Appendix
... There are oscillations only in the perturbation δϕ, the background ϕ̄ is homogeneous and evolving slowly in time. For the particle point of view, the background solution represents the vacuum,2 i.e., particles are quanta of oscillations around that value. ...
... There are oscillations only in the perturbation δϕ, the background ϕ̄ is homogeneous and evolving slowly in time. For the particle point of view, the background solution represents the vacuum,2 i.e., particles are quanta of oscillations around that value. ...
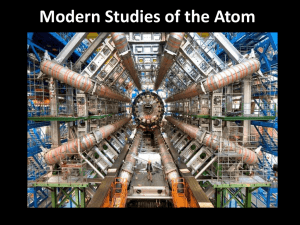
The Standard Model of the Atom
... mass-energy. • Regular Matter makes up only 17% of all matter. ...
... mass-energy. • Regular Matter makes up only 17% of all matter. ...
Rabi oscillations
... xz-plane by changing the gate voltage Vg . As we discussed in connection to the Bloch sphere, any single qubit gate can be performed by three consecutive rotations along two non-parallel axes. Thus, arbitrary single qubit gates can be performed by quickly changing the gate voltage between two differ ...
... xz-plane by changing the gate voltage Vg . As we discussed in connection to the Bloch sphere, any single qubit gate can be performed by three consecutive rotations along two non-parallel axes. Thus, arbitrary single qubit gates can be performed by quickly changing the gate voltage between two differ ...
Standard Model is an Effective Theory
... • SUSY requires 2 Higgs doublets to cancel anomalies and to give mass to both up- and down-type particles • Anomaly cancellation requires Σ Y3 = 0, where Y is hypercharge and the sum is over all fermions • SUSY adds an extra fermion with Y = -1 ...
... • SUSY requires 2 Higgs doublets to cancel anomalies and to give mass to both up- and down-type particles • Anomaly cancellation requires Σ Y3 = 0, where Y is hypercharge and the sum is over all fermions • SUSY adds an extra fermion with Y = -1 ...
Slide - University of Maryland
... In SEG&Wald we proved that, at first order, the above description is equivalent to the linearized Einstein equation sourced by a point paticle. (This derives the point particle description from extended bodies! See also Pound’s work.) ...
... In SEG&Wald we proved that, at first order, the above description is equivalent to the linearized Einstein equation sourced by a point paticle. (This derives the point particle description from extended bodies! See also Pound’s work.) ...
The beginning of physics
... All ordinary matter made of up quark, down quark, electrons and electron neutrinos. All forces (except gravity) mediated by photon, Z boson, W boson and gluon. ...
... All ordinary matter made of up quark, down quark, electrons and electron neutrinos. All forces (except gravity) mediated by photon, Z boson, W boson and gluon. ...
Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2006
... • To keep local gauge invariance, new particles had to be introduced in gauge theories – U(1) gauge introduced a new field (particle) that mediates the electromagnetic force: Photon – SU(2) gauge introduces three new fields that mediates weak force • Charged current mediator: W+ and W• Neutral curre ...
... • To keep local gauge invariance, new particles had to be introduced in gauge theories – U(1) gauge introduced a new field (particle) that mediates the electromagnetic force: Photon – SU(2) gauge introduces three new fields that mediates weak force • Charged current mediator: W+ and W• Neutral curre ...
Aspen-Winter08-summary
... M À TeV Scale – No Observable Flavor Violating Effects Beyond Renormalizable Standard Model If M Near TeV Scale or Additional State Which Carry Flavor Near the Weak Scale – Potential Conflict With Observation ...
... M À TeV Scale – No Observable Flavor Violating Effects Beyond Renormalizable Standard Model If M Near TeV Scale or Additional State Which Carry Flavor Near the Weak Scale – Potential Conflict With Observation ...
Ross.pdf
... Thus if the fermion mass mψ is forbidden by a chiral symmetry as discussed above the scalar mass will also vanish. In this case there must be supersymmetric partners to the Standard Model states. In order to prevent radiative corrections reintroducing the hierarchy problem, the states must be quite ...
... Thus if the fermion mass mψ is forbidden by a chiral symmetry as discussed above the scalar mass will also vanish. In this case there must be supersymmetric partners to the Standard Model states. In order to prevent radiative corrections reintroducing the hierarchy problem, the states must be quite ...
The Mass Spectrophotometer
... • When a charged particle is moving within a magnetic field there is an interaction of the moving charge with the interacting magnetic field: ...
... • When a charged particle is moving within a magnetic field there is an interaction of the moving charge with the interacting magnetic field: ...
Anomaly driven signatures of new invisible physics
... of heavy particles. A similar setup, with completely different phenomenology, has been previously considered in [11, 12]. The paper is organized as follows. We first consider in section 2 the general theory of D’Hoker-Farhi terms arising from the existence of heavy states that contribute to anomalie ...
... of heavy particles. A similar setup, with completely different phenomenology, has been previously considered in [11, 12]. The paper is organized as follows. We first consider in section 2 the general theory of D’Hoker-Farhi terms arising from the existence of heavy states that contribute to anomalie ...
Wednesday, Nov. 15, 2006
... • To keep local gauge invariance, new particles had to be introduced in gauge theories – U(1) gauge introduced a new field (particle) that mediates the electromagnetic force: Photon – SU(2) gauge introduces three new fields that mediates weak force • Charged current mediator: W+ and W• Neutral curre ...
... • To keep local gauge invariance, new particles had to be introduced in gauge theories – U(1) gauge introduced a new field (particle) that mediates the electromagnetic force: Photon – SU(2) gauge introduces three new fields that mediates weak force • Charged current mediator: W+ and W• Neutral curre ...
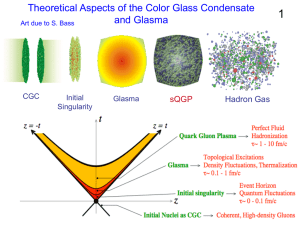
Non perturbative QCD
... example: the proton, neutron, lambda, …. one quark and one anti-quark, mésons, example: the pion, kaon, B, the J/psi,.. confinement has not yet been derived from QCD Image: we pull afar two heavy quarks, a strong « string » binds them (linear potential). At som point the string breaks, a quark-ant ...
... example: the proton, neutron, lambda, …. one quark and one anti-quark, mésons, example: the pion, kaon, B, the J/psi,.. confinement has not yet been derived from QCD Image: we pull afar two heavy quarks, a strong « string » binds them (linear potential). At som point the string breaks, a quark-ant ...
Aleksan_Vietnam_2014-8-14_v1
... Recommendation #1 c) The discovery of the Higgs boson is the start of a major programme of work to measure this particle’s properties with the highest possible precision for testing the validity of the Standard Model and to search for further new physics at the energy frontier. The LHC is in a uniqu ...
... Recommendation #1 c) The discovery of the Higgs boson is the start of a major programme of work to measure this particle’s properties with the highest possible precision for testing the validity of the Standard Model and to search for further new physics at the energy frontier. The LHC is in a uniqu ...
Some beautiful equations of mathematical physics
... by saying that a particle is elementary if one can associate with it a wave equation and a local interaction Lagrangian and use these to account for experimental results within a certain range of scales. Those wave equations are restricted by Lorentz invariance and other symmetries. Underlying this ...
... by saying that a particle is elementary if one can associate with it a wave equation and a local interaction Lagrangian and use these to account for experimental results within a certain range of scales. Those wave equations are restricted by Lorentz invariance and other symmetries. Underlying this ...
Spontaneous electromagnetic superconductivity of QCDxQED
... At the critical value of the magnetic field: imaginary mass (=condensation)! ...
... At the critical value of the magnetic field: imaginary mass (=condensation)! ...
Hamiltonian of the quantum and classical Ising model with skew
... The chain has N spatial sites and satisfies periodic spatial boundary conditions. The coupling strength J between first-neighbor z-components of spin can either be positive (antiferromagnetic case) or negative (ferromagnetic case). Due to the rotational symmetry of the hamiltonian with respect to th ...
... The chain has N spatial sites and satisfies periodic spatial boundary conditions. The coupling strength J between first-neighbor z-components of spin can either be positive (antiferromagnetic case) or negative (ferromagnetic case). Due to the rotational symmetry of the hamiltonian with respect to th ...
ppt - HEP Educational Outreach
... – Aims to describe the most fundamental objects in nature and the force laws that govern their interactions. – Currently: Standard Model (SM) • 6 Quarks, 6 leptons, and force carriers (g, gluon, W±, Z) • Works very well, but certainly an effective theory ...
... – Aims to describe the most fundamental objects in nature and the force laws that govern their interactions. – Currently: Standard Model (SM) • 6 Quarks, 6 leptons, and force carriers (g, gluon, W±, Z) • Works very well, but certainly an effective theory ...
The origin of space-time as seen from matrix model simulations
... Future directions Extending the study of supersymmetric gauge theory to higher dimensions ...
... Future directions Extending the study of supersymmetric gauge theory to higher dimensions ...
list of abstracts - Faculdade de Ciências
... This talk looks at different aspects of the lives of Marie Curie, Iréne Curie and Maria Goeppert-Mayer, female Nobel Prize winners in history, to illuminate the conditions of women in scientific research today. It is based on current research on gender in the academy and in particular on the experie ...
... This talk looks at different aspects of the lives of Marie Curie, Iréne Curie and Maria Goeppert-Mayer, female Nobel Prize winners in history, to illuminate the conditions of women in scientific research today. It is based on current research on gender in the academy and in particular on the experie ...
Experimental Tests of the Standard Model
... fails and overwhelming evidence that it works. • It is the most precisely tested theory in the history of physics. • But it has problems ...
... fails and overwhelming evidence that it works. • It is the most precisely tested theory in the history of physics. • But it has problems ...
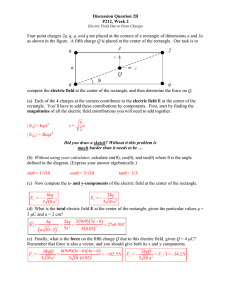
q q q 2 x y Q 3 a ϑ
... compute the electric field at the center of the rectangle, and then determine the force on Q. (a) Each of the 4 charges at the corners contributes to the electric field E at the center of the rectangle. You’ll have to add these contributions by components. First, start by finding the magnitudes of a ...
... compute the electric field at the center of the rectangle, and then determine the force on Q. (a) Each of the 4 charges at the corners contributes to the electric field E at the center of the rectangle. You’ll have to add these contributions by components. First, start by finding the magnitudes of a ...
Goldstone Bosons and Chiral Symmetry Breaking in QCD
... Again, it is important to stress that q and q̄ are both left-handed fermions. q annihilates quarks and creates (right-handed) andtiquarks; q̄ annihilates (left-handed) anti-quarks and creates (right-handed) quarks. ...
... Again, it is important to stress that q and q̄ are both left-handed fermions. q annihilates quarks and creates (right-handed) andtiquarks; q̄ annihilates (left-handed) anti-quarks and creates (right-handed) quarks. ...