MouseTrap Cars - cloudfront.net
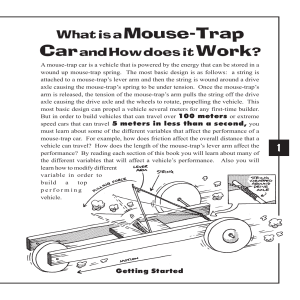
... Speed is the measure of how fast something is traveling or the rate at which distance is being covered, another way of describing speed is to say that it is the distance that is being covered per time where the word per means divided by. In most cases, when you calculate the speed of a mousetrap rac ...
... Speed is the measure of how fast something is traveling or the rate at which distance is being covered, another way of describing speed is to say that it is the distance that is being covered per time where the word per means divided by. In most cases, when you calculate the speed of a mousetrap rac ...
Rigid Body Dynamics
... which Newton’s second law holds (we have also allowed general coordinates, in which the Euler-Lagrange equations hold). However, it is sometimes useful to use non-inertial frames, and particularly when a system is rotating. When we affix an orthonormal frame to the surface of Earth, for example, tha ...
... which Newton’s second law holds (we have also allowed general coordinates, in which the Euler-Lagrange equations hold). However, it is sometimes useful to use non-inertial frames, and particularly when a system is rotating. When we affix an orthonormal frame to the surface of Earth, for example, tha ...
Chapter 5: Problems
... sketching a free-body diagram for the box, showing the force of gravity and the contact force. (a) What are the magnitude and direction of the contact force applied by the ramp on the box? (b) What is the magnitude of the normal force applied by the ramp on the box? (c) What is the magnitude of the ...
... sketching a free-body diagram for the box, showing the force of gravity and the contact force. (a) What are the magnitude and direction of the contact force applied by the ramp on the box? (b) What is the magnitude of the normal force applied by the ramp on the box? (c) What is the magnitude of the ...
Physics 1422 - Introduction
... Note that the tension does a not need to be the same on two sides of a massive pulley. ...
... Note that the tension does a not need to be the same on two sides of a massive pulley. ...
Topic 9_2__Gravitational field, potential and energy
... Explain the concept of escape speed from a planet. We define the escape speed to be the minimum speed an object needs to escape a planet’s gravitational pull. We can further define escape speed vesc to be that minimum speed which will carry an object to infinity and bring it to rest there. Thus w ...
... Explain the concept of escape speed from a planet. We define the escape speed to be the minimum speed an object needs to escape a planet’s gravitational pull. We can further define escape speed vesc to be that minimum speed which will carry an object to infinity and bring it to rest there. Thus w ...
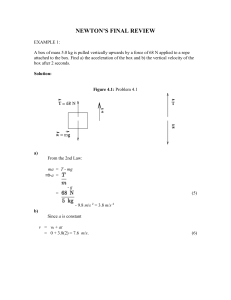
Final Newtons Review
... g. A pendulum bob is set into its usual back-and-forth periodic motion. After some time (perhaps 10 minutes), the pendulum bob comes to a rest position. This is best explained by the idea of inertia - all objects eventually resist motion. h. If a 3-kg rock is thrown at a speed of 2 m/s in a gravity- ...
... g. A pendulum bob is set into its usual back-and-forth periodic motion. After some time (perhaps 10 minutes), the pendulum bob comes to a rest position. This is best explained by the idea of inertia - all objects eventually resist motion. h. If a 3-kg rock is thrown at a speed of 2 m/s in a gravity- ...
Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion - Pearson-Global
... Newton’s first law states that if no net force is acting on an object at rest, the object remains at rest; or if the object is moving, it continues moving with constant speed in a straight line. But what happens if a net force is exerted on an object? Newton perceived that the object’s velocity will ...
... Newton’s first law states that if no net force is acting on an object at rest, the object remains at rest; or if the object is moving, it continues moving with constant speed in a straight line. But what happens if a net force is exerted on an object? Newton perceived that the object’s velocity will ...
Physical Science 1st Semester Exam Study Guide 2010 Introduction
... b. rate at which velocity changes. c. resistance of an object to a change in its velocity. d. speed of an object in a particular direction. 13. Weight is best described as a. an object’s resistance to acceleration. b. what causes an object to fall. c. the downward force exerted on objects due to gra ...
... b. rate at which velocity changes. c. resistance of an object to a change in its velocity. d. speed of an object in a particular direction. 13. Weight is best described as a. an object’s resistance to acceleration. b. what causes an object to fall. c. the downward force exerted on objects due to gra ...
Oscillatory Motion and Waves
... are also the simplest oscillatory systems. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is the name given to oscillatory motion for a system where the net force can be described by Hooke’s law, and such a system is called a simple harmonic oscillator. If the net force can be described by Hooke’s law and there is no ...
... are also the simplest oscillatory systems. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) is the name given to oscillatory motion for a system where the net force can be described by Hooke’s law, and such a system is called a simple harmonic oscillator. If the net force can be described by Hooke’s law and there is no ...
Principles of Time and Space Hiroshige Goto
... overlap. In other words, each coordinate axis of the four-dimensional space–time has a coordinate that is part of the positive world as well as one that is part of the negative world; the temporal-axis parts are ct0 h and ct1 , the x-axis parts are x0 i and x1 hi, the y-axis parts are y0 j and y1 hj ...
... overlap. In other words, each coordinate axis of the four-dimensional space–time has a coordinate that is part of the positive world as well as one that is part of the negative world; the temporal-axis parts are ct0 h and ct1 , the x-axis parts are x0 i and x1 hi, the y-axis parts are y0 j and y1 hj ...
paper pattern - Target Publications
... Angular acceleration is negative if angular velocity decreases with time. iii. Angular acceleration is an axial vector. iv. In uniform circular motion, angular velocity is constant, so angular acceleration is zero. ...
... Angular acceleration is negative if angular velocity decreases with time. iii. Angular acceleration is an axial vector. iv. In uniform circular motion, angular velocity is constant, so angular acceleration is zero. ...