Volcanoes - Blacklick Valley School District
... Opening at the top of the vent is called a crater Pyroclastic flow – massive avalanches of hot glowing rock and gases (complete destruction) ...
... Opening at the top of the vent is called a crater Pyroclastic flow – massive avalanches of hot glowing rock and gases (complete destruction) ...
volcanoes ppt
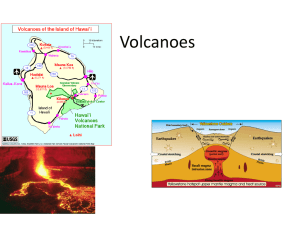
... Hot spot-area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust like a blow torch Often lies in the middle of plates far from boundaries Gradually forms volcanic mountains Ex- ocean, Hawaiian islands in the Pacific Ex- land Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming ...
... Hot spot-area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust like a blow torch Often lies in the middle of plates far from boundaries Gradually forms volcanic mountains Ex- ocean, Hawaiian islands in the Pacific Ex- land Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming ...
32 - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... • Explain how the composition of magma influences the processes that occur during volcanic eruptions • Discuss the major types of volcanic landforms, and the hazards associated with them • Cite some dramatic historical examples of human interaction with volcanic environments • Describe the landscape ...
... • Explain how the composition of magma influences the processes that occur during volcanic eruptions • Discuss the major types of volcanic landforms, and the hazards associated with them • Cite some dramatic historical examples of human interaction with volcanic environments • Describe the landscape ...
Volcanoes
... The word Volcano is derived from the name of the ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
... The word Volcano is derived from the name of the ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
Volcanoes
... 2) What is the difference between magma and lava? 3) Why are so many volcanoes found on the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean? 4) What do you know about Magma? 5) List magma types in order of increasing viscosity (least viscous first). 6) Which magma types will flow the fastest? 7) Which type of mag ...
... 2) What is the difference between magma and lava? 3) Why are so many volcanoes found on the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean? 4) What do you know about Magma? 5) List magma types in order of increasing viscosity (least viscous first). 6) Which magma types will flow the fastest? 7) Which type of mag ...
Volcanoes Crossword
... vent as the water cools quickly. 6 the smallest of the rock fragments that erupts from a volcano 10 a huge crater formed by the collapse of a volcano when magma rapidly erupts from underneath it. 12 magma __________ in silica resists flowing so the gases in the magma build up pressure until it viole ...
... vent as the water cools quickly. 6 the smallest of the rock fragments that erupts from a volcano 10 a huge crater formed by the collapse of a volcano when magma rapidly erupts from underneath it. 12 magma __________ in silica resists flowing so the gases in the magma build up pressure until it viole ...
Volcano Review
... d. produced by thick, sticky lava with high viscosity and a high volume of trapped gases e. a vent or fissure in Earth’s surface through which magma and gases are expelled f. a volcanically active area of Earth’s surface, commonly far from a tectonic plate boundary g. produced by runny lava with low ...
... d. produced by thick, sticky lava with high viscosity and a high volume of trapped gases e. a vent or fissure in Earth’s surface through which magma and gases are expelled f. a volcanically active area of Earth’s surface, commonly far from a tectonic plate boundary g. produced by runny lava with low ...
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... • Not all volcanoes erupt with the same intensity • Some may release lava, while other volcanoes only let out ash and gases • Volcanoes can be classified as… – Active – Dormant (not currently active) – Extinct (not expected to erupt again) ...
... • Not all volcanoes erupt with the same intensity • Some may release lava, while other volcanoes only let out ash and gases • Volcanoes can be classified as… – Active – Dormant (not currently active) – Extinct (not expected to erupt again) ...
Chapter 6 Volcanoes
... ash and other gases reach upper atmosphere ash and gases spread around globe block sunlight enough to cause surface temp. drops ...
... ash and other gases reach upper atmosphere ash and gases spread around globe block sunlight enough to cause surface temp. drops ...
Volcanism and Its Landforms - Cal State LA
... Distribution of Volcanic Activity • Volcanoes occur along plate boundaries • Divergent boundaries – mid-ocean ridges ...
... Distribution of Volcanic Activity • Volcanoes occur along plate boundaries • Divergent boundaries – mid-ocean ridges ...
Volcano Notes
... 2. Composite Volcanoes – these are formed by a combination of both types of lava. These volcanoes give off pyroclastic material and have extremely explosive eruptions. Composite cones are the most common kind of volcano. Example: Mount St. Helens 3. Shield Volcanoes – these look like an ancient shi ...
... 2. Composite Volcanoes – these are formed by a combination of both types of lava. These volcanoes give off pyroclastic material and have extremely explosive eruptions. Composite cones are the most common kind of volcano. Example: Mount St. Helens 3. Shield Volcanoes – these look like an ancient shi ...
Challenge Box - Activity 1
... What are some of the disadvantages of living close to active zones? ...
... What are some of the disadvantages of living close to active zones? ...
Volcanoes - Fairfield-Suisun Unified School District
... • An active volcano is currently erupting or has erupted recently (in geological terms) • A dormant volcano has not erupted lately but is considered likely to do so in the future. • An extinct volcano has not erupted for a very long time and is considered unlikely to do so in the future. ...
... • An active volcano is currently erupting or has erupted recently (in geological terms) • A dormant volcano has not erupted lately but is considered likely to do so in the future. • An extinct volcano has not erupted for a very long time and is considered unlikely to do so in the future. ...
3.2 Reinforcing Key Concepts
... Complete the table by filling in the missing information. Molten Rock ...
... Complete the table by filling in the missing information. Molten Rock ...
Impact of Volcanoes
... The amount of dust and ________________ blasted into the sky was enough to change the atmosphere, causing what people call "The Year without a Summer." Temperatures fell, crops died, and 117,000 people eventually __________ of starvation. Other Natural Disasters from Volcanoes If a volcano erupts un ...
... The amount of dust and ________________ blasted into the sky was enough to change the atmosphere, causing what people call "The Year without a Summer." Temperatures fell, crops died, and 117,000 people eventually __________ of starvation. Other Natural Disasters from Volcanoes If a volcano erupts un ...
Chapter 12 - Fill-in-the
... o The __________-walled depression around a volcano’s vent is called the __________. __________ of Volcanoes o Form at divergent & __________ plate boundaries. o __________Spots : An unusually hot area between the __________ & core that forces melted rock upward to form __________ in the middle ...
... o The __________-walled depression around a volcano’s vent is called the __________. __________ of Volcanoes o Form at divergent & __________ plate boundaries. o __________Spots : An unusually hot area between the __________ & core that forces melted rock upward to form __________ in the middle ...
Chapter 13 Study Notes Volcanoes
... • _____ lava forms on a _________ ridge. – Pillow – mid-ocean ...
... • _____ lava forms on a _________ ridge. – Pillow – mid-ocean ...
Chapter 13 Study Notes Volcanoes
... • _______ are igneous rock formations created when magma ____ __ reach Earth’s surface, but cools and solidifies ____ the crust. – Pluton – does – not – inside ...
... • _______ are igneous rock formations created when magma ____ __ reach Earth’s surface, but cools and solidifies ____ the crust. – Pluton – does – not – inside ...
Section
... 2. The Hawaiian Islands are all shield volcanoes. What are shield volcanoes, and why are they not especially hazardous to life? Shield volcanoes are low, broad, flat volcanoes formed from many thin flows of (generally basaltic) lava. Because the lowviscosity lavas that build shield volcanoes tend no ...
... 2. The Hawaiian Islands are all shield volcanoes. What are shield volcanoes, and why are they not especially hazardous to life? Shield volcanoes are low, broad, flat volcanoes formed from many thin flows of (generally basaltic) lava. Because the lowviscosity lavas that build shield volcanoes tend no ...
Volcano: Creator or Destroyer?
... person survive a volcanic eruption? Where do they happen? Only in far away exotic locations like Hawaii and the Philippines? Can they be anywhere? ...
... person survive a volcanic eruption? Where do they happen? Only in far away exotic locations like Hawaii and the Philippines? Can they be anywhere? ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.