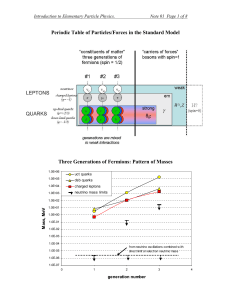
Periodic Table of Particles/Forces in the Standard Model
... quantum numbers like charge (electric, color, etc.), magnetic moment, etc. For photon , Z, and H, an anti-particle is the same as a particle. Same can be true for neutrinos, but we do not yet know this… In general, fermions—particles with half-integral spin: ½ , 3/2, …. Bosons—particles with integra ...
... quantum numbers like charge (electric, color, etc.), magnetic moment, etc. For photon , Z, and H, an anti-particle is the same as a particle. Same can be true for neutrinos, but we do not yet know this… In general, fermions—particles with half-integral spin: ½ , 3/2, …. Bosons—particles with integra ...
How stable are extra dimensions? - Theoretical High
... No point particles, but small strings Unique theory Bonus: gauge forces Unification of four forces of Nature? ...
... No point particles, but small strings Unique theory Bonus: gauge forces Unification of four forces of Nature? ...
Classes of Particles - Liberty Union
... momentum" which is possessed by particles as if they were spinning around their axis (but, in fact, they aren't). The values cited for spin are not (usually) the real magnitude of that angular momentum, but the component of the angular momentum along one axis. Quantum mechanics restricts that compon ...
... momentum" which is possessed by particles as if they were spinning around their axis (but, in fact, they aren't). The values cited for spin are not (usually) the real magnitude of that angular momentum, but the component of the angular momentum along one axis. Quantum mechanics restricts that compon ...
Physics with Negative Masses
... It is clear that ak and âk must be adjoint to each other rather than hermitian conjugate. The latter relationship is connected to a probabilistic (non-negative) interpretation of wave-functions. However, here adjointness allows for either sign, which is interpreted as a mass density which is positiv ...
... It is clear that ak and âk must be adjoint to each other rather than hermitian conjugate. The latter relationship is connected to a probabilistic (non-negative) interpretation of wave-functions. However, here adjointness allows for either sign, which is interpreted as a mass density which is positiv ...
PARTICLE PHYSICS - STFC home | Science & Technology
... The very heavy top quark mass is “explained” in the theory by saying that the top quark has a very large coupling (interaction) with the Higgs field !!! (significantly larger than that of the W and Z bosons) All the other “matter” particles have much smaller couplings to the Higgs field and hence mu ...
... The very heavy top quark mass is “explained” in the theory by saying that the top quark has a very large coupling (interaction) with the Higgs field !!! (significantly larger than that of the W and Z bosons) All the other “matter” particles have much smaller couplings to the Higgs field and hence mu ...
Studies of effective theories beyond the Standard Model
... The vast majority of all experimental results in particle physics can be described by the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics. However, neither the existence of neutrino masses nor the mixing in the leptonic sector, which have been observed, can be described within this model. In fact, the model ...
... The vast majority of all experimental results in particle physics can be described by the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics. However, neither the existence of neutrino masses nor the mixing in the leptonic sector, which have been observed, can be described within this model. In fact, the model ...
Effective lattice models for two-dimensional
... The destruction of Néel order in d = 2 antiferromagnets by zero temperature quantum fluctuations is of great current interest [1]. An intriguing possibility that has emerged from large-N [2, 3] expansions of unfrustrated SU (N ) antiferromagnets, and from numerical [4] and series [5] work on weakl ...
... The destruction of Néel order in d = 2 antiferromagnets by zero temperature quantum fluctuations is of great current interest [1]. An intriguing possibility that has emerged from large-N [2, 3] expansions of unfrustrated SU (N ) antiferromagnets, and from numerical [4] and series [5] work on weakl ...
Today in Physics 218: gauge transformations
... “Reference points” for potentials Our usual reference point for the scalar potential in electrostatics is V → 0 at r → ∞. For the vector potential in magnetostatics we imposed the condition — ⋅ A = 0. These reference points arise from exploitation of the builtin ambiguities in the static potentia ...
... “Reference points” for potentials Our usual reference point for the scalar potential in electrostatics is V → 0 at r → ∞. For the vector potential in magnetostatics we imposed the condition — ⋅ A = 0. These reference points arise from exploitation of the builtin ambiguities in the static potentia ...
Introduction a la Physique des Saveur Lourdes
... • 2. What holds them together? • 3. What is the correct mathematical framework to describe how the constituents are put together to form matter, how do they interact with each other and how can one predict its behavior under different conditions? ...
... • 2. What holds them together? • 3. What is the correct mathematical framework to describe how the constituents are put together to form matter, how do they interact with each other and how can one predict its behavior under different conditions? ...
The Universal Extra Dimensional Model with S^2/Z_2 extra
... Simple extension of SM to higher dimensional spacetime Introducing compact extra space All the SM particles can propagate on extra space Providing a candidate of the dark matter as a stable lightest Kaluza-Klein (KK) particle ...
... Simple extension of SM to higher dimensional spacetime Introducing compact extra space All the SM particles can propagate on extra space Providing a candidate of the dark matter as a stable lightest Kaluza-Klein (KK) particle ...
***** 1
... The physical Hamiltonian H(ph) depends, in general, on a chosen parametrization and gauge. In particular, for the ADM parametrization and the condition N = 1 the left-hand side of this equation coincides with the lefthand side of the Wheeler − DeWitt equation. In Quantum Geometrodynamics in extended ...
... The physical Hamiltonian H(ph) depends, in general, on a chosen parametrization and gauge. In particular, for the ADM parametrization and the condition N = 1 the left-hand side of this equation coincides with the lefthand side of the Wheeler − DeWitt equation. In Quantum Geometrodynamics in extended ...
unification of couplings
... in several ways—mediating forces among them, being emitted as radiation when the quarks or leptons accelerate, and even changing one kind of quark or lepton into another. The original and most familiar gauge theory is also the most basic. Quantum electrodynamics is properly understood, in modern ter ...
... in several ways—mediating forces among them, being emitted as radiation when the quarks or leptons accelerate, and even changing one kind of quark or lepton into another. The original and most familiar gauge theory is also the most basic. Quantum electrodynamics is properly understood, in modern ter ...
Principles of Computer Architecture Dr. Mike Frank
... – There are only two square roots of 1: Namely, 1 and 1. ...
... – There are only two square roots of 1: Namely, 1 and 1. ...
e - National Centre for Physics
... whose other facet is electromagnetism. The unification of two seemingly different forces, namely, weak and electromagnetic is analogous to the 19th century unification of electricity with magnetism. The theory referred to the above predicted: The existence of a new type of neutral weak interaction ( ...
... whose other facet is electromagnetism. The unification of two seemingly different forces, namely, weak and electromagnetic is analogous to the 19th century unification of electricity with magnetism. The theory referred to the above predicted: The existence of a new type of neutral weak interaction ( ...
1 Press release Brussels, 8 October 2013 Nobel Prize for
... universe. The ULB now has a count of 4 science-related Nobel Prizes (of the six awarded to Belgians). The Brout-Englert-Higgs boson implied by their theories had to wait nearly fifty years before being discovered, in July 2012, by the CMS and ATLAS collaborations at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) a ...
... universe. The ULB now has a count of 4 science-related Nobel Prizes (of the six awarded to Belgians). The Brout-Englert-Higgs boson implied by their theories had to wait nearly fifty years before being discovered, in July 2012, by the CMS and ATLAS collaborations at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) a ...
Particle Physics on Noncommutative Spaces
... • How does the Standard Model of particle physics which is a gauge theory based on the group SU(3)SU(2)U(1), emerge as a low energy action of a noncommutative gauge theory? • The main difficulty is to implement symmetries on NC spaces. • We need to understand how to implement SU(N) gauge symmetrie ...
... • How does the Standard Model of particle physics which is a gauge theory based on the group SU(3)SU(2)U(1), emerge as a low energy action of a noncommutative gauge theory? • The main difficulty is to implement symmetries on NC spaces. • We need to understand how to implement SU(N) gauge symmetrie ...
Gauge Field Theories Second Edition - Assets
... class of symmetries of the physical system. Let us consider a Lie group of continuous global (x-independent) infinitesimal transformations (here we restrict ourselves to unitary transformations; conformal transformations are discussed in ...
... class of symmetries of the physical system. Let us consider a Lie group of continuous global (x-independent) infinitesimal transformations (here we restrict ourselves to unitary transformations; conformal transformations are discussed in ...
PHY 551 - Stony Brook University
... Coupling constant: numerical coefficient that occur as a parameter whenever there’s an interaction. Strength of interaction ~ magnitude of a coupling constant ...
... Coupling constant: numerical coefficient that occur as a parameter whenever there’s an interaction. Strength of interaction ~ magnitude of a coupling constant ...
Electromagnetic Preons as Particles of Everything
... Strings> elementary particles are one dimensional particle strands. It predicts a different number of dimensions 10-11 0r 26. In other dimensions, gravity have an equal or greater strength than other fundamental forces. Branes - M-theory> universe is one large brane with four dimensions. gravity ...
... Strings> elementary particles are one dimensional particle strands. It predicts a different number of dimensions 10-11 0r 26. In other dimensions, gravity have an equal or greater strength than other fundamental forces. Branes - M-theory> universe is one large brane with four dimensions. gravity ...
The Hierarchy Problem and New Dimensions at a Millimeter
... induced. Any extension of the SM at the weak scale must also not give dangerously large corrections to precision electroweak observables. Again, there could be unknown contributions from the physics above mEW . However, at least the purely gravitational corrections do not introduce any new electrowe ...
... induced. Any extension of the SM at the weak scale must also not give dangerously large corrections to precision electroweak observables. Again, there could be unknown contributions from the physics above mEW . However, at least the purely gravitational corrections do not introduce any new electrowe ...
Matter and antimatter: very similar, but not exactly - Physik
... of the two mu as a function of m2(μ,u) depends on features of the loop particle ...
... of the two mu as a function of m2(μ,u) depends on features of the loop particle ...























