Megatsunami - SchoolNova
... initial wave heights much larger than normal tsunamis. • Origin: a large scale landslide, collision, or volcanic eruption event as opposed to raising or lowering of the sea floor due to tectonic activity. ...
... initial wave heights much larger than normal tsunamis. • Origin: a large scale landslide, collision, or volcanic eruption event as opposed to raising or lowering of the sea floor due to tectonic activity. ...
LAKE TOBA
... volcano some 70,000 years ago. Whether there was anyone around at the time on the island of Sumatra to witness the eruption(s) is unknown but if there were, they would have been incinerated or choked to death. According to the experts, the eruption(s) put some 2,000 km3 of ash into the atmosphere an ...
... volcano some 70,000 years ago. Whether there was anyone around at the time on the island of Sumatra to witness the eruption(s) is unknown but if there were, they would have been incinerated or choked to death. According to the experts, the eruption(s) put some 2,000 km3 of ash into the atmosphere an ...
File
... 15. Which of the following is NOT true regarding tsunamis? a. Tsunamis gain height as the drag on the shallow bottom of the coast b. They usually occur in the Pacific Ocean c. They can be caused by underwater earthquakes d. Tsunamis start as giant waves in the open ocean that are much taller than r ...
... 15. Which of the following is NOT true regarding tsunamis? a. Tsunamis gain height as the drag on the shallow bottom of the coast b. They usually occur in the Pacific Ocean c. They can be caused by underwater earthquakes d. Tsunamis start as giant waves in the open ocean that are much taller than r ...
Lecture 2b: Hot spots
... big thermal anomaly at the base of the continental lithosphere. – The first products are small degree, high-pressure melts of the plume itself, that escape quickly. – Then heat flow, a slow process, raises the temperature of the cold nonconvecting part of the mantle attached to the base of the conti ...
... big thermal anomaly at the base of the continental lithosphere. – The first products are small degree, high-pressure melts of the plume itself, that escape quickly. – Then heat flow, a slow process, raises the temperature of the cold nonconvecting part of the mantle attached to the base of the conti ...
LETTERS
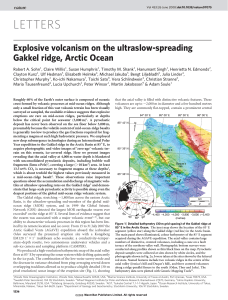
... Roughly 60% of the Earth’s outer surface is composed of oceanic crust formed by volcanic processes at mid-ocean ridges. Although only a small fraction of this vast volcanic terrain has been visually surveyed or sampled, the available evidence suggests that explosive eruptions are rare on mid-ocean r ...
... Roughly 60% of the Earth’s outer surface is composed of oceanic crust formed by volcanic processes at mid-ocean ridges. Although only a small fraction of this vast volcanic terrain has been visually surveyed or sampled, the available evidence suggests that explosive eruptions are rare on mid-ocean r ...
Slide 1
... the edge. Why do these types of convergent boundary make volcanoes while a continent-continent boundary does not? (5 min / 5 pts) Ocean-Ocean and Ocean-Continent boundaries both have oceanic crust as one of the plates ...
... the edge. Why do these types of convergent boundary make volcanoes while a continent-continent boundary does not? (5 min / 5 pts) Ocean-Ocean and Ocean-Continent boundaries both have oceanic crust as one of the plates ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... resources which form from hot, molten material deep beneath the Earth’s surface. The Earth is made of 3 main layers: The crust, mantle, and core (inner and outer). ...
... resources which form from hot, molten material deep beneath the Earth’s surface. The Earth is made of 3 main layers: The crust, mantle, and core (inner and outer). ...
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
... Volcanoes and earthquakes often occur at plate boundaries due to friction and collisions between plates. The “Ring of Fire” on Pacific coastlines is so named due to this phenomenon. ...
... Volcanoes and earthquakes often occur at plate boundaries due to friction and collisions between plates. The “Ring of Fire” on Pacific coastlines is so named due to this phenomenon. ...
Earth*s Layers notes Part 2
... subduction the more dense plate goes under the less dense plate. The more dense plate gets pushed into the mantle where it melts and the buildup of new magma escapes to the surface as a hot spot or volcano. ...
... subduction the more dense plate goes under the less dense plate. The more dense plate gets pushed into the mantle where it melts and the buildup of new magma escapes to the surface as a hot spot or volcano. ...
Teaching Activity Guide
... vocabulary words that will then be used as the beginning vocabulary list for a science lesson. Select an illustration from the book and give the children a specific length of time (five minutes?) to write down all the words they can think of about the particular subject. It is helpful to project an ...
... vocabulary words that will then be used as the beginning vocabulary list for a science lesson. Select an illustration from the book and give the children a specific length of time (five minutes?) to write down all the words they can think of about the particular subject. It is helpful to project an ...
volcanoes - Discovery Education
... The video opens with dramatic scenes of volcanoes erupting of the island of Hawaii. We see how Hawaiian volcanoes erupt in towering "fountains" spewing lava high into the air. Then we see how the lava proceeds downhill in "rivers of fire" before it reaches the ocean where it sizzles and splatters an ...
... The video opens with dramatic scenes of volcanoes erupting of the island of Hawaii. We see how Hawaiian volcanoes erupt in towering "fountains" spewing lava high into the air. Then we see how the lava proceeds downhill in "rivers of fire" before it reaches the ocean where it sizzles and splatters an ...
Chapter 6 Volcanoes - Huntington Catholic School
... • Subduction Produces Magma As descending oceanic crust scrapes past the continental crust, the temperature and pressure increase. • The following Visual Concepts presentation shows how subduction produces magma, and how that magma can rise to form a volcano. http://youtu.be/jRfEGvp6wDU ...
... • Subduction Produces Magma As descending oceanic crust scrapes past the continental crust, the temperature and pressure increase. • The following Visual Concepts presentation shows how subduction produces magma, and how that magma can rise to form a volcano. http://youtu.be/jRfEGvp6wDU ...
Document
... apart. A fissure develops,allowing hot ,molten rock to well up from the mantle and to from new materials as it solidifies,the fissure is called a spreading,or “pull apart” centre. ...
... apart. A fissure develops,allowing hot ,molten rock to well up from the mantle and to from new materials as it solidifies,the fissure is called a spreading,or “pull apart” centre. ...
What is a Rock?
... near tectonic plate boundaries because of the enormous stresses that are generated when tectonic plates separate, collide or slip past each other. • Over the past 15 million to 20 million years, large numbers of earthquakes have occurred along the San Andreas fault in California, where parts of the ...
... near tectonic plate boundaries because of the enormous stresses that are generated when tectonic plates separate, collide or slip past each other. • Over the past 15 million to 20 million years, large numbers of earthquakes have occurred along the San Andreas fault in California, where parts of the ...
Course Syllabus: Volcanic Geology of the Snake River Plain
... and 2 million years ago. Sediments shed from the highlands north and south of the plain were deposited in these lakes as the basin subsided. The lower part of this sedimentary sequence is known as the Chalk Hills Formation and the upper part constitutes the Glenns Ferry Formation. These units are co ...
... and 2 million years ago. Sediments shed from the highlands north and south of the plain were deposited in these lakes as the basin subsided. The lower part of this sedimentary sequence is known as the Chalk Hills Formation and the upper part constitutes the Glenns Ferry Formation. These units are co ...
Study Guide – Plate Tectonics (Chapter 21) Name _____ Question
... 13. What is a subduction zone? ...
... 13. What is a subduction zone? ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.