Muon Lifetime
... sits in the bottom of the asymmetric well with non-zero value • universe F of the field (called the vacuum expectation value of the Higgs) - asymmetric ground state doesn’t respect symmetry of theory (SSB) states corresponding to motion in the bottom of the well become the • 3longitudinal polarizati ...
... sits in the bottom of the asymmetric well with non-zero value • universe F of the field (called the vacuum expectation value of the Higgs) - asymmetric ground state doesn’t respect symmetry of theory (SSB) states corresponding to motion in the bottom of the well become the • 3longitudinal polarizati ...
PMA-ChairCouncil-3dec2008-preskill
... • A quantum system with two parts is entangled when its joint state is more definite and less random than the state of each part by itself. Looking at the parts one at a time, you can learn everything about a pair of socks, but not about a pair of qubits! ...
... • A quantum system with two parts is entangled when its joint state is more definite and less random than the state of each part by itself. Looking at the parts one at a time, you can learn everything about a pair of socks, but not about a pair of qubits! ...
Quantum Field Theory I: Basics in Mathematics and Physics
... • the physics of the Standard Model of particle physics and • the magic formulas in quantum field theory, and we touch the following mathematical subjects: • finite-dimensional Hilbert spaces and a rigorous approach to the basic ideas of quantum field theory, • elements of functional differentiation and ...
... • the physics of the Standard Model of particle physics and • the magic formulas in quantum field theory, and we touch the following mathematical subjects: • finite-dimensional Hilbert spaces and a rigorous approach to the basic ideas of quantum field theory, • elements of functional differentiation and ...
Lecture02
... • The system is N particles (non-interacting), fixed in position. Each has intrinsic spin ½ so EACH particle’s quantum number mi (i = 1,2,…N) can have one of the 2 values ½. Suppose that N is HUGE: N ~ 1024. • The state of this system is then specified by specifying the values of EACH of the quantu ...
... • The system is N particles (non-interacting), fixed in position. Each has intrinsic spin ½ so EACH particle’s quantum number mi (i = 1,2,…N) can have one of the 2 values ½. Suppose that N is HUGE: N ~ 1024. • The state of this system is then specified by specifying the values of EACH of the quantu ...
Ex 2
... 1.1. Show that the Toffoli gate is a universal gate with respect to reversible classical computation. 1.2. Show that there is no set of 2 bit gates which is universal with respect to reversible classical computation. 2. Teleportation Suppose Alice and Bob share two pairs of EPR states, and they wish ...
... 1.1. Show that the Toffoli gate is a universal gate with respect to reversible classical computation. 1.2. Show that there is no set of 2 bit gates which is universal with respect to reversible classical computation. 2. Teleportation Suppose Alice and Bob share two pairs of EPR states, and they wish ...
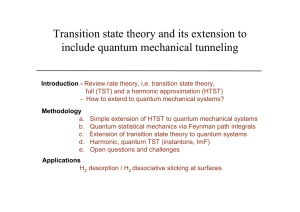
Transition state theory and its extension to include quantum
... quantum mechanical transition state theory can be used to estimate rates, even sticking probability of molecules at surface (good agreement with wave packet propagation results). The harmonic approximation even gives good results in these ...
... quantum mechanical transition state theory can be used to estimate rates, even sticking probability of molecules at surface (good agreement with wave packet propagation results). The harmonic approximation even gives good results in these ...
“Quantum Computing: Dream or Nightmare”, Physics Today, 49, 51
... such entangled states common in the laboratory, any lapse of our watchdog's attention (in other words, any detection efficiency less than 100%) will result in a loss of coherence, and any imperfection in the sequence of operations required to control the system is bound to cause additional errors. T ...
... such entangled states common in the laboratory, any lapse of our watchdog's attention (in other words, any detection efficiency less than 100%) will result in a loss of coherence, and any imperfection in the sequence of operations required to control the system is bound to cause additional errors. T ...
The Differential Geometry and Physical Basis for the Application of
... Chern, Steenrod and Ehresmann—led to the development of fiber bundle theory, which is used in explaining the geometric content of Maxwell’s equations. It was later used to explain Yang-Mills theory and to develop string theory. In 1959 Aharonov and Bohm established the primacy of the vector potentia ...
... Chern, Steenrod and Ehresmann—led to the development of fiber bundle theory, which is used in explaining the geometric content of Maxwell’s equations. It was later used to explain Yang-Mills theory and to develop string theory. In 1959 Aharonov and Bohm established the primacy of the vector potentia ...
Space-time description of squeezing
... does not lead to any progress in our understanding of the physics of these phenomena. To defend ourselves against such criticism, we would like to point out that the description of squeezing based on the field-theoretical foundations can be more easily extended to situations in which the standard ap ...
... does not lead to any progress in our understanding of the physics of these phenomena. To defend ourselves against such criticism, we would like to point out that the description of squeezing based on the field-theoretical foundations can be more easily extended to situations in which the standard ap ...
PPT - Louisiana State University
... A statistical distinguishability based on relative entropy characterizes the fitness of quantum states for phase estimation. This criterion is used to interpolate between two regimes, of local and global phase distinguishability. The analysis demonstrates that, in a passive MZI, the Heisenberg limit ...
... A statistical distinguishability based on relative entropy characterizes the fitness of quantum states for phase estimation. This criterion is used to interpolate between two regimes, of local and global phase distinguishability. The analysis demonstrates that, in a passive MZI, the Heisenberg limit ...