Distillability of Inseparable Quantum Systems
... of spin- 21 particles in the singlet state from a large ensemble described by a density matrix, provided that the latter has fidelity greater than 1/2. The fidelity is defined as [1] f = maxhψ|̺|ψi, ...
... of spin- 21 particles in the singlet state from a large ensemble described by a density matrix, provided that the latter has fidelity greater than 1/2. The fidelity is defined as [1] f = maxhψ|̺|ψi, ...
The Current Model of the Atom Name This Element Building on Bohr
... Defining the orbital • Schroedinger’s calculations suggest the maximum probability of finding an e- in a given region of space with a particular quantity of energy (orbital) • Different orbitals are present in atoms having different sizes, shapes and properties • There are 4 parameters (called quant ...
... Defining the orbital • Schroedinger’s calculations suggest the maximum probability of finding an e- in a given region of space with a particular quantity of energy (orbital) • Different orbitals are present in atoms having different sizes, shapes and properties • There are 4 parameters (called quant ...
Localization and the Semiclassical Limit in Quantum Field Theories
... This work is associated to another larger project in collaboration with Christian Jäkel (Cardiff University, Wales) and Jens Mund (UFJF, Brasil) • Construction of interacting P (φ)2 models in 1 + 1 dimensional de Sitter space. • Construction of non-trivial nets of von Neumann Algebras describing c ...
... This work is associated to another larger project in collaboration with Christian Jäkel (Cardiff University, Wales) and Jens Mund (UFJF, Brasil) • Construction of interacting P (φ)2 models in 1 + 1 dimensional de Sitter space. • Construction of non-trivial nets of von Neumann Algebras describing c ...
A Review and Prospects of Quantum Teleportation
... contain no information about |χ〉. The two subsystems are now like an open quantum channel that is ready to transmit information. Step 3: To perform the teleportation, now Alice brings the teleported state |χ〉 into contact with the entangled state |ϕ〉 and performs a Bell state measurement on the comb ...
... contain no information about |χ〉. The two subsystems are now like an open quantum channel that is ready to transmit information. Step 3: To perform the teleportation, now Alice brings the teleported state |χ〉 into contact with the entangled state |ϕ〉 and performs a Bell state measurement on the comb ...
WAVE MECHANICS (Schrödinger, 1926)
... The currently accepted version of quantum mechanics which takes into account the wave nature of matter and the uncertainty principle. * The state of an electron is described by a function y, called the “wave function”. * y can be obtained by solving Schrödinger’s equation (a differential equation): ...
... The currently accepted version of quantum mechanics which takes into account the wave nature of matter and the uncertainty principle. * The state of an electron is described by a function y, called the “wave function”. * y can be obtained by solving Schrödinger’s equation (a differential equation): ...
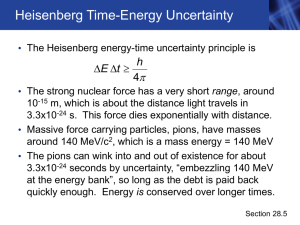
Chapter 28 - Purdue Physics
... molecule can absorb a photon only if the photon energy precisely matches the pigment energy level • More realistically (C), a range of energies is absorbed • Quantum mechanics and the existence of quantized energies for both photons and pigment molecules are ...
... molecule can absorb a photon only if the photon energy precisely matches the pigment energy level • More realistically (C), a range of energies is absorbed • Quantum mechanics and the existence of quantized energies for both photons and pigment molecules are ...
Quantum chaos: an introduction
... •System can get “trapped” for very long times in regions of cantori. These are the fractal remnants of invarient tori. •K = 1.0; i.e. last torus has been destroyed (K=0.97..). ...
... •System can get “trapped” for very long times in regions of cantori. These are the fractal remnants of invarient tori. •K = 1.0; i.e. last torus has been destroyed (K=0.97..). ...
Measuring And Manipulating Coherence In Photonic And Atomic
... Currently setting up LCD waveplates which will allow us to introduce a random phase shift between orthogonal polarizations to produce a variable degree of coherence Could produce a “better” maximally mixed state by using four photons. Similar to Paul Kwiat’s work on Remote State ...
... Currently setting up LCD waveplates which will allow us to introduce a random phase shift between orthogonal polarizations to produce a variable degree of coherence Could produce a “better” maximally mixed state by using four photons. Similar to Paul Kwiat’s work on Remote State ...
SEPTEMBER 21, 2013 THESKEPTICARENA.COM QUANTUM
... time the two halves are compared to each other. In that way, the scientists can measure the amount of quantum mechanical connection between the clouds. Initially, this connection is perfect; all atoms are in a highly ordered quantum state. But as the cloud is a large object consisting of thousands o ...
... time the two halves are compared to each other. In that way, the scientists can measure the amount of quantum mechanical connection between the clouds. Initially, this connection is perfect; all atoms are in a highly ordered quantum state. But as the cloud is a large object consisting of thousands o ...
Quantum teleportation
Quantum teleportation is a process by which quantum information (e.g. the exact state of an atom or photon) can be transmitted (exactly, in principle) from one location to another, with the help of classical communication and previously shared quantum entanglement between the sending and receiving location. Because it depends on classical communication, which can proceed no faster than the speed of light, it cannot be used for faster-than-light transport or communication of classical bits. It also cannot be used to make copies of a system, as this violates the no-cloning theorem. While it has proven possible to teleport one or more qubits of information between two (entangled) atoms, this has not yet been achieved between molecules or anything larger.Although the name is inspired by the teleportation commonly used in fiction, there is no relationship outside the name, because quantum teleportation concerns only the transfer of information. Quantum teleportation is not a form of transportation, but of communication; it provides a way of transporting a qubit from one location to another, without having to move a physical particle along with it.The seminal paper first expounding the idea was published by C. H. Bennett, G. Brassard, C. Crépeau, R. Jozsa, A. Peres and W. K. Wootters in 1993. Since then, quantum teleportation was first realized with single photons and later demonstrated with various material systems such as atoms, ions, electrons and superconducting circuits. The record distance for quantum teleportation is 143 km (89 mi).