Shield Volcanoes Composite Volcanoes Cinder Cone Volcanoes
... While many people think of volcanic eruptions as being explosive, many volcanic areas produce quiet, oozing lava. Fissures and hot spots are two examples. Fissures are long fractures in the earth’s crust. Instead of erupting from one central vent, lava erupts gently like a fountain from the fissure ...
... While many people think of volcanic eruptions as being explosive, many volcanic areas produce quiet, oozing lava. Fissures and hot spots are two examples. Fissures are long fractures in the earth’s crust. Instead of erupting from one central vent, lava erupts gently like a fountain from the fissure ...
volcanoes - Discovery Education
... boundary, a subduction zone. This is where two plates collide and one dives beneath the other. As the leading edge of the diving plate is consumed back into the earth's mantle, it causes solid rock to liquefy and the molten rock rises through fractures in the crust, erupting on the earth's surface. ...
... boundary, a subduction zone. This is where two plates collide and one dives beneath the other. As the leading edge of the diving plate is consumed back into the earth's mantle, it causes solid rock to liquefy and the molten rock rises through fractures in the crust, erupting on the earth's surface. ...
Extremely thin crust in the Indian Ocean possibly resulting from
... (Singh et al. 2007) but no other deep subhorizontal reflections are observed that could be interpreted as reflections from the Moho. Fig. 4 shows the seismic image along orthogonal profile WG1 (Singh et al. 2008) with respect to the blow-up of the image along profile WG3 with a 3-D perspective. Alth ...
... (Singh et al. 2007) but no other deep subhorizontal reflections are observed that could be interpreted as reflections from the Moho. Fig. 4 shows the seismic image along orthogonal profile WG1 (Singh et al. 2008) with respect to the blow-up of the image along profile WG3 with a 3-D perspective. Alth ...
Chapter 13 Section 2
... iron and that is generally dark in color • Felsic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in feldspar and silica and that is generally light in color • Mafic rock commonly makes up the oceanic crust, whereas felsic rock is more common in continental crust. ...
... iron and that is generally dark in color • Felsic - describes magma or igneous rock that is rich in feldspar and silica and that is generally light in color • Mafic rock commonly makes up the oceanic crust, whereas felsic rock is more common in continental crust. ...
preparation of manuscripts for conference proceedings
... Archean to produce volcaniclastic deposits and later also intruded as dikes. A highly explosive eruption style that produces volcaniclastic rocks is not characteristic of lamprophyric magmas that commonly intrude as dykes. Thus, the Wawa diamondiferous rocks could be one of few known lamprophyric v ...
... Archean to produce volcaniclastic deposits and later also intruded as dikes. A highly explosive eruption style that produces volcaniclastic rocks is not characteristic of lamprophyric magmas that commonly intrude as dykes. Thus, the Wawa diamondiferous rocks could be one of few known lamprophyric v ...
Plant Tectonics and Climate
... Even we can compile spreading rates over enough of the world’s ocean to estimate the global mean rate of creation and destruction of ocean crust. ...
... Even we can compile spreading rates over enough of the world’s ocean to estimate the global mean rate of creation and destruction of ocean crust. ...
PPT - nsf margins
... Does the 200-300 km spacing of shallow-upper-mantle, low-seismic-velocity anomalies represent dynamic upwelling of the asthenosphere on this length scale? If so, how does the magma produced in the upwelling zones migrate to the shallow rift segments that are on a significantly smaller length scale? ...
... Does the 200-300 km spacing of shallow-upper-mantle, low-seismic-velocity anomalies represent dynamic upwelling of the asthenosphere on this length scale? If so, how does the magma produced in the upwelling zones migrate to the shallow rift segments that are on a significantly smaller length scale? ...
Geodynamical interpretation of crustal and upper mantle electrical conductivity
... the asthenosphere (Kiselev and Popov, 1992). Mantle xenoliths drawn to the surface by basaltic eruptions in different parts of the rift bear evidence of thermal and compositional heterogeneity of the underlying mantle. The most widely spread are spinel lherzolites that give way to garnet varieties d ...
... the asthenosphere (Kiselev and Popov, 1992). Mantle xenoliths drawn to the surface by basaltic eruptions in different parts of the rift bear evidence of thermal and compositional heterogeneity of the underlying mantle. The most widely spread are spinel lherzolites that give way to garnet varieties d ...
GEOGRAPHIC PATTERNS OF EARTHQUAKE DISASTERS
... eruption and implosion of Krakatao in 1883 at the east end of Sumatra generated a tsunami that killed an estimated 36,000 around the Indian Ocean. In 1896, a tsunami was generated by an undersea earthquake that killed 27,120 Japanese. But the deadliest of all tsunamis was the recent one generated by ...
... eruption and implosion of Krakatao in 1883 at the east end of Sumatra generated a tsunami that killed an estimated 36,000 around the Indian Ocean. In 1896, a tsunami was generated by an undersea earthquake that killed 27,120 Japanese. But the deadliest of all tsunamis was the recent one generated by ...
Diamonds in Ophiolites
... The chromite grains and perhaps some small chromitites carrying diamonds appear to have formed at or near the top of the mantle transition zone. The presence of many silicate minerals, such as zircon, corundum, kyanite, and rutile in ophiolitic chromitites and peridotites (Robinson et al. 2011; Yam ...
... The chromite grains and perhaps some small chromitites carrying diamonds appear to have formed at or near the top of the mantle transition zone. The presence of many silicate minerals, such as zircon, corundum, kyanite, and rutile in ophiolitic chromitites and peridotites (Robinson et al. 2011; Yam ...
Anisotropy and deformation beneath the Eastern Alps
... Based on seismic observations, our planet is separated into three major zones; cores, mantle, and crust. According to rock rheology and thermal divisions the outer shell of the Earth is defined as the lithosphere. This body, consisting of the rigid upper mantle and crust, is considered to be cold an ...
... Based on seismic observations, our planet is separated into three major zones; cores, mantle, and crust. According to rock rheology and thermal divisions the outer shell of the Earth is defined as the lithosphere. This body, consisting of the rigid upper mantle and crust, is considered to be cold an ...
Geological Effects of Plate
... idea that Pangea was the original continent at the Earth's start (few educational earth science films mention what came before Pangea & emphasis on Atlantic spreading leads to Pacific being overlooked). Plate movement is imperceptible on a human timeframe (common use of fingernail growth analogy is ...
... idea that Pangea was the original continent at the Earth's start (few educational earth science films mention what came before Pangea & emphasis on Atlantic spreading leads to Pacific being overlooked). Plate movement is imperceptible on a human timeframe (common use of fingernail growth analogy is ...
Earthquakes and volcanoes CH. 11
... over large distances and great water depths. • When tsunamis approach land, the waves slow down and their wave heights increase as they encounter the bottom of the seafloor. ...
... over large distances and great water depths. • When tsunamis approach land, the waves slow down and their wave heights increase as they encounter the bottom of the seafloor. ...
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
... you are vacationing on a beautiful beach in Thailand. You look up from the book you’re reading to see the sea suddenly retreat from the shoreline, exposing a vast expanse of seafloor that had moments before been underwater and teeming with exotic and colorful fish. It is hard to believe that within ...
... you are vacationing on a beautiful beach in Thailand. You look up from the book you’re reading to see the sea suddenly retreat from the shoreline, exposing a vast expanse of seafloor that had moments before been underwater and teeming with exotic and colorful fish. It is hard to believe that within ...
Metamorphic rocks
... • Metamorphism of rocks is a result of high temperature and pressure (usually deep within the Earth). The extreme temperature and pressure conditions cause the atoms in existing minerals to rearrange (or change ...
... • Metamorphism of rocks is a result of high temperature and pressure (usually deep within the Earth). The extreme temperature and pressure conditions cause the atoms in existing minerals to rearrange (or change ...
Continents on the move
... An ocean trench could be almost ten times longer and ten times deeper than the Grand Canyon. Ocean trenches are staggeringly huge things! The edge of the continental plate may also be compressed and changed as the oceanic plate grinds into it as it slides underneath. This may produce different kinds ...
... An ocean trench could be almost ten times longer and ten times deeper than the Grand Canyon. Ocean trenches are staggeringly huge things! The edge of the continental plate may also be compressed and changed as the oceanic plate grinds into it as it slides underneath. This may produce different kinds ...
(3.9Mb pdf)
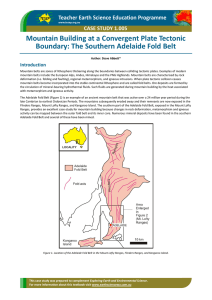
... Mountain belts are zones of lithosphere thickening along the boundaries between colliding tectonic plates. Examples of modern mountain belts include the European Alps, Andes, Himalayas and the PNG Highlands. Mountain belts are characterised by rock deformation (i.e. folding and faulting), regional m ...
... Mountain belts are zones of lithosphere thickening along the boundaries between colliding tectonic plates. Examples of modern mountain belts include the European Alps, Andes, Himalayas and the PNG Highlands. Mountain belts are characterised by rock deformation (i.e. folding and faulting), regional m ...
Geologic Time - Tulane University
... the relative ages of rocks. Once these age relations were worked out, another principle fell into place - the principle of fossil succession. We discuss the 7 principles of stratigraphy first and then see how these apply to fossils. Principle of Uniformitarianism The principle of Uniformitarianism w ...
... the relative ages of rocks. Once these age relations were worked out, another principle fell into place - the principle of fossil succession. We discuss the 7 principles of stratigraphy first and then see how these apply to fossils. Principle of Uniformitarianism The principle of Uniformitarianism w ...
aegean island arc - Ψηφιακή Βιβλιοθήκη Θεόφραστος
... subductIon of the Mediterranean sea floor beneQth the Aege~n Sea. AlthoVgh the lavae from all the major volcanic centres of the arc exhibit typical calc-alkaline major and trace element characteristics it is clear that there are consistent differences jn trace-element abundances and ratios in the la ...
... subductIon of the Mediterranean sea floor beneQth the Aege~n Sea. AlthoVgh the lavae from all the major volcanic centres of the arc exhibit typical calc-alkaline major and trace element characteristics it is clear that there are consistent differences jn trace-element abundances and ratios in the la ...
Volcanoes - 6th Grade Science with Mrs. Harlow
... But eruptions are also creative forces—they help form fertile farmland. They also create some of the largest mountains on Earth. ...
... But eruptions are also creative forces—they help form fertile farmland. They also create some of the largest mountains on Earth. ...
rocks
... www.rocksandminerals.com http://nesen.unl.edu www.cuug.ab.ca:8001/~johnstos/geosci.html www.bced.gov.bc.ca/irp/sciencek7/apf.htm www.enchantedLearning.com http://volcano.und.nodak.edu/vwdocs/vwlessons/lessons/lesson. ...
... www.rocksandminerals.com http://nesen.unl.edu www.cuug.ab.ca:8001/~johnstos/geosci.html www.bced.gov.bc.ca/irp/sciencek7/apf.htm www.enchantedLearning.com http://volcano.und.nodak.edu/vwdocs/vwlessons/lessons/lesson. ...
view as pdf - KITP Online
... - direct sampling to only ~15 km. - eruptive “entrainment” sampling to 200 km, and possibly to 500 km. - mantle plume advection from the base of the mantle (2900 km). If plumes exist. - no bona fide samples yet from the core. ...
... - direct sampling to only ~15 km. - eruptive “entrainment” sampling to 200 km, and possibly to 500 km. - mantle plume advection from the base of the mantle (2900 km). If plumes exist. - no bona fide samples yet from the core. ...
EARTH QUAKES
... lithosphere, deformation is spread out over a much larger area than the plate boundary itself. In the case of the San Andreas fault continental transform, many earthquakes occur away from the plate boundary and are related to strains developed within the broader zone of deformation caused by major i ...
... lithosphere, deformation is spread out over a much larger area than the plate boundary itself. In the case of the San Andreas fault continental transform, many earthquakes occur away from the plate boundary and are related to strains developed within the broader zone of deformation caused by major i ...
EARTH SYSTEM SCIENCE II
... we obtain v ≈ 10 cm/yr. Can play a little with parameters such as viscosity, L and D but we will get the same order of magnitude estimate for velocity. Summary: this section shows, using basic scale analysis, that the velocity of downwelling currents is indeed the correct order of magnitude for velo ...
... we obtain v ≈ 10 cm/yr. Can play a little with parameters such as viscosity, L and D but we will get the same order of magnitude estimate for velocity. Summary: this section shows, using basic scale analysis, that the velocity of downwelling currents is indeed the correct order of magnitude for velo ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.