F g - mrbernabo
... For a given torque, the bigger the rotational inertia the slower it will spin rate will change ...
... For a given torque, the bigger the rotational inertia the slower it will spin rate will change ...
Ch. 4 Motion and Forces
... 1. What do snowshoes do that makes it easier for the person wearing them to travel in deep snow? Snowshoes distribute a person’s weight over the large area of the snowshoes, resulting in less downward pressure on the snow compared to regular shoes. With less downward pressure, the person doesn’t sin ...
... 1. What do snowshoes do that makes it easier for the person wearing them to travel in deep snow? Snowshoes distribute a person’s weight over the large area of the snowshoes, resulting in less downward pressure on the snow compared to regular shoes. With less downward pressure, the person doesn’t sin ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • A worker uses more power running up the stairs than climbing the same stairs slowly. • Twice the power of an engine can do twice the work of one engine in the same amount of time, or twice the work of one engine in half the time or at a rate at which energy is changed from one form to another. ...
... • A worker uses more power running up the stairs than climbing the same stairs slowly. • Twice the power of an engine can do twice the work of one engine in the same amount of time, or twice the work of one engine in half the time or at a rate at which energy is changed from one form to another. ...
Energy Transformations and Conservation
... friction, some of its kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy. So, the mechanical energy of the spinning top is transformed to thermal energy. The top slows and eventually falls on its side, but its energy is not destroyed—it is transformed. The fact that friction transforms mechanical ene ...
... friction, some of its kinetic energy is transformed into thermal energy. So, the mechanical energy of the spinning top is transformed to thermal energy. The top slows and eventually falls on its side, but its energy is not destroyed—it is transformed. The fact that friction transforms mechanical ene ...
Current and Electricity
... 13. All real heat engines are less efficient than carnot engine due to:A. Friction B. Working substance C. Temperature of cold reservoirs D. Temperature of reservoirs 14. For one mole of an ideal gas, the gas equation become:A. PV = 3RT B. PV = RT C. PV = nRT D. PV = 2RT 15. The curve representing a ...
... 13. All real heat engines are less efficient than carnot engine due to:A. Friction B. Working substance C. Temperature of cold reservoirs D. Temperature of reservoirs 14. For one mole of an ideal gas, the gas equation become:A. PV = 3RT B. PV = RT C. PV = nRT D. PV = 2RT 15. The curve representing a ...
Lecture 7
... Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem If there are several forces ac6ng then W is the work done by the net (total) force: ...
... Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem If there are several forces ac6ng then W is the work done by the net (total) force: ...
Middle School Physical Science
... Students in middle school continue to develop understanding of four core ideas in the physical sciences. The middle school performance expectations in the Physical Sciences build on the K – 5 ideas and capabilities to allow learners to explain phenomena central to the physical sciences but also to t ...
... Students in middle school continue to develop understanding of four core ideas in the physical sciences. The middle school performance expectations in the Physical Sciences build on the K – 5 ideas and capabilities to allow learners to explain phenomena central to the physical sciences but also to t ...
Kinetic energy
... since he does the same work in less time P = W/d Ben 500J/10sec = 50 watts Bonnie 500J/60sec 8.3 watts ...
... since he does the same work in less time P = W/d Ben 500J/10sec = 50 watts Bonnie 500J/60sec 8.3 watts ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
... Newton’s laws of force and motion 1. An object continues in a state of rest or in a state of motion at a constant speed along a straight line, unless compelled to change that state by a net force. (One object) 2. When a net external force acts on an object of mass m, the acceleration that results is ...
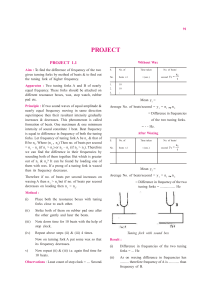
PROJECT
... moving object is called its velocity. It is also defined as distance traveled by an object in a unit time along a given direction. It is a vector quantity. Its S.I. unit is m–1, and its dimensions are (MºLT –1) Uniform velocity : If an object covers equal displacements in equal intervals of time, it ...
... moving object is called its velocity. It is also defined as distance traveled by an object in a unit time along a given direction. It is a vector quantity. Its S.I. unit is m–1, and its dimensions are (MºLT –1) Uniform velocity : If an object covers equal displacements in equal intervals of time, it ...
introduction to vibration and stability
... Depending on excitation: Deterministic: If the value or magnitude of the excitation (force or motion) acting on a vibratory system is known at any given time, the excitation is called deterministic. The resulting vibration is known as deterministic vibration. Random Vibration: In the cases where the ...
... Depending on excitation: Deterministic: If the value or magnitude of the excitation (force or motion) acting on a vibratory system is known at any given time, the excitation is called deterministic. The resulting vibration is known as deterministic vibration. Random Vibration: In the cases where the ...
Newton`s Laws and Friction
... the floor. You must apply a force on the battery to move it from one point to another. The greater the force you apply, the faster the battery will accelerate (f=ma) When you cease to exert a pulling force on the string, the battery comes to a rest. Some force must be acting in opposition to the for ...
... the floor. You must apply a force on the battery to move it from one point to another. The greater the force you apply, the faster the battery will accelerate (f=ma) When you cease to exert a pulling force on the string, the battery comes to a rest. Some force must be acting in opposition to the for ...