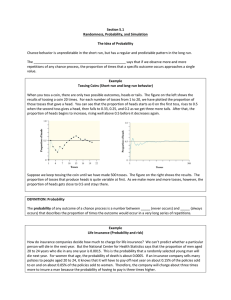
File - Glorybeth Becker
... semester of Calculus, and the rest have taken two or more semesters of Calculus. The professor randomly assigns students to groups of three to work on the project for the course. What is the probability that the first groupmate you meet has studied a) two or more semesters of calculus? b) some Calcu ...
... semester of Calculus, and the rest have taken two or more semesters of Calculus. The professor randomly assigns students to groups of three to work on the project for the course. What is the probability that the first groupmate you meet has studied a) two or more semesters of calculus? b) some Calcu ...
Lecture 2 - CMU Statistics
... and is interested in the probability that the client will default on the loan. Based on historical data, the bank knows that there is a 5% chance that a customer who has overdrawn an account will default, while there is only a 0.5% chance that a customer who has never overdrawn an account will defau ...
... and is interested in the probability that the client will default on the loan. Based on historical data, the bank knows that there is a 5% chance that a customer who has overdrawn an account will default, while there is only a 0.5% chance that a customer who has never overdrawn an account will defau ...
Targil 10
... Remark. In the definition of both beta function and gamma function the exponents are always n – 1 and not n. I think the aesthetic reason for that definition was that m n people prefer to get the formula m, n and not m + n + 1 below. m n There are also some ideological reaso ...
... Remark. In the definition of both beta function and gamma function the exponents are always n – 1 and not n. I think the aesthetic reason for that definition was that m n people prefer to get the formula m, n and not m + n + 1 below. m n There are also some ideological reaso ...
Probability
... • Because we are drawing conclusions about the population based on a sample, we can never be certain that our conclusions are 100% correct. • That is, there is some uncertainty. • Probability is the study of uncertainty and provides some of the foundation for our study of inferential statistics – co ...
... • Because we are drawing conclusions about the population based on a sample, we can never be certain that our conclusions are 100% correct. • That is, there is some uncertainty. • Probability is the study of uncertainty and provides some of the foundation for our study of inferential statistics – co ...
Axioms of Probability Math 217 Probability and Statistics
... a study of the continuous case, we should at least survey what they are. In a continuous distribution there are uncountably many outcomes, and the probability of each outcome x is 0. Therefore, the probability of any event that has only finitely many outcomes in it will also be 0. Furthermore, the p ...
... a study of the continuous case, we should at least survey what they are. In a continuous distribution there are uncountably many outcomes, and the probability of each outcome x is 0. Therefore, the probability of any event that has only finitely many outcomes in it will also be 0. Furthermore, the p ...
Document
... Although simple enough, Bayes’ theorem has an interesting interpretation: P(A) represents the a-priori probability of the event A. Suppose B has occurred, and assume that A and B are not independent. How can this new information be used to update our knowledge about A? Bayes’ rule in (1-46) take in ...
... Although simple enough, Bayes’ theorem has an interesting interpretation: P(A) represents the a-priori probability of the event A. Suppose B has occurred, and assume that A and B are not independent. How can this new information be used to update our knowledge about A? Bayes’ rule in (1-46) take in ...
Math 2 Review – Unit 7: Probability Name 1. Use the table on the left
... d) Your drawer actually contains 16 pairs of white socks, 2 pairs of blue socks, 6 pairs of black socks, and 8 pairs of tan socks. How accurate was your prediction? 3. Teachers A, B, and C all teach Math 2. Because their classrooms are different sizes, students have a 25% chance of getting teacher A ...
... d) Your drawer actually contains 16 pairs of white socks, 2 pairs of blue socks, 6 pairs of black socks, and 8 pairs of tan socks. How accurate was your prediction? 3. Teachers A, B, and C all teach Math 2. Because their classrooms are different sizes, students have a 25% chance of getting teacher A ...
Conditional Probability and Independence
... the P (A). Let’s say I toss a fair coin. I tell you that I got a tail. I then give you the coin to toss. Does the knowledge that I got a tail affect what you think the chance is that you will get a head? Intuitively, two events A and B are independent if the event B does not have any influcence on t ...
... the P (A). Let’s say I toss a fair coin. I tell you that I got a tail. I then give you the coin to toss. Does the knowledge that I got a tail affect what you think the chance is that you will get a head? Intuitively, two events A and B are independent if the event B does not have any influcence on t ...
Syllabus
... sheet of paper, writing heads as “1” and tails as “0”. The second group is instructed to create a sequence of 100 “0”s ans “1”s that are intended to look like the result of coin flips- but they are to do this without flipping any coins or randomization device- and to write this sequence on a sheet o ...
... sheet of paper, writing heads as “1” and tails as “0”. The second group is instructed to create a sequence of 100 “0”s ans “1”s that are intended to look like the result of coin flips- but they are to do this without flipping any coins or randomization device- and to write this sequence on a sheet o ...
Ars Conjectandi

Ars Conjectandi (Latin for The Art of Conjecturing) is a book on combinatorics and mathematical probability written by Jakob Bernoulli and published in 1713, eight years after his death, by his nephew, Niklaus Bernoulli. The seminal work consolidated, apart from many combinatorial topics, many central ideas in probability theory, such as the very first version of the law of large numbers: indeed, it is widely regarded as the founding work of that subject. It also addressed problems that today are classified in the twelvefold way, and added to the subjects; consequently, it has been dubbed an important historical landmark in not only probability but all combinatorics by a plethora of mathematical historians. The importance of this early work had a large impact on both contemporary and later mathematicians; for example, Abraham de Moivre.Bernoulli wrote the text between 1684 and 1689, including the work of mathematicians such as Christiaan Huygens, Gerolamo Cardano, Pierre de Fermat, and Blaise Pascal. He incorporated fundamental combinatorial topics such as his theory of permutations and combinations—the aforementioned problems from the twelvefold way—as well as those more distantly connected to the burgeoning subject: the derivation and properties of the eponymous Bernoulli numbers, for instance. Core topics from probability, such as expected value, were also a significant portion of this important work.