Ex. 37 PowerPoint
... physics problems, it is often convenient to assume a system is frictionless. Once the problem is solved without friction, the effects caused by friction are added to the system. Remember that in an ideal system, there is no loss of energy due to friction. A real system is one that has friction. All ...
... physics problems, it is often convenient to assume a system is frictionless. Once the problem is solved without friction, the effects caused by friction are added to the system. Remember that in an ideal system, there is no loss of energy due to friction. A real system is one that has friction. All ...
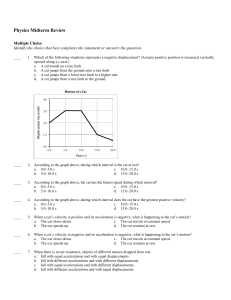
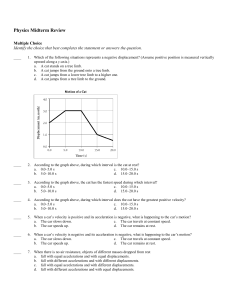
Physics Midterm Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... heads 57.0 north of west for 10.3 m and then turns and heads west for 4.00 m? 71. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an initial speed of 15 m/s. A stopwatch measures the stone’s trajectory time from the top of the cliff to the bottom at 6.3 ...
... heads 57.0 north of west for 10.3 m and then turns and heads west for 4.00 m? 71. A stone is thrown at an angle of 30.0 above the horizontal from the top edge of a cliff with an initial speed of 15 m/s. A stopwatch measures the stone’s trajectory time from the top of the cliff to the bottom at 6.3 ...
Adams2010-MechanicalVibrations.pdf
... involve extensive amounts of kinematic algebra, which can be complicated when rotating body coordinate systems are used. The key to applying Newtonian methods is to select the generalized coordinates so as to balance the effort required to mathematically express the physics (ΣF) and kinematics (ACM= ...
... involve extensive amounts of kinematic algebra, which can be complicated when rotating body coordinate systems are used. The key to applying Newtonian methods is to select the generalized coordinates so as to balance the effort required to mathematically express the physics (ΣF) and kinematics (ACM= ...
2015 Honors Stay at home cedar point packet
... a. What part of your body senses your orientation and if you are in motion? (1 pt) ...
... a. What part of your body senses your orientation and if you are in motion? (1 pt) ...
1st semester EXAM review and key
... 65. A car on a roller coaster loaded with passengers has a mass of 2.0 10 kg. At the lowest point of the track, the radius of curvature of the track is 24 m and the roller car has a tangential speed of 17 m/s. What is the centripetal force acting on the roller coaster car at the lowest point on th ...
... 65. A car on a roller coaster loaded with passengers has a mass of 2.0 10 kg. At the lowest point of the track, the radius of curvature of the track is 24 m and the roller car has a tangential speed of 17 m/s. What is the centripetal force acting on the roller coaster car at the lowest point on th ...
The Hopping Hoop
... Figure 3. The hopping hoop. The hop is not large, but its existence is very surprising. The trajectory of the center of mass is indicated by the downward sloping curve that appears in the vicinity of the large dots. Exercise 1 formally defines the center of mass. We show, in exercise 2, that the tra ...
... Figure 3. The hopping hoop. The hop is not large, but its existence is very surprising. The trajectory of the center of mass is indicated by the downward sloping curve that appears in the vicinity of the large dots. Exercise 1 formally defines the center of mass. We show, in exercise 2, that the tra ...
Simple Machines: Pulley
... In other words this means the ratio of the length of string pulled through the system to the distance the load is raised is the same as the mechanical advantage of the system. For example if a system had a mechanical advantage of 4:1 and the user wished to raise the load 1 m then he/she would have ...
... In other words this means the ratio of the length of string pulled through the system to the distance the load is raised is the same as the mechanical advantage of the system. For example if a system had a mechanical advantage of 4:1 and the user wished to raise the load 1 m then he/she would have ...
click to check
... question. If a question is answered correctly by any team, that team adds those points to their team score. If a question is answered incorrectly, the team score does not change. MORE RULES ...
... question. If a question is answered correctly by any team, that team adds those points to their team score. If a question is answered incorrectly, the team score does not change. MORE RULES ...
Unit 1 Practice Test
... b. when stepping from a curb d. all of the above ____ 26. The product of an object’s mass and velocity is its a. centripetal force. c. net force. b. momentum. d. weight. ____ 27. What is conserved when two objects collide in a closed system? a. acceleration c. speed b. momentum d. velocity Problem 2 ...
... b. when stepping from a curb d. all of the above ____ 26. The product of an object’s mass and velocity is its a. centripetal force. c. net force. b. momentum. d. weight. ____ 27. What is conserved when two objects collide in a closed system? a. acceleration c. speed b. momentum d. velocity Problem 2 ...
Pulley
... In other words this means the ratio of the length of string pulled through the system to the distance the load is raised is the same as the mechanical advantage of the system. For example if a system had a mechanical advantage of 4:1 and the user wished to raise the load 1 m then he/she would have ...
... In other words this means the ratio of the length of string pulled through the system to the distance the load is raised is the same as the mechanical advantage of the system. For example if a system had a mechanical advantage of 4:1 and the user wished to raise the load 1 m then he/she would have ...
FREE Sample Here
... 25) Which direction does a table push a book resting on it? A) up B) left C) right D) down Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.6 26) When can an object be in a state of equilibrium? A) when two or more forces are acting on it B) when it is at rest and no forces are acting on it C) only when one force is ...
... 25) Which direction does a table push a book resting on it? A) up B) left C) right D) down Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.6 26) When can an object be in a state of equilibrium? A) when two or more forces are acting on it B) when it is at rest and no forces are acting on it C) only when one force is ...
Physicsskiing3
... human force to push yourself along the snow, still wearing skies. There are many types of skiing, different ways to ski, conditions which suite different people, and different types of ski equipment but in general many different variables but everything comes down do to one sure thing: without physi ...
... human force to push yourself along the snow, still wearing skies. There are many types of skiing, different ways to ski, conditions which suite different people, and different types of ski equipment but in general many different variables but everything comes down do to one sure thing: without physi ...
Ch 14 - Keene ISD
... positive velocity. There is no net force, so the acceleration is zero. 8. The mass continues moving upward. The velocity is positive but its magnitude is decreasing, so the acceleration is negative. 9. The mass is now back at its starting position. This is another turning point. The mass is at rest ...
... positive velocity. There is no net force, so the acceleration is zero. 8. The mass continues moving upward. The velocity is positive but its magnitude is decreasing, so the acceleration is negative. 9. The mass is now back at its starting position. This is another turning point. The mass is at rest ...
Conceptual Integrated Science, 2e (Hewitt et al
... 25) Which direction does a table push a book resting on it? A) up B) left C) right D) down Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.6 26) When can an object be in a state of equilibrium? A) when two or more forces are acting on it B) when it is at rest and no forces are acting on it C) only when one force is ...
... 25) Which direction does a table push a book resting on it? A) up B) left C) right D) down Answer: A Diff: 1 Objective: 2.6 26) When can an object be in a state of equilibrium? A) when two or more forces are acting on it B) when it is at rest and no forces are acting on it C) only when one force is ...