Example or Rigor
... EQ: How does Cornell Notes weathering, erosion, and deposition change the Earth’s surface? Models/Diagrams ...
... EQ: How does Cornell Notes weathering, erosion, and deposition change the Earth’s surface? Models/Diagrams ...
The Dynamic Earth Name
... Directions: Click on Preface to begin the tour. 1) What started a revolution in the Earth Sciences? When was this? 2) How are people at the mercy of plate tectonics? 3) What volcano and where is it located is in the picture at the bottom of the page? 4) CLICK THE RIGHT ARROW>>>>>> 5) What is a plate ...
... Directions: Click on Preface to begin the tour. 1) What started a revolution in the Earth Sciences? When was this? 2) How are people at the mercy of plate tectonics? 3) What volcano and where is it located is in the picture at the bottom of the page? 4) CLICK THE RIGHT ARROW>>>>>> 5) What is a plate ...
WGCh2Notetaking
... within the Earth the temperature is hotter than normal. The __________________________________________ were formed by this type of volcanic activity. c. Molten rock may also heat underground water to create _____________________ or hot springs, like those found in Yellowstone National Park in Wyomin ...
... within the Earth the temperature is hotter than normal. The __________________________________________ were formed by this type of volcanic activity. c. Molten rock may also heat underground water to create _____________________ or hot springs, like those found in Yellowstone National Park in Wyomin ...
Earth’s Structure
... produced when the earth’s uppermost layer moves suddenly. • Earthquakes produce shock waves that travel through the earth. • Another name for shock waves is seismic waves. ...
... produced when the earth’s uppermost layer moves suddenly. • Earthquakes produce shock waves that travel through the earth. • Another name for shock waves is seismic waves. ...
PPT - Hss-1.us
... The types of rocks are: • (1) Igneous - Rocks that are formed by first heating the earth's material (elements) to a molten lava state. The when the molten lava cools it forms igneous rocks. Today we can see this happening in association with volcanoes. • (2) Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form wh ...
... The types of rocks are: • (1) Igneous - Rocks that are formed by first heating the earth's material (elements) to a molten lava state. The when the molten lava cools it forms igneous rocks. Today we can see this happening in association with volcanoes. • (2) Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form wh ...
Slide 1
... Earth’s functional layers Crust – we know most about it; continental crust is less dense Moho – a density discontinuity that separates crust from the mantle – Depth varies under continents and oceans – First thought that this was layer where crust moved relative to earth’s interior BUT, outer ...
... Earth’s functional layers Crust – we know most about it; continental crust is less dense Moho – a density discontinuity that separates crust from the mantle – Depth varies under continents and oceans – First thought that this was layer where crust moved relative to earth’s interior BUT, outer ...
The Layers of Earth
... Because the core is so hot, it radiates a natural heat to the upper layers. Because of this a current of heat comes into being. Those are also known as the convection currents. The convection currents cause the movement of the tectonic plates. This movement is called plate tectonics. The outer core ...
... Because the core is so hot, it radiates a natural heat to the upper layers. Because of this a current of heat comes into being. Those are also known as the convection currents. The convection currents cause the movement of the tectonic plates. This movement is called plate tectonics. The outer core ...
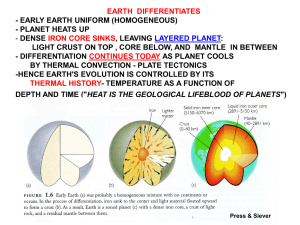
EARTH DIFFERENTIATES
... Plate tectonics causes volcanism, that produces atmospheric gasses (carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O) needed to support life and keep planet warm (“greenhouse effect”) ...
... Plate tectonics causes volcanism, that produces atmospheric gasses (carbon dioxide CO2 and water H2O) needed to support life and keep planet warm (“greenhouse effect”) ...
Plate Tectonics
... called Pangaea had existed in the past. • It broke up starting 200 million years ago, and the pieces ``drifted'' to their present positions. • He cited the fit of South America and Africa, ancient climate similarities, fossil evidence (such as the fern Glossopteris and mesosaurus), and similarity of ...
... called Pangaea had existed in the past. • It broke up starting 200 million years ago, and the pieces ``drifted'' to their present positions. • He cited the fit of South America and Africa, ancient climate similarities, fossil evidence (such as the fern Glossopteris and mesosaurus), and similarity of ...
FAQs
... more agricultural level. As a result the disturbances in the ecological balance of nature and environment has taken place. Constructions of roads, buildings over urbanization, unplanned industrial growth are some activities performed by human beings which have changed the face of the earth. (16) Wha ...
... more agricultural level. As a result the disturbances in the ecological balance of nature and environment has taken place. Constructions of roads, buildings over urbanization, unplanned industrial growth are some activities performed by human beings which have changed the face of the earth. (16) Wha ...
Planet Earth in Cross Section
... get the full diameter of the earth. Compare this to the earth in space poster that every good earth scientist has hanging in their classroom and talk about scale, size of mtns. etc (but only for a few minutes because that’s old syllabus). I spent some time at the end discussing why earth systems at ...
... get the full diameter of the earth. Compare this to the earth in space poster that every good earth scientist has hanging in their classroom and talk about scale, size of mtns. etc (but only for a few minutes because that’s old syllabus). I spent some time at the end discussing why earth systems at ...
Section 8.4 Earths Layered Structure
... Explain how scientists determined Earth’s structure and composition. ...
... Explain how scientists determined Earth’s structure and composition. ...
Explain briefly what is Geology, it`s branches and it`s importance and
... This course introduces students with the introduction of geology and subtitles of physical geology. The course emphasis on the Earth Physical & Chemical characteristic, especially it’s surface and internal features. Then, turn to a discussion of Earth materials and the related processes. Earth’s int ...
... This course introduces students with the introduction of geology and subtitles of physical geology. The course emphasis on the Earth Physical & Chemical characteristic, especially it’s surface and internal features. Then, turn to a discussion of Earth materials and the related processes. Earth’s int ...
Unit 5 - Structure and Composition of the Earth
... • Paleontologists had also found that there were fossils of similar species found on continents that are now separated by great geographic distance. • Wegener's ideas were very controversial because he didn't have an explanation for why the continents moved, just that there was observational evide ...
... • Paleontologists had also found that there were fossils of similar species found on continents that are now separated by great geographic distance. • Wegener's ideas were very controversial because he didn't have an explanation for why the continents moved, just that there was observational evide ...
01 00_Earth_Layers 1
... to the other three layers. only about 3-5 miles (8 kilometers) thick under the oceans (oceanic crust) 25 miles (32 kilometers) thick under the continents (continental crust). ...
... to the other three layers. only about 3-5 miles (8 kilometers) thick under the oceans (oceanic crust) 25 miles (32 kilometers) thick under the continents (continental crust). ...
Changing Earth`s Surface
... rocks and boulders are pulled down from cliffs by gravity. Large masses of ice, called glaciers, flow downward under the force of gravity. During the process of erosion, sediment is removed from one area on Earth’s surface and carried to another. Several different agents of erosion can transport sed ...
... rocks and boulders are pulled down from cliffs by gravity. Large masses of ice, called glaciers, flow downward under the force of gravity. During the process of erosion, sediment is removed from one area on Earth’s surface and carried to another. Several different agents of erosion can transport sed ...
6th - inside earth study guide1
... volcano – forms where plates diverge and magma reaches earths surface & where plates collide and one subducts into the mantle forming molten material mountain building – when two plates collide & crush together causing land to be pushed up, resulting in the folding and breaking of Earth’s crust ...
... volcano – forms where plates diverge and magma reaches earths surface & where plates collide and one subducts into the mantle forming molten material mountain building – when two plates collide & crush together causing land to be pushed up, resulting in the folding and breaking of Earth’s crust ...
Unit B: Geology of the Seafloor
... a substantial range of phenomena; thus, a scientific theory represents the most powerful explanation scientists have to offer. SC.912.N.3.5 Describe the function of models in science, and identify the wide range of models used in science. ...
... a substantial range of phenomena; thus, a scientific theory represents the most powerful explanation scientists have to offer. SC.912.N.3.5 Describe the function of models in science, and identify the wide range of models used in science. ...
Inside Earth Test Study Guide
... volcano – forms where plates diverge and magma reaches earths surface & where plates collide and one subducts into the mantle forming molten material mountain building – when two plates collide & crush together causing land to be pushed up, resulting in the folding and breaking of Earth’s crust ...
... volcano – forms where plates diverge and magma reaches earths surface & where plates collide and one subducts into the mantle forming molten material mountain building – when two plates collide & crush together causing land to be pushed up, resulting in the folding and breaking of Earth’s crust ...
9 - Cengage
... As we saw in the chapter, recent research has shown that slabs of Earth's relatively cool and solid surface -- its lithosphere -- float and move independently of one another over the hotter, partially molten asthenosphere layer directly below. The physical properties of each make this possible, so c ...
... As we saw in the chapter, recent research has shown that slabs of Earth's relatively cool and solid surface -- its lithosphere -- float and move independently of one another over the hotter, partially molten asthenosphere layer directly below. The physical properties of each make this possible, so c ...
midterm review sheet
... 5.) Be able to explain Alfred Wegener’s Theory of Continental Drift. Include evidence that he found that supported his theory. 6.) Understand the Scientific Method and how it was used to determine different theories such as Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics. ...
... 5.) Be able to explain Alfred Wegener’s Theory of Continental Drift. Include evidence that he found that supported his theory. 6.) Understand the Scientific Method and how it was used to determine different theories such as Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics. ...
Earth Science
... • Must have features that clearly distinguish it from other fossils • Organism must have lived during a short span of geologic time • Must occur in fairly large numbers within the rock layers ...
... • Must have features that clearly distinguish it from other fossils • Organism must have lived during a short span of geologic time • Must occur in fairly large numbers within the rock layers ...