Appendix #5: Volcanoes on Hawaiian Islands
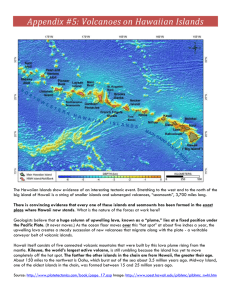
... Geologists believe that a huge column of upwelling lava, known as a “plume,” lies at a fixed position under the Pacific Plate. (It never moves.) As the ocean floor moves over this “hot spot” at about five inches a year, the upwelling lava creates a steady succession of new volcanoes that migrate alo ...
... Geologists believe that a huge column of upwelling lava, known as a “plume,” lies at a fixed position under the Pacific Plate. (It never moves.) As the ocean floor moves over this “hot spot” at about five inches a year, the upwelling lava creates a steady succession of new volcanoes that migrate alo ...
the free PDF resource
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
... 1. What is the difference between magma and lava? Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fo ...
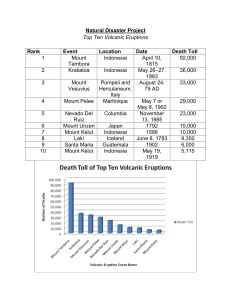
Natural Disaster Project Top Ten Volcanic Eruptions Rank Event
... active from 1990 to 1995, and a large eruption in 1991 generated a pyroclastic flow that killed 43 people, including three volcanologists. ...
... active from 1990 to 1995, and a large eruption in 1991 generated a pyroclastic flow that killed 43 people, including three volcanologists. ...
File
... • From lava and ash • Instead of forming mountains, some eruptions of lava form high, level areas called lava plateaus. First, lava flows out of several long cracks in an area. The thin, runny lava travels far before cooling and solidifying. Again and again, floods of lava flow on top of earlier flo ...
... • From lava and ash • Instead of forming mountains, some eruptions of lava form high, level areas called lava plateaus. First, lava flows out of several long cracks in an area. The thin, runny lava travels far before cooling and solidifying. Again and again, floods of lava flow on top of earlier flo ...
Types of Volcanoes
... • Quiet eruptions of _____________________ lava spread out in flat ____________________. • The buildup of these layers forms a broad ___________________ with gently sloping sides called a _____________________ volcano. • The ____________________ islands are examples of _________________ volcanoes. • ...
... • Quiet eruptions of _____________________ lava spread out in flat ____________________. • The buildup of these layers forms a broad ___________________ with gently sloping sides called a _____________________ volcano. • The ____________________ islands are examples of _________________ volcanoes. • ...
A Geological Guidebook to Dante`s Peak
... volcanic ash in the movie looked more like snow (low density) as it fell. For geologists who have seen the movie, the hot, runny lava, seen issuing from the volcano, is the most bothersome issue. Generally, runny, fast-flowing lava (basalt) erupts from Hawaiian or "shield" volcanoes; but we underst ...
... volcanic ash in the movie looked more like snow (low density) as it fell. For geologists who have seen the movie, the hot, runny lava, seen issuing from the volcano, is the most bothersome issue. Generally, runny, fast-flowing lava (basalt) erupts from Hawaiian or "shield" volcanoes; but we underst ...
Earthquakes - domenicoscience
... • 66,000 people died making it the deadliest earthquake in South America. • The 7.8 magnitude quake had a high death toll because many of the adobe houses collapsed and there were massive landslides in the Andes. ...
... • 66,000 people died making it the deadliest earthquake in South America. • The 7.8 magnitude quake had a high death toll because many of the adobe houses collapsed and there were massive landslides in the Andes. ...
What is a Volcano?
... Subduction or one plate to submerge beneath the other late to submerge beneath the other plate to submerge beneath the other ollision of plates, causing Subduction or. ...
... Subduction or one plate to submerge beneath the other late to submerge beneath the other plate to submerge beneath the other ollision of plates, causing Subduction or. ...
Volcanoes - BHS Science Department
... occurs when the plates move apart form each other where plates separate, they form long, deep crack called rifts as more lava flows, it builds up the sea floor sometimes there is enough buildup to form an island (Iceland) 2. Convergent Plate Boundary occurs when plates move together one ...
... occurs when the plates move apart form each other where plates separate, they form long, deep crack called rifts as more lava flows, it builds up the sea floor sometimes there is enough buildup to form an island (Iceland) 2. Convergent Plate Boundary occurs when plates move together one ...
File
... Eruptions are typically non-explosive. Shield volcanoes produce fast flowing fluid [lava] that can flow for many miles. • Ash and Cinder volcanoes are typically violent and destructive, characterized by narrow tall cones. ...
... Eruptions are typically non-explosive. Shield volcanoes produce fast flowing fluid [lava] that can flow for many miles. • Ash and Cinder volcanoes are typically violent and destructive, characterized by narrow tall cones. ...
Volcanoes
... Water and wind tear down the Earth’s surface. Volcanoes push molten rock back onto the surface and the collision of tectonic plates creates mountains. Otherwise - water world. 12. Based on the theory of evolution, what theories are given to explain the roll of volcanoes in the forming of life on Ear ...
... Water and wind tear down the Earth’s surface. Volcanoes push molten rock back onto the surface and the collision of tectonic plates creates mountains. Otherwise - water world. 12. Based on the theory of evolution, what theories are given to explain the roll of volcanoes in the forming of life on Ear ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
Volcano Lab 16-17 File
... Highly variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra andesite composition variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra with an overall andesite composition Gentle lower slopes, but steep upper slopes; concave upward; small summit crater ...
... Highly variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra andesite composition variable; alternating basaltic to rhyolitic lavas and tephra with an overall andesite composition Gentle lower slopes, but steep upper slopes; concave upward; small summit crater ...
GCSE Revision session.
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes are violent and Fold Mountains are found eg West coast of South America where Nazca plate meets South American plate. ...
... Earthquakes and Volcanoes are violent and Fold Mountains are found eg West coast of South America where Nazca plate meets South American plate. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... – Produced by mild eruptions of large volumes of lava – Mauna Loa on Hawaii is a good example ...
... – Produced by mild eruptions of large volumes of lava – Mauna Loa on Hawaii is a good example ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes Quiz
... 15. The sea floor is spreading in the above pictures. This allows mantle material to rise up and fill the gap that is created as these plates move apart. The country of Iceland is a volcanic island that formed as this process happened over millions of years eventually causing the volcano to rise abo ...
... 15. The sea floor is spreading in the above pictures. This allows mantle material to rise up and fill the gap that is created as these plates move apart. The country of Iceland is a volcanic island that formed as this process happened over millions of years eventually causing the volcano to rise abo ...
Notes-Volcanoes
... Flood basalts - The previous examples represent small-scale activity - But basaltic eruptions can be huge, forming lava plateaus - These huge outpourings may occur quickly (1-3 Ma) and may contribute to mass extinctions ...
... Flood basalts - The previous examples represent small-scale activity - But basaltic eruptions can be huge, forming lava plateaus - These huge outpourings may occur quickly (1-3 Ma) and may contribute to mass extinctions ...
Plate Tectonic - Hazards (1) Lab
... again. Dormant volcanoes often have small earthquakes, suggesting magma is moving underneath them. Volcanic areas may have active hot springs, triggered by water heated by the magma. A third type of volcano, an extinct volcano, does not have a magma sources, and will never erupt again. Your students ...
... again. Dormant volcanoes often have small earthquakes, suggesting magma is moving underneath them. Volcanic areas may have active hot springs, triggered by water heated by the magma. A third type of volcano, an extinct volcano, does not have a magma sources, and will never erupt again. Your students ...
Extraterrestrial Volcanism
... b.Mars, Earth’s moon, and Io (a moon of Jupiter) are three examples. ...
... b.Mars, Earth’s moon, and Io (a moon of Jupiter) are three examples. ...
VOLCANO RESEARCH PAPER: Big scientific ideas for which you
... Earth’s surface. Volcanic Eruptions- explosive or nonexplosive depending on the type of magma emitted (lava or pyroclastic) Explosive – caused by magma with high water content; produces mostly pyroclastic materials – Pyroclastic Material - material that forms when magma explodes from a volcano and s ...
... Earth’s surface. Volcanic Eruptions- explosive or nonexplosive depending on the type of magma emitted (lava or pyroclastic) Explosive – caused by magma with high water content; produces mostly pyroclastic materials – Pyroclastic Material - material that forms when magma explodes from a volcano and s ...
Volcano

A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle. Therefore, on Earth, volcanoes are generally found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging. For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates pulling apart; the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates coming together. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's interior plates, e.g., in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America. This type of volcanism falls under the umbrella of ""plate hypothesis"" volcanism. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has also been explained as mantle plumes. These so-called ""hotspots"", for example Hawaii, are postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs with magma from the core–mantle boundary, 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide past one another.Erupting volcanoes can pose many hazards, not only in the immediate vicinity of the eruption. One such hazard is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft, in particular those with jet engines where ash particles can be melted by the high operating temperature; the melted particles then adhere to the turbine blades and alter their shape, disrupting the operation of the turbine. Large eruptions can affect temperature as ash and droplets of sulfuric acid obscure the sun and cool the Earth's lower atmosphere (or troposphere); however, they also absorb heat radiated up from the Earth, thereby warming the upper atmosphere (or stratosphere). Historically, so-called volcanic winters have caused catastrophic famines.