1. Trying to break down a door, a man pushes futilely against it with
... been lost to dissipative forces? (Wnc = 71 J) 29. A skier starts from rest at the top of a 45 m hill. He skis down a 30 degree incline into a valley, then up a 40 m hill. Ignore friction. a) What is the skier’s speed at the bottom of the hill? (V = 30 m/s) b) What is the skier’s speed at the top of ...
... been lost to dissipative forces? (Wnc = 71 J) 29. A skier starts from rest at the top of a 45 m hill. He skis down a 30 degree incline into a valley, then up a 40 m hill. Ignore friction. a) What is the skier’s speed at the bottom of the hill? (V = 30 m/s) b) What is the skier’s speed at the top of ...
Physical Science
... grass with a 100N force of friction. What will Patty’s acceleration be this time? (Hint: sketch a diagram first) ...
... grass with a 100N force of friction. What will Patty’s acceleration be this time? (Hint: sketch a diagram first) ...
Rigid Body Dynamics - UCSD Computer Graphics Lab
... all cancel out and have no effect on the total momentum or angular momentum The rigid body can actually have an infinite number of particles, spread out over a finite volume Instead of mass being concentrated at discrete points, we will consider the density as being variable over the ...
... all cancel out and have no effect on the total momentum or angular momentum The rigid body can actually have an infinite number of particles, spread out over a finite volume Instead of mass being concentrated at discrete points, we will consider the density as being variable over the ...
Impulse Momentum (Problem and Solutions) 1. An object travels
... ΔP=40kg.m/s Impulse=change in momentum I=ΔP=40kg.m/s 3. Find the impulse and force which make 12m/s change in the velocity of object having 16kg mass in 4 s. F.Δt=ΔP=m.ΔV F.4s=16kg.12m/s F=48N F.Δt=Impulse=192kg.m/s 4. Applied force vs. time graph of object is given below. Find the impulse of the ob ...
... ΔP=40kg.m/s Impulse=change in momentum I=ΔP=40kg.m/s 3. Find the impulse and force which make 12m/s change in the velocity of object having 16kg mass in 4 s. F.Δt=ΔP=m.ΔV F.4s=16kg.12m/s F=48N F.Δt=Impulse=192kg.m/s 4. Applied force vs. time graph of object is given below. Find the impulse of the ob ...
lecture2.pdf
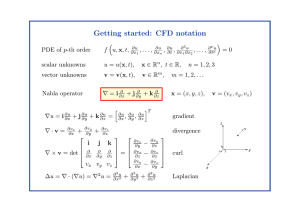
... • representing all equations in the same generic form simplifies the programming • it suffices to develop discretization techniques for the generic conservation law ...
... • representing all equations in the same generic form simplifies the programming • it suffices to develop discretization techniques for the generic conservation law ...
Force and Momentum - the SASPhysics.com
... • The club was in contact with the ball for 0.5 ms. What force did it exert on the ball? ∆p = force × time, F = ∆p/t = 2/0.0005 F = 4000 N ...
... • The club was in contact with the ball for 0.5 ms. What force did it exert on the ball? ∆p = force × time, F = ∆p/t = 2/0.0005 F = 4000 N ...
Unit 7 Bell Ringers - Trimble County Schools
... = distance (centimeters) divided by time (seconds) Momentum = mass x velocity ...
... = distance (centimeters) divided by time (seconds) Momentum = mass x velocity ...
Work and Energy - IES Guillermina Brito
... The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion. ...
... The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion. ...
Name
... 1. A reference point is a location to which you can compare other locations 2. Speed is measured using the following units: km/hr, mi/hr, m/s 3. You need to know direction and distance from a reference point to measure an object’s position. 4. A girl runs 100 meters in 20 seconds. What is her speed? ...
... 1. A reference point is a location to which you can compare other locations 2. Speed is measured using the following units: km/hr, mi/hr, m/s 3. You need to know direction and distance from a reference point to measure an object’s position. 4. A girl runs 100 meters in 20 seconds. What is her speed? ...
Physical Science – Ch. 5 – Energy Study Guide ANSWERS
... GPE = 9.8mh mgh PE = weight x height 5. Describe how energy can be transformed from one form to another. ...
... GPE = 9.8mh mgh PE = weight x height 5. Describe how energy can be transformed from one form to another. ...
Quaternions - UCSD Computer Graphics Lab
... all cancel out and have no effect on the total momentum or angular momentum The rigid body can actually have an infinite number of particles, spread out over a finite volume Instead of mass being concentrated at discrete points, we will consider the density as being variable over the ...
... all cancel out and have no effect on the total momentum or angular momentum The rigid body can actually have an infinite number of particles, spread out over a finite volume Instead of mass being concentrated at discrete points, we will consider the density as being variable over the ...
Elastic Collisions Momentum is conserved m 1 ѵ 1i +
... Priscila drive by (she sees Andrew and speeds up! Haha). Andrew attempts to throw his 7.7 kg backpack at her car with a velocity of 2.9 m/s. If Andrew and his skateboard move in the opposite direction at 2.5 m/s, find his mass. ...
... Priscila drive by (she sees Andrew and speeds up! Haha). Andrew attempts to throw his 7.7 kg backpack at her car with a velocity of 2.9 m/s. If Andrew and his skateboard move in the opposite direction at 2.5 m/s, find his mass. ...
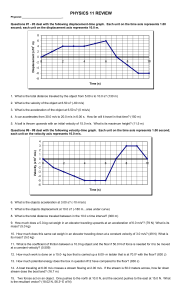
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
... 21. An object is thrown directly upwards with an initial velocity of 25 m/s. (A) What is the maximum height the object will travel? (32 m) (B) How long will it take to return to its starting point? (5.15 s) (C) What will its velocity be when it is 2.0 meters above its starting point as it travels do ...
Slide 1
... Work is the transfer of energy through motion. In order for work to take place, a force must be exerted through a distance. The amount of work done depends on two things: the amount of force exerted and the distance over which the force is applied. There are two factors to keep in mind when decidin ...
... Work is the transfer of energy through motion. In order for work to take place, a force must be exerted through a distance. The amount of work done depends on two things: the amount of force exerted and the distance over which the force is applied. There are two factors to keep in mind when decidin ...