Meta3-14Basites
... The beginning of metamorphism in volcanic rocks and volcanogenic sediments is marked by the development of zeolites in vesicles and fractures under conditions of shallow burial. In consequence, volcanic rocks change from being vesicular to amygdular. Apart from the filling of vesicules and void spac ...
... The beginning of metamorphism in volcanic rocks and volcanogenic sediments is marked by the development of zeolites in vesicles and fractures under conditions of shallow burial. In consequence, volcanic rocks change from being vesicular to amygdular. Apart from the filling of vesicules and void spac ...
deep-ocean basin
... direction of plate motions, they break into segments that are bounded by faults. ...
... direction of plate motions, they break into segments that are bounded by faults. ...
Carib PISI Stern GSA Denver 2016
... Late Jurassic (M16; 141 Ma) reconstruction of the Proto-Caribbean ...
... Late Jurassic (M16; 141 Ma) reconstruction of the Proto-Caribbean ...
Comment in Earth Magazine about formation of Hadean zircon
... John Valley, a petrologist at the Uniproduced by melts formed at plate bound- plate tectonics hyphothesis. “Our view versity of Wisconsin-Madison who has aries, which hinges on the controversial of the early Earth is one dominated been involved in pioneering zircon work idea that plate tectonic proc ...
... John Valley, a petrologist at the Uniproduced by melts formed at plate bound- plate tectonics hyphothesis. “Our view versity of Wisconsin-Madison who has aries, which hinges on the controversial of the early Earth is one dominated been involved in pioneering zircon work idea that plate tectonic proc ...
ttu_gs0001_000468
... The second word indicates the principal rock type, or if of mixed rock types, the word formation is used: The Morrison Formation -the Wingate Sandstone-the Todilto Limestone-the Mancos Shale. The second diagram (page 10-11) is a composite geologic section, greatly simplified. This example correlates ...
... The second word indicates the principal rock type, or if of mixed rock types, the word formation is used: The Morrison Formation -the Wingate Sandstone-the Todilto Limestone-the Mancos Shale. The second diagram (page 10-11) is a composite geologic section, greatly simplified. This example correlates ...
Iceland is cool: An origin for the Iceland volcanic province in the
... margins of Greenland (Boutilier and Keen, 1999). This may have resulted from EDGE convection, which is driven by lateral temperature gradients where thick lithosphere meets hotter mantle (Anderson, 1994a; Anderson, 1995; Boutilier and Keen, 1999; Korenaga and Kelemen, 2000). Increased mantle fertili ...
... margins of Greenland (Boutilier and Keen, 1999). This may have resulted from EDGE convection, which is driven by lateral temperature gradients where thick lithosphere meets hotter mantle (Anderson, 1994a; Anderson, 1995; Boutilier and Keen, 1999; Korenaga and Kelemen, 2000). Increased mantle fertili ...
Homework #2 - Relative dating excercise
... -Principle of Continuity — Sedimentary layers were deposited as single units -Principle of Fossil Successions—specific groups of fossils follow, or succeed, one another in the rock record in a definite order (won’t use in this assignment) Anytime you have regional metamorphic rocks near the surface, ...
... -Principle of Continuity — Sedimentary layers were deposited as single units -Principle of Fossil Successions—specific groups of fossils follow, or succeed, one another in the rock record in a definite order (won’t use in this assignment) Anytime you have regional metamorphic rocks near the surface, ...
Understanding the thermal evolution of deep
... At the other end of the spectrum are ‘cold’ margins, where there is little evidence for magmatism until new oceanic crust has formed16. The best-studied margin occurs west of the Iberian Peninsula17, but this type of margin is more widespread than ‘hot’ ones (Figs 2, 3c). As before, crustal thicknes ...
... At the other end of the spectrum are ‘cold’ margins, where there is little evidence for magmatism until new oceanic crust has formed16. The best-studied margin occurs west of the Iberian Peninsula17, but this type of margin is more widespread than ‘hot’ ones (Figs 2, 3c). As before, crustal thicknes ...
Alteration of the oceanic lithosphere and its implications for seafloor
... referred to as the “Penrose ophiolite model” or “Penrose-type crust”, defined during a Penrose conference and published in Geotimes in 1972. This model is generally applicable for crust formed at fast spreading ridges, such as the East Pacific Rise, where melt supply is able to keep up with extensio ...
... referred to as the “Penrose ophiolite model” or “Penrose-type crust”, defined during a Penrose conference and published in Geotimes in 1972. This model is generally applicable for crust formed at fast spreading ridges, such as the East Pacific Rise, where melt supply is able to keep up with extensio ...
WHAT TYPE - LambertEarth
... 2) Ryan is visiting the mountains in Colorado. What d. Transform fault boundary type of tectonic plate boundary is Ryan near? a. Tectonic plate boundary 5) What was the main question that b. Divergent boundary the theory of plate tectonics c. Convergent boundary ...
... 2) Ryan is visiting the mountains in Colorado. What d. Transform fault boundary type of tectonic plate boundary is Ryan near? a. Tectonic plate boundary 5) What was the main question that b. Divergent boundary the theory of plate tectonics c. Convergent boundary ...
Geography - Bure Valley School
... are typically non-explosive. Shield volcanoes produce fast flowing fluid [lava] that can flow for many miles. Eruptions tend to be frequent but relatively gentle. Shield volcanoes are usually found at constructive boundaries and sometimes at volcanic hotspots. Examples of shield volcanoes include Mo ...
... are typically non-explosive. Shield volcanoes produce fast flowing fluid [lava] that can flow for many miles. Eruptions tend to be frequent but relatively gentle. Shield volcanoes are usually found at constructive boundaries and sometimes at volcanic hotspots. Examples of shield volcanoes include Mo ...
Earth`s Moving Crust: A Movement Lab for Plate Tectonics Activity
... Fault – linear feature along which movement of the Earth’s crust occurs. Asthenosphere – the lower part of the mantle where rocks are weak and easily deformed, like butter. During plate tectonics, huge plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere. Sliding plates – When plates slide along eac ...
... Fault – linear feature along which movement of the Earth’s crust occurs. Asthenosphere – the lower part of the mantle where rocks are weak and easily deformed, like butter. During plate tectonics, huge plates of the lithosphere float on the asthenosphere. Sliding plates – When plates slide along eac ...
View/Open - Earth
... mantle-lithosphere-necking breakup before crustal-necking breakup. Independent alongaxis centres of upwelling form at the rifting stage just before oceanic crust accretion, with buoyancy-driven convection within a hot, low viscosity asthenosphere. Each initial axial cell taps a different asthenosphe ...
... mantle-lithosphere-necking breakup before crustal-necking breakup. Independent alongaxis centres of upwelling form at the rifting stage just before oceanic crust accretion, with buoyancy-driven convection within a hot, low viscosity asthenosphere. Each initial axial cell taps a different asthenosphe ...
Plate Tectonics
... Relatively strong compared to the asthenosphere Tends to resist stress to the point of fracture Relatively high viscosity Relatively low temperature ...
... Relatively strong compared to the asthenosphere Tends to resist stress to the point of fracture Relatively high viscosity Relatively low temperature ...
Ch 8 lecture notes
... What were early Precambrian organisms like? What were the major events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras? ...
... What were early Precambrian organisms like? What were the major events of the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic Eras? ...
Abby Murray Geology 11 Final Project December 20, 2007 Geologic
... pressure to create glaucophane. Since the subducted ocean lithosphere is cold, it provides the low temperatures also needed. The mylonite revealed by the drill data signifies the presence of an orogenic belt. Mylonite is a metamorphic rock created purely under the effects of shear, with no change in ...
... pressure to create glaucophane. Since the subducted ocean lithosphere is cold, it provides the low temperatures also needed. The mylonite revealed by the drill data signifies the presence of an orogenic belt. Mylonite is a metamorphic rock created purely under the effects of shear, with no change in ...
Carlin-type gold deposits are world-class gold producers and their
... explaining why so many of these world-class gold producing mines are located in central Nevada has been lacking. Increased interest in gold, renewed interest in Nevada and at a time when we now have an improved understanding of what controls the location of these world-class gold deposits suggests t ...
... explaining why so many of these world-class gold producing mines are located in central Nevada has been lacking. Increased interest in gold, renewed interest in Nevada and at a time when we now have an improved understanding of what controls the location of these world-class gold deposits suggests t ...
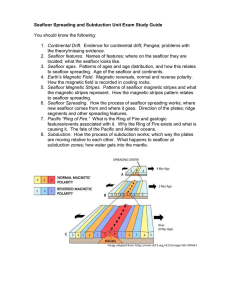
Seafloor Spreading and Subduction Unit Exam Study Guide You
... You should know the following: 1. Continental Drift. Evidence for continental drift; Pangea; problems with the theory/missing evidence. 2. Seafloor features. Names of features; where on the seafloor they are located; what the seafloor looks like. 3. Seafloor ages. Patterns of ages and age distributi ...
... You should know the following: 1. Continental Drift. Evidence for continental drift; Pangea; problems with the theory/missing evidence. 2. Seafloor features. Names of features; where on the seafloor they are located; what the seafloor looks like. 3. Seafloor ages. Patterns of ages and age distributi ...
Earthquakes
... sudden shock of the earth’s surface. They are the Earth's natural means of releasing stress. More than a million earthquakes rattle the world each year. The West Coast is most at risk of having an earthquake, but earthquakes can happen in the Midwest and along the East Coast. Earthquakes can be felt ...
... sudden shock of the earth’s surface. They are the Earth's natural means of releasing stress. More than a million earthquakes rattle the world each year. The West Coast is most at risk of having an earthquake, but earthquakes can happen in the Midwest and along the East Coast. Earthquakes can be felt ...
File
... show HOW the plates move. • Back then, we had no GPS (global position satellites) nor did we know much about atomic radiation nor CONVECTION! ...
... show HOW the plates move. • Back then, we had no GPS (global position satellites) nor did we know much about atomic radiation nor CONVECTION! ...
What is an Earthquake
... two plates meet, called faults. They are mostly generated deep within the earth's crust, when the pressure between two plates is too great for them to be held in place. The underground rocks then snap, sending shock waves out in all directions. These are called seismic waves. The point at which an e ...
... two plates meet, called faults. They are mostly generated deep within the earth's crust, when the pressure between two plates is too great for them to be held in place. The underground rocks then snap, sending shock waves out in all directions. These are called seismic waves. The point at which an e ...
Origin of the modern Chiapanecan Volcanic arc in southern México
... (Fig. 1). The Miocene Sierra Madre arc was abandoned between 9 and 3 Ma, when the modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc was formed (Damon and Montesinos, 1978). There are a series of characteristics that make this new modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc special. First, the position of the arc is well inside t ...
... (Fig. 1). The Miocene Sierra Madre arc was abandoned between 9 and 3 Ma, when the modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc was formed (Damon and Montesinos, 1978). There are a series of characteristics that make this new modern Chiapanecan volcanic arc special. First, the position of the arc is well inside t ...
Earth Geodynamic Hypotheses Updated
... affects the rate of rotation. Chandler wobble “resides in the natural resonances in the body of the spinning earth due to detailed distribution of mass in its surface, interior, oceans, and atmosphere. The entire system is teleconnected.” Primarily, though, Earth expansion is a discussion of philoso ...
... affects the rate of rotation. Chandler wobble “resides in the natural resonances in the body of the spinning earth due to detailed distribution of mass in its surface, interior, oceans, and atmosphere. The entire system is teleconnected.” Primarily, though, Earth expansion is a discussion of philoso ...
Faults
... ES1102 Brittle and Ductile Deformation 1. What are the two ways rocks respond to stress? ________________________________________ 2. When a rock breaks, it is called ______________________. 3. When rocks bend or flow, like clay, it is called _________________________ 4. Which image shows an example ...
... ES1102 Brittle and Ductile Deformation 1. What are the two ways rocks respond to stress? ________________________________________ 2. When a rock breaks, it is called ______________________. 3. When rocks bend or flow, like clay, it is called _________________________ 4. Which image shows an example ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.