RNDr. Aleš Špičák, CSc. - Sopečná činnost
... magmas. Three times in the past 2.1 million years, large batches of these magmas have erupted explosively, forming huge calderas. ...
... magmas. Three times in the past 2.1 million years, large batches of these magmas have erupted explosively, forming huge calderas. ...
ProQuest Scientific Source
... ground. A geyser erupts. The melted magma is part of one of the world's largest volcanoes. It is so large that geologists, scientists who study Earth, call it a supervolcano. This volcano is buried beneath the ground. It has erupted in the past. The most recent eruption happened 640,000 years ago. I ...
... ground. A geyser erupts. The melted magma is part of one of the world's largest volcanoes. It is so large that geologists, scientists who study Earth, call it a supervolcano. This volcano is buried beneath the ground. It has erupted in the past. The most recent eruption happened 640,000 years ago. I ...
Soil and Rapid Changes Review
... B. quickly move large amounts of material C. are the result of heat from within the Earth D. build rock layers to create mountains ...
... B. quickly move large amounts of material C. are the result of heat from within the Earth D. build rock layers to create mountains ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 47. A tectonic plate boundary where colliding plates slide past each other (such as the San Andreas fault in California) is an example of: 48. What is the minimum number of seismograph stations from which scientists must collect data to locate the epicenter of an earthquake? 49. What is the differen ...
... 47. A tectonic plate boundary where colliding plates slide past each other (such as the San Andreas fault in California) is an example of: 48. What is the minimum number of seismograph stations from which scientists must collect data to locate the epicenter of an earthquake? 49. What is the differen ...
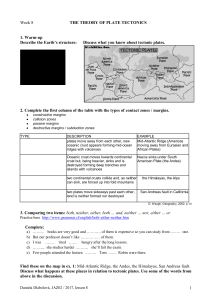
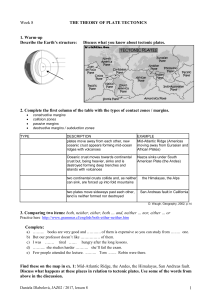
1 Week 8 THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS 1. Warm
... South American plate, and because it is denser it is subducted underneath. The South American plate is less dense so it sits on top of this subduction zone, but the rocks of the South American plate have been folded upwards and crumpled into fold mountains. There are also volcanoes and earthquakes a ...
... South American plate, and because it is denser it is subducted underneath. The South American plate is less dense so it sits on top of this subduction zone, but the rocks of the South American plate have been folded upwards and crumpled into fold mountains. There are also volcanoes and earthquakes a ...
divergent boundaries - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... 1. Oceanic-Continental When a continental plate collides with an oceanic plate, the less dense plate will continue on its course while the denser plate will sink under the continental plate and into the . As the descending plate increases in depth, the heat generated causes partial melting of the ma ...
... 1. Oceanic-Continental When a continental plate collides with an oceanic plate, the less dense plate will continue on its course while the denser plate will sink under the continental plate and into the . As the descending plate increases in depth, the heat generated causes partial melting of the ma ...
8_Plate_Tectonics
... South American plate, and because it is denser it is subducted underneath. The South American plate is less dense so it sits on top of this subduction zone, but the rocks of the South American plate have been folded upwards and crumpled into fold mountains. There are also volcanoes and earthquakes a ...
... South American plate, and because it is denser it is subducted underneath. The South American plate is less dense so it sits on top of this subduction zone, but the rocks of the South American plate have been folded upwards and crumpled into fold mountains. There are also volcanoes and earthquakes a ...
What causes Earth`s surface to change?
... Cinder-cone volcanoes are built by thick lava that is ____________________ thrown high into the air and falls as chunks or cinders. cinder-cone volcanoes hot spot lava shield volcanoes ...
... Cinder-cone volcanoes are built by thick lava that is ____________________ thrown high into the air and falls as chunks or cinders. cinder-cone volcanoes hot spot lava shield volcanoes ...
Impact cratering
... – No atmosphere on Moon and Mercury (too small) – Despite its thick atmosphere, Venus rotates too slowly (no or very little wind) and is too close to the Sun (no precipitation). – Earth has an atmosphere and most of the water has condensed onto the surface. – Mars has a very thin atmosphere. ...
... – No atmosphere on Moon and Mercury (too small) – Despite its thick atmosphere, Venus rotates too slowly (no or very little wind) and is too close to the Sun (no precipitation). – Earth has an atmosphere and most of the water has condensed onto the surface. – Mars has a very thin atmosphere. ...
Year 4 Overview
... Chester Visit- plan and map their journey using public transport (distance, time etc) children can produce detailed sketches of different monument they have visited. (Residential and orienteering) Italy – Volcanoes and Earthquakes (Mount Vesuvius) Children will use Mount Vesuvius as their case study ...
... Chester Visit- plan and map their journey using public transport (distance, time etc) children can produce detailed sketches of different monument they have visited. (Residential and orienteering) Italy – Volcanoes and Earthquakes (Mount Vesuvius) Children will use Mount Vesuvius as their case study ...
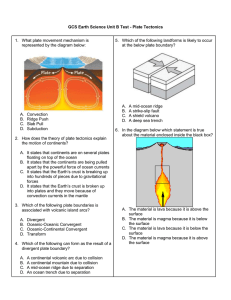
GCS Earth Science Unit B Test
... A. It states that continents are on several plates floating on top of the ocean B. It states that the continents are being pulled apart by the powerful force of ocean currents C. It states that the Earth’s crust is breaking up into hundreds of pieces due to gravitational ...
... A. It states that continents are on several plates floating on top of the ocean B. It states that the continents are being pulled apart by the powerful force of ocean currents C. It states that the Earth’s crust is breaking up into hundreds of pieces due to gravitational ...
Volcanism - FacultyWeb Support Center
... Flood Basalts: high volume flows over surface of Earth, stack into’ Layers that can be 100m or more thick (India) 3 types of Volcanoes: -Cinder Cones: high relief, conical shape -Shield volcanoes: low relief, built up by flows and intrusions Stratovolcano or Composite: formed by an alternating serie ...
... Flood Basalts: high volume flows over surface of Earth, stack into’ Layers that can be 100m or more thick (India) 3 types of Volcanoes: -Cinder Cones: high relief, conical shape -Shield volcanoes: low relief, built up by flows and intrusions Stratovolcano or Composite: formed by an alternating serie ...
ttu_gs0001_000430
... form of lava flows and, less commonly, as fragmented lava such as volcanic bombs, cinders, pumice, and ash. Basalt magma is more fluid than the other types of magma (andesite, dacite, and rhyolite). Consequently, expanding volcanic gases can escape from basalt relatively easily and can propel lava h ...
... form of lava flows and, less commonly, as fragmented lava such as volcanic bombs, cinders, pumice, and ash. Basalt magma is more fluid than the other types of magma (andesite, dacite, and rhyolite). Consequently, expanding volcanic gases can escape from basalt relatively easily and can propel lava h ...
Landforms
... • Plate Tectonics: how forces within Earth create landforms – Plates can be compared to the cracked shell of a hard boiled egg ...
... • Plate Tectonics: how forces within Earth create landforms – Plates can be compared to the cracked shell of a hard boiled egg ...
Mount Etna Kilauea
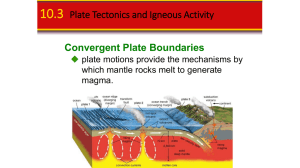
... Mount Etna is the tallest active volcano in Europe, and the 59th tallest volcano in the world. It is also one of the most active volcanoes in the world, in an almost constant state of volcanic activity. This is due to the fact that it sits on top of the convergent boundary between the Eurasian and A ...
... Mount Etna is the tallest active volcano in Europe, and the 59th tallest volcano in the world. It is also one of the most active volcanoes in the world, in an almost constant state of volcanic activity. This is due to the fact that it sits on top of the convergent boundary between the Eurasian and A ...
earthsciencechap17qu..
... 12: Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift. 13: According to plate tectonics, the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several huge, moving pieces. 14: Scientists believe that the sea floor is constantly being created or destroyed. 15: Convergent plate boundaries are places where two ...
... 12: Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift. 13: According to plate tectonics, the Earth’s lithosphere is divided into several huge, moving pieces. 14: Scientists believe that the sea floor is constantly being created or destroyed. 15: Convergent plate boundaries are places where two ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.