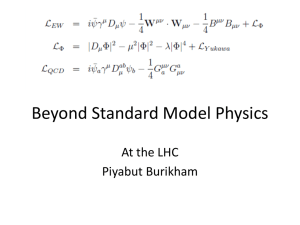
The standard model of particle physics
... with the Compton wavelengths of the charged W and neutral Z bosons that mediate it. Their couplings to the ‘‘weak charges’’ of quarks and leptons are comparable in strength to the electromagnetic coupling. When the weak interaction is measured over distances much larger than its range, its effects a ...
... with the Compton wavelengths of the charged W and neutral Z bosons that mediate it. Their couplings to the ‘‘weak charges’’ of quarks and leptons are comparable in strength to the electromagnetic coupling. When the weak interaction is measured over distances much larger than its range, its effects a ...
PowerPoint
... SUSY models with an anomalous U(1) gauge symmetry can explain * the origin of U(1)PQ, * the origin of the intermediate PQ-scale 109 GeV < vPQ < 1011 GeV, * why μ ≈ mSUSY , rather than μ ≈ MPlanck ? ...
... SUSY models with an anomalous U(1) gauge symmetry can explain * the origin of U(1)PQ, * the origin of the intermediate PQ-scale 109 GeV < vPQ < 1011 GeV, * why μ ≈ mSUSY , rather than μ ≈ MPlanck ? ...
Electron discovered 1897, Thomson Atom model 1913, Bohr
... • Bosons • Fotons, He4, even number of fermions • Inverse Pauli principle • Prefer to behave alike • Bose-kondensation ...
... • Bosons • Fotons, He4, even number of fermions • Inverse Pauli principle • Prefer to behave alike • Bose-kondensation ...
Fysiikan historia
... • The quark model did not tell much about the strong force that keeps quarks together in hadrons. In particular, why quarks were never observed as free particles. There were also problems with Pauli’s exclusion princible: For example, in omega particle there are three s quarks with their spins para ...
... • The quark model did not tell much about the strong force that keeps quarks together in hadrons. In particular, why quarks were never observed as free particles. There were also problems with Pauli’s exclusion princible: For example, in omega particle there are three s quarks with their spins para ...
Zerwas_PASCOSMerida
... • vertex reco for mass resolution • CMS: use of BDT based on the reconstructed photons (higher sensitivity) ...
... • vertex reco for mass resolution • CMS: use of BDT based on the reconstructed photons (higher sensitivity) ...
Contents
... 1. it has a charge of -1/3 and a mass of 4GeV …………………… 2. it is from the muon generation and has no charge ……………… 3. it has a charge of +1 and mass of 511keV ……………………….. 4. it is a quark with a mass 1.2GeV……………………………….. ...
... 1. it has a charge of -1/3 and a mass of 4GeV …………………… 2. it is from the muon generation and has no charge ……………… 3. it has a charge of +1 and mass of 511keV ……………………….. 4. it is a quark with a mass 1.2GeV……………………………….. ...
Anticipating New Physics at the LHC
... Quantum Corrections: Virtual Effects drag Weak Scale to MPl ...
... Quantum Corrections: Virtual Effects drag Weak Scale to MPl ...