Wk16-Volcanoes-p2
... • Magma needs to get out, too much pressure!!!!!! • Rise in temperature or drop in pressure causes magma to form faster. ...
... • Magma needs to get out, too much pressure!!!!!! • Rise in temperature or drop in pressure causes magma to form faster. ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. A composite volcano are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension made of bombs, blocks, cinders, volcanic a ...
... ejected from a single vent. When the lava is blown into the air it breaks into little pieces that solidify and fall as cinders around the vent to form an oval or circular cone. A composite volcano are mostly steep-sided, symmetrical cones of large dimension made of bombs, blocks, cinders, volcanic a ...
Unit 3 Section 2 Volcanoes Answer Key - WAHS
... surface. The stiff lava forms volcanic domes with steep slopes. If the volcano’s vent gets plugged, gasses cannot escape and pressure builds. The pressure can be released in a volcanic eruption that blasts pieces of lava and rock into the atmosphere. (pyroclastics) A composite cone forms by many eru ...
... surface. The stiff lava forms volcanic domes with steep slopes. If the volcano’s vent gets plugged, gasses cannot escape and pressure builds. The pressure can be released in a volcanic eruption that blasts pieces of lava and rock into the atmosphere. (pyroclastics) A composite cone forms by many eru ...
Volcanoes
... A volcano is shaped like a mountain constructed from lava and/or pyroclastics. They erupt when “magma is generated by partial melting of the rock peridotite in the upper mantle to form magma with a basaltic composition”, ultimatly resulting in “buoyant molten rock will rise toward the surface” (Foun ...
... A volcano is shaped like a mountain constructed from lava and/or pyroclastics. They erupt when “magma is generated by partial melting of the rock peridotite in the upper mantle to form magma with a basaltic composition”, ultimatly resulting in “buoyant molten rock will rise toward the surface” (Foun ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – Gases expand within a magma as it nears the Earth’s surface due to decreasing pressure – The violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape ...
... – Gases expand within a magma as it nears the Earth’s surface due to decreasing pressure – The violence of an eruption is related to how easily gases escape ...
EXTRUSIVE VOLCANIC LANDFORMS inc.Mont
... content, and generally erupt at temperatures in excess of 950 °C. Basaltic magma is high in iron and magnesium, and has relatively lower aluminium and silica, which taken together reduces the degree of polymerization within the melt. Owing to the higher temperatures, viscosities can be relatively lo ...
... content, and generally erupt at temperatures in excess of 950 °C. Basaltic magma is high in iron and magnesium, and has relatively lower aluminium and silica, which taken together reduces the degree of polymerization within the melt. Owing to the higher temperatures, viscosities can be relatively lo ...
Magma - Geography1000
... • Small earthquakes around the area of a volcano • Monitoring thermal, magnetic, and hydrologic conditions • Magma accumulation can heat rock or water, change magnetic stimulus or change water temperature • Monitoring the land surface to detect tilting or swelling of the volcano • The change in the ...
... • Small earthquakes around the area of a volcano • Monitoring thermal, magnetic, and hydrologic conditions • Magma accumulation can heat rock or water, change magnetic stimulus or change water temperature • Monitoring the land surface to detect tilting or swelling of the volcano • The change in the ...
Surtseyan Eruption - NATSCI-A7
... lava piles up into a dome, which may grow by inflating from the inside or by squeezing out lobes of lava (something like toothpaste coming out of a tube). These lava lobes can be short and blobby, long and thin, or even form spikes that rise tens of meters into the air before they fall over. Lava do ...
... lava piles up into a dome, which may grow by inflating from the inside or by squeezing out lobes of lava (something like toothpaste coming out of a tube). These lava lobes can be short and blobby, long and thin, or even form spikes that rise tens of meters into the air before they fall over. Lava do ...
geomythology - TheVirtualNeal
... Tremors were the result of struggling giants imprisoned in the Earth by Zeus ...
... Tremors were the result of struggling giants imprisoned in the Earth by Zeus ...
Subject
... Together, create a quiz to test the knowledge of others on volcanoes. Parts of a volcano Kinds of volcanic eruptions Life cycle of a volcano 3 types of volcanoes ...
... Together, create a quiz to test the knowledge of others on volcanoes. Parts of a volcano Kinds of volcanic eruptions Life cycle of a volcano 3 types of volcanoes ...
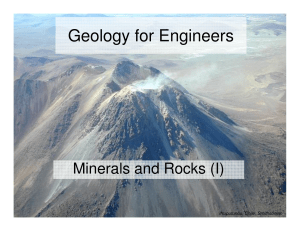
L02-Rocks and minerals 1
... • Volcanic: – Lavas erupt from volcanoes either as molten fluids, or are blown out as volcanic ash by violent explosions – Black volcanoes (effusive, mostly basaltic) – Red volcanoes (explosive, mostly felsic) This classification is based on composition. Formation of phenocrysts on cooling increases ...
... • Volcanic: – Lavas erupt from volcanoes either as molten fluids, or are blown out as volcanic ash by violent explosions – Black volcanoes (effusive, mostly basaltic) – Red volcanoes (explosive, mostly felsic) This classification is based on composition. Formation of phenocrysts on cooling increases ...
Volcanic Fatalities
... lake to prevent a further tragedy. An artificial vent to the lake surface was created with pipe. Water is pumped from the bottom of the lake to the surface through the pipe, where it can degas. ...
... lake to prevent a further tragedy. An artificial vent to the lake surface was created with pipe. Water is pumped from the bottom of the lake to the surface through the pipe, where it can degas. ...
Climate and Volcanism - Natural Climate Change
... About 90 percent of all volcanoes exist within the Ring of Fire along the edges of the Pacific Ocean. ...
... About 90 percent of all volcanoes exist within the Ring of Fire along the edges of the Pacific Ocean. ...
How Does Magma Reach the Surface?
... abundance of dissolved gases • Does not flow readily through the vent so it clogs up and becomes blocked • Pressure builds up and a violent eruption is produced • Ejects solid pieces of tephra to form a narrow cone ...
... abundance of dissolved gases • Does not flow readily through the vent so it clogs up and becomes blocked • Pressure builds up and a violent eruption is produced • Ejects solid pieces of tephra to form a narrow cone ...
The Origin and Petrogenesis of Mount Hasan (Small Mt. Hasan) and
... volcano consists of compositions ranging from basaltic andesite to rhyolite and associated pyroclastic rocks, with a silica content ranging from 52.21 to 72.49 wt %. The volcanic rocks of Keçiboyduran volcano have rather uniform compositions including andesite and dacite lavas and related pyroclasti ...
... volcano consists of compositions ranging from basaltic andesite to rhyolite and associated pyroclastic rocks, with a silica content ranging from 52.21 to 72.49 wt %. The volcanic rocks of Keçiboyduran volcano have rather uniform compositions including andesite and dacite lavas and related pyroclasti ...
Physical Process
... Sometimes volcanoes occur far from plate boundaries. These areas are called hot spots. A good example of a hot spot is the formation of the Hawaiian Islands in the middle of the Pacific. ...
... Sometimes volcanoes occur far from plate boundaries. These areas are called hot spots. A good example of a hot spot is the formation of the Hawaiian Islands in the middle of the Pacific. ...
location of volcanoes in british columbia
... the result of the dense heavier oceanic Juan de Fuca Plate subducting beneath the lighter, less dense North American Plate that has created the energy to produce these volcanoes along the West Coast of North America. Mt. Baker has been releasing steam, as recently as 2001, from Sherman Crater and is ...
... the result of the dense heavier oceanic Juan de Fuca Plate subducting beneath the lighter, less dense North American Plate that has created the energy to produce these volcanoes along the West Coast of North America. Mt. Baker has been releasing steam, as recently as 2001, from Sherman Crater and is ...
Physical and Ecological Processes
... Sometimes volcanoes occur far from plate boundaries. These areas are called hot spots. A good example of a hot spot is the formation of the Hawaiian Islands in the middle of the Pacific. ...
... Sometimes volcanoes occur far from plate boundaries. These areas are called hot spots. A good example of a hot spot is the formation of the Hawaiian Islands in the middle of the Pacific. ...
More Fun with plates
... Caldera An older volcano with a large crater which can be 62 miles(100km) wide. In this crater many little new craters are formed. VERY dangerous. Larger Caldera’s can be very hard to notice at first. Signs of Calderas include hot springs, or ...
... Caldera An older volcano with a large crater which can be 62 miles(100km) wide. In this crater many little new craters are formed. VERY dangerous. Larger Caldera’s can be very hard to notice at first. Signs of Calderas include hot springs, or ...
Chapter 18- Volcanoes - Independence High School
... – oceanic crust or oceanic sediment – 60% silica (high) – intermediate viscosity – intermediate eruptions – melted andesite ...
... – oceanic crust or oceanic sediment – 60% silica (high) – intermediate viscosity – intermediate eruptions – melted andesite ...
Volcanoes & Earthquakes
... chimney) of his furnace was an island named Volcano… this was a simple attempt by people to try to understand the complex processes that cause volcanic activity ...
... chimney) of his furnace was an island named Volcano… this was a simple attempt by people to try to understand the complex processes that cause volcanic activity ...
Volcanoes Directed Readings
... The rock of the Earth’s mantle a. Flows very quickly b. Has a puttylike consistency c. Is cooler than the Earth’s crust d. Is solid and rock-hard Rock usually melts to form magma a. When there is an increase in pressure b. When there is a decrease in pressure c. When there is a decrease e in tempera ...
... The rock of the Earth’s mantle a. Flows very quickly b. Has a puttylike consistency c. Is cooler than the Earth’s crust d. Is solid and rock-hard Rock usually melts to form magma a. When there is an increase in pressure b. When there is a decrease in pressure c. When there is a decrease e in tempera ...
powerpoint_Volcanoes Lava and Types of Eruptions
... • Check the temperature of the ground water to see if the magma is heating it. • Monitor the many small earthquakes triggered by magma moving from the chamber to the pipe. ...
... • Check the temperature of the ground water to see if the magma is heating it. • Monitor the many small earthquakes triggered by magma moving from the chamber to the pipe. ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.