Geo 102 Practice Exam 1: True or false, to be considered a mineral
... 25. True or false, Mafic rocks are high in iron and magnesium, but low in silica content. 26. True or false, explosive volcanoes have high viscosity magma. 27. Scenario: You are a prominent Volcanologist and are studying a volcano that is on the verge of an eruption. You are trying to determine whic ...
... 25. True or false, Mafic rocks are high in iron and magnesium, but low in silica content. 26. True or false, explosive volcanoes have high viscosity magma. 27. Scenario: You are a prominent Volcanologist and are studying a volcano that is on the verge of an eruption. You are trying to determine whic ...
Physical processes taking place at different types of plate margin
... ______________ from each other, e.g. at the mid-Atlantic ridge. ___________ (molten rock) ____________ from the mantle to fill the gap and cools to ___________________________. Magma create new crust ...
... ______________ from each other, e.g. at the mid-Atlantic ridge. ___________ (molten rock) ____________ from the mantle to fill the gap and cools to ___________________________. Magma create new crust ...
Lecture 2: Dynamic Earth: Plate Tectonics
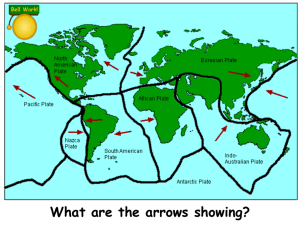
... • The theory was put together in late 1960s and early 1970s.The lithosphere is broken into a dozen of rigid blocks "plates", which are moving continuously. • Seven major plates: North American, South American, Pacific, African, Eurasian, Australian-Indian, and Antarctic. ...
... • The theory was put together in late 1960s and early 1970s.The lithosphere is broken into a dozen of rigid blocks "plates", which are moving continuously. • Seven major plates: North American, South American, Pacific, African, Eurasian, Australian-Indian, and Antarctic. ...
File
... the plates pull away from each other. 2. Convergent boundaries -- where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. 3. Transform boundaries -- where crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. ...
... the plates pull away from each other. 2. Convergent boundaries -- where crust is destroyed as one plate dives under another. 3. Transform boundaries -- where crust is neither produced nor destroyed as the plates slide horizontally past each other. ...
Plate Tectonics
... proposed the theory in the 1920’s • Based on matching fossils in different world locations • Believed that everything started from a super continent named Pangaea ...
... proposed the theory in the 1920’s • Based on matching fossils in different world locations • Believed that everything started from a super continent named Pangaea ...
VOLCANIC FEATURES OF THE CENTRAL ATLANTIC OCEAN
... Similar to other ocean basins, the central Atlantic Ocean (roughly latitude 10° to 50° N) contains many (more than a hundred) volcanic seamounts grouped in chains, clusters, and individual features. Although the Atlantic Ocean crust has been forming continuously from the Early Jurassic to the presen ...
... Similar to other ocean basins, the central Atlantic Ocean (roughly latitude 10° to 50° N) contains many (more than a hundred) volcanic seamounts grouped in chains, clusters, and individual features. Although the Atlantic Ocean crust has been forming continuously from the Early Jurassic to the presen ...
an integrated framework for global volcano disaster resilience
... USE GLOBAL VOLCANIC ERUPTION DISASTER LABORATORIES AS A BASIS FOR PREPARING FROM “A” (Emergency Response) TO “Z” (Recovery and Reconstruction) ...
... USE GLOBAL VOLCANIC ERUPTION DISASTER LABORATORIES AS A BASIS FOR PREPARING FROM “A” (Emergency Response) TO “Z” (Recovery and Reconstruction) ...
Document
... Old oceanic crust dense & heavy Heavy vs. light => subduction AKA destructive margins Large earthquake & explosive volcanoes Melting triggered at ~100km depth ...
... Old oceanic crust dense & heavy Heavy vs. light => subduction AKA destructive margins Large earthquake & explosive volcanoes Melting triggered at ~100km depth ...
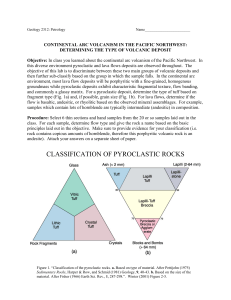
CLASSIFICATION OF PYROCLASTIC ROCKS
... then further sub-classify based on the group in which the sample falls. In the continental arc environment, most lava flow deposits will be porphyritic with a fine-grained, homogenous groundmass while pyroclastic deposits exhibit characteristic fragmental texture, flow banding, and commonly a glassy ...
... then further sub-classify based on the group in which the sample falls. In the continental arc environment, most lava flow deposits will be porphyritic with a fine-grained, homogenous groundmass while pyroclastic deposits exhibit characteristic fragmental texture, flow banding, and commonly a glassy ...
Integrated Science Chapter 19 Notes Section 1: Earth`s Interior and
... ⇒ When magma reaches the surface, its physical behavior changes, and it is called lava ⇒ There are three types of volcanoes → A shield volcano produces magma rich in iron and magnesium which is very fluid so the lava flows great distances. ♦ Eruptions from shield volcanoes are usually mild and can o ...
... ⇒ When magma reaches the surface, its physical behavior changes, and it is called lava ⇒ There are three types of volcanoes → A shield volcano produces magma rich in iron and magnesium which is very fluid so the lava flows great distances. ♦ Eruptions from shield volcanoes are usually mild and can o ...
Minerals, Igneous Rocks, Volcano, Plate Tectonics, Weathering
... Scenario: You are a prominent Volcanologist and are studying a volcano that is on the verge of an eruption. You are trying to determine which type of volcano it is and whether it will be an explosive of non-explosive eruption. Here are your clues: gentle slopes, high magma volume, basaltic magma, lo ...
... Scenario: You are a prominent Volcanologist and are studying a volcano that is on the verge of an eruption. You are trying to determine which type of volcano it is and whether it will be an explosive of non-explosive eruption. Here are your clues: gentle slopes, high magma volume, basaltic magma, lo ...
VOLCANIC HAZARDS
... FORMATION OF A VOLCANO The term VOLCANO signifies a vent, hill or mountain from which molten or hot rocks with gaseous materials are ejected. The term also applies to craters, hills or mountains formed by removal of preexisting materials or by accumulation of ejected materials. ...
... FORMATION OF A VOLCANO The term VOLCANO signifies a vent, hill or mountain from which molten or hot rocks with gaseous materials are ejected. The term also applies to craters, hills or mountains formed by removal of preexisting materials or by accumulation of ejected materials. ...
third quarter - New Haven Science
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
THIRD QUARTER II. UNIT 5: PLATE TECTONICS Time
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Modelessayplatetectheory 18.46KB 2017-03-29
... observation of the way in which South America and Africa’s coastlines appeared to match one another, as if they had once been joined together and then drifted apart. His theory was supported by the fossil evidence of plants and animals existing at the same time on continents separated by vast oceans ...
... observation of the way in which South America and Africa’s coastlines appeared to match one another, as if they had once been joined together and then drifted apart. His theory was supported by the fossil evidence of plants and animals existing at the same time on continents separated by vast oceans ...
TYPES OF PLATE BOUNDARIES
... A rift area occurs where plate movement creates a crack in Earth’s crust. Lava flows through to fill the crack, creating new crust. Volcanoes and earthquakes occur here. ...
... A rift area occurs where plate movement creates a crack in Earth’s crust. Lava flows through to fill the crack, creating new crust. Volcanoes and earthquakes occur here. ...
4TH YEAR - HCC Restless EARTH
... • Consequences 61 deaths, most of them caused by poisonous gases.several logging camps were destroyed.This killed all fish, including those in a hatchery.Floodwater washed away roads and railway bridges. • Telephone wires are cut. • Roads and bridges are washed away. • There is a danger of more erup ...
... • Consequences 61 deaths, most of them caused by poisonous gases.several logging camps were destroyed.This killed all fish, including those in a hatchery.Floodwater washed away roads and railway bridges. • Telephone wires are cut. • Roads and bridges are washed away. • There is a danger of more erup ...
Podcast Outline Key - KMS 8th Science
... earthquakes (that could lead to tsunamis), Igneous rock ...
... earthquakes (that could lead to tsunamis), Igneous rock ...
Igneous Processes Page 1 of 2 Intrusive igneous activity I. Plutons
... a. confining pressure raises melting temperature 1) Release of pressure on hot solid rock can trigger melting 2) Can occur when rock is brought higher in crust by convection ...
... a. confining pressure raises melting temperature 1) Release of pressure on hot solid rock can trigger melting 2) Can occur when rock is brought higher in crust by convection ...
student worksheet
... comes to the surface of Earth. The material released by volcanoes is known as magma when it is below Earth's crust and lava once it reaches the surface . This material (magma or lava) comes to the surface as a result of energy transfers that occur inside the earth. When volcanoes erupt, the lava, ro ...
... comes to the surface of Earth. The material released by volcanoes is known as magma when it is below Earth's crust and lava once it reaches the surface . This material (magma or lava) comes to the surface as a result of energy transfers that occur inside the earth. When volcanoes erupt, the lava, ro ...
Tectonic Hazards - Bedford Free School
... the oceanic plate and may trigger earthquakes. Magma rises up through cracks and erupts onto the surface. An example of a destructive plate boundary is where the Nazca plate is forced under the South American Plate. Produces composite volcanoes. Collision plate boundary form when two continental pla ...
... the oceanic plate and may trigger earthquakes. Magma rises up through cracks and erupts onto the surface. An example of a destructive plate boundary is where the Nazca plate is forced under the South American Plate. Produces composite volcanoes. Collision plate boundary form when two continental pla ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.