Discrete Distributions
... Discrete Distributions place probability on specific numbers. For example, the Binomial distribution places probability only on the values 0,1,2, …, n. This is why the probability distributions for discrete random variables are often referred to as probability mass functions. Some random variables, ...
... Discrete Distributions place probability on specific numbers. For example, the Binomial distribution places probability only on the values 0,1,2, …, n. This is why the probability distributions for discrete random variables are often referred to as probability mass functions. Some random variables, ...
A Counterexample in Probability
... Now consider an extreme example. Suppose n is large, A = i Bi , and each Bi is the union of 2 parts, A and Ci , where the measure of Ci is small compared to that of A, the Ci are pairwise disjoint, and the measure of A is small compared to 1. Geometrically, we can imagine this as A is a sphere, the ...
... Now consider an extreme example. Suppose n is large, A = i Bi , and each Bi is the union of 2 parts, A and Ci , where the measure of Ci is small compared to that of A, the Ci are pairwise disjoint, and the measure of A is small compared to 1. Geometrically, we can imagine this as A is a sphere, the ...
Chapter 7
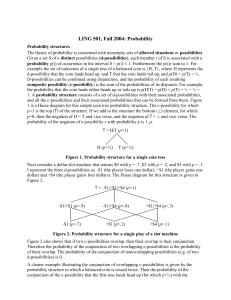
... Ex. A store stocks light bulbs from three suppliers. Suppliers A, B, and C supply 10%, 20%, and 70% of the bulbs respectively. It has been determined that company A’s bulbs are 1% defective while company B’s are 3% defective and company C’s are 4% defective. If a bulb is selected at random and foun ...
... Ex. A store stocks light bulbs from three suppliers. Suppliers A, B, and C supply 10%, 20%, and 70% of the bulbs respectively. It has been determined that company A’s bulbs are 1% defective while company B’s are 3% defective and company C’s are 4% defective. If a bulb is selected at random and foun ...
Probability - NC State Department of Statistics
... the probability that you have HIV? (Remember: we know that if a person has the virus, the test result will be positive with probability .999; if a person does not have the virus, the test result will be negative with probability .990). ...
... the probability that you have HIV? (Remember: we know that if a person has the virus, the test result will be positive with probability .999; if a person does not have the virus, the test result will be negative with probability .990). ...
Fundamental Principles of Probability (7-1) Sample Space: Event:
... Definition: For n, a positive integer, n factorial is the product of the positive integers from 1 to n. In symbols, n! = (n) (n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3)…(3) (2) (1) Selections without Replacement: Let S be a set with n elements. Then there are n! possible arrangements of the n elements without replaceme ...
... Definition: For n, a positive integer, n factorial is the product of the positive integers from 1 to n. In symbols, n! = (n) (n – 1) (n – 2) (n – 3)…(3) (2) (1) Selections without Replacement: Let S be a set with n elements. Then there are n! possible arrangements of the n elements without replaceme ...
Level 1 Mathematics, 2009 - SMC-Math
... He spins each spinner once, and records the total of the two numbers that the spinners land on. If Brent spins a 3 on the first spinner what is the probability he records a total of at least 12? ...
... He spins each spinner once, and records the total of the two numbers that the spinners land on. If Brent spins a 3 on the first spinner what is the probability he records a total of at least 12? ...
Homework 1 Solutions
... 12. In a large town, Kennedy Avenue is a long north-south avenue with many intersections. A drunken man is wandering along the avenue and does not really know which way he is going. He is currently at an intersection O somewhere in the middle of the avenue. Suppose that, at the end of each block, he ...
... 12. In a large town, Kennedy Avenue is a long north-south avenue with many intersections. A drunken man is wandering along the avenue and does not really know which way he is going. He is currently at an intersection O somewhere in the middle of the avenue. Suppose that, at the end of each block, he ...
MCS 224 - Introduction to Probability and Statistics FIRST MIDTERM
... 3) There are three departments in a Faculty: Math, English and Translation. The Math department has 3 times as many students as the Translation, and 2 times as many students as the English department. 40% of all students in the Math department, 80% of English department and 90% of the Translation de ...
... 3) There are three departments in a Faculty: Math, English and Translation. The Math department has 3 times as many students as the Translation, and 2 times as many students as the English department. 40% of all students in the Math department, 80% of English department and 90% of the Translation de ...
In this part we are going to prove a technical lemma which is used
... • Next, let D2 = {A ∈ D : ∀B ∈ D A ∩ B ∈ D}. Prove that D2 is a d-system, which, by the previous step contains I . • Conclude that D2 = D and show that this ends the proof of Dynkin’s lemma. 2. Applications: Let I be a π-system of subsets of some space Ω and let µ1 and µ2 be two probability measures ...
... • Next, let D2 = {A ∈ D : ∀B ∈ D A ∩ B ∈ D}. Prove that D2 is a d-system, which, by the previous step contains I . • Conclude that D2 = D and show that this ends the proof of Dynkin’s lemma. 2. Applications: Let I be a π-system of subsets of some space Ω and let µ1 and µ2 be two probability measures ...
Conditional Probability and Independence
... Two events A and B are independent if the occurrence of one event has no effect on the chance that the other event will happen. In other words, events A and B are independent if P(A | B) = P(A) and P(B | A) = P(B). Example Lefties Down Under (Checking for independence) Is there a relationship betwee ...
... Two events A and B are independent if the occurrence of one event has no effect on the chance that the other event will happen. In other words, events A and B are independent if P(A | B) = P(A) and P(B | A) = P(B). Example Lefties Down Under (Checking for independence) Is there a relationship betwee ...
Ars Conjectandi

Ars Conjectandi (Latin for The Art of Conjecturing) is a book on combinatorics and mathematical probability written by Jakob Bernoulli and published in 1713, eight years after his death, by his nephew, Niklaus Bernoulli. The seminal work consolidated, apart from many combinatorial topics, many central ideas in probability theory, such as the very first version of the law of large numbers: indeed, it is widely regarded as the founding work of that subject. It also addressed problems that today are classified in the twelvefold way, and added to the subjects; consequently, it has been dubbed an important historical landmark in not only probability but all combinatorics by a plethora of mathematical historians. The importance of this early work had a large impact on both contemporary and later mathematicians; for example, Abraham de Moivre.Bernoulli wrote the text between 1684 and 1689, including the work of mathematicians such as Christiaan Huygens, Gerolamo Cardano, Pierre de Fermat, and Blaise Pascal. He incorporated fundamental combinatorial topics such as his theory of permutations and combinations—the aforementioned problems from the twelvefold way—as well as those more distantly connected to the burgeoning subject: the derivation and properties of the eponymous Bernoulli numbers, for instance. Core topics from probability, such as expected value, were also a significant portion of this important work.