experience in field work and I spend usually 3-4 months a year in the field in various geological settings including remote and politically unstable areas: Among others in Achaean high grade metamorphic terrains/greenstone belts (NE Zimbabwe), in foreland fold and thrust belts (Glar ...
... I have extensive experience in field work and I spend usually 3-4 months a year in the field in various geological settings including remote and politically unstable areas: Among others in Achaean high grade metamorphic terrains/greenstone belts (NE Zimbabwe), in foreland fold and thrust belts (Glar ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.