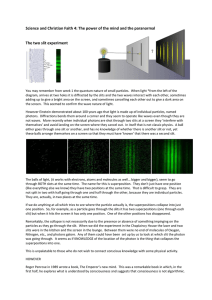
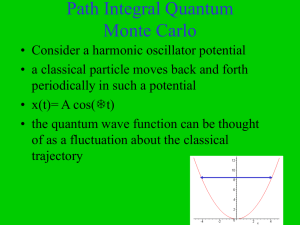
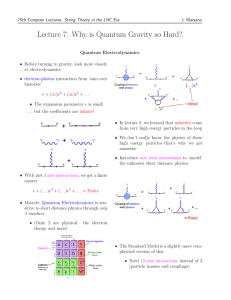
Unit 2 Review KEY
... Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on a metal. Quantum – minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. Photon – particle of electromagnetic radiation hav ...
... Frequency (v) – number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time (1 sec) Photoelectric Effect – an emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on a metal. Quantum – minimum quantity of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom. Photon – particle of electromagnetic radiation hav ...
Problem Set 1 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... the particle cannot have E = 0 while respecting the uncertainty principle. ASIDE: Quantum mechanically, then, there must be some minimum energy this system can have which cannot be predicted classically! For a particle on a table, this may not seem so important – but for Hydrogen, which you’ve just ...
... the particle cannot have E = 0 while respecting the uncertainty principle. ASIDE: Quantum mechanically, then, there must be some minimum energy this system can have which cannot be predicted classically! For a particle on a table, this may not seem so important – but for Hydrogen, which you’ve just ...
Document
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
... de Broglie’s intriguing idea of “matter wave” (1924) Extend notation of “wave-particle duality” from light to matter For photons, P E hf h ...
Quantum Computing Lecture 1 What is Quantum Computing?
... A building block of classical computational devices is a two-state system. ...
... A building block of classical computational devices is a two-state system. ...
CHEM 532 Physical Chemistry II (Quantum Chemistry) Fall 2013
... the variation method, time independent perturbation theory, degenerate perturbation theory, the anharmonic oscillator VIII. The Helium atom electron spin, ground state of He, excited electronic states of He, spin eigenfunctions of He IX. Many-electron wavefunctions indistinguishable particles, the P ...
... the variation method, time independent perturbation theory, degenerate perturbation theory, the anharmonic oscillator VIII. The Helium atom electron spin, ground state of He, excited electronic states of He, spin eigenfunctions of He IX. Many-electron wavefunctions indistinguishable particles, the P ...
Quantum teleportation
Quantum teleportation is a process by which quantum information (e.g. the exact state of an atom or photon) can be transmitted (exactly, in principle) from one location to another, with the help of classical communication and previously shared quantum entanglement between the sending and receiving location. Because it depends on classical communication, which can proceed no faster than the speed of light, it cannot be used for faster-than-light transport or communication of classical bits. It also cannot be used to make copies of a system, as this violates the no-cloning theorem. While it has proven possible to teleport one or more qubits of information between two (entangled) atoms, this has not yet been achieved between molecules or anything larger.Although the name is inspired by the teleportation commonly used in fiction, there is no relationship outside the name, because quantum teleportation concerns only the transfer of information. Quantum teleportation is not a form of transportation, but of communication; it provides a way of transporting a qubit from one location to another, without having to move a physical particle along with it.The seminal paper first expounding the idea was published by C. H. Bennett, G. Brassard, C. Crépeau, R. Jozsa, A. Peres and W. K. Wootters in 1993. Since then, quantum teleportation was first realized with single photons and later demonstrated with various material systems such as atoms, ions, electrons and superconducting circuits. The record distance for quantum teleportation is 143 km (89 mi).