Atomistic description of wave function localization effects in InxGa1
... experimental data in Refs.,?, ?, ?, ? we treat Inx Ga1−x N as a random alloy and include WWFs at the upper QW interface.? The experimentally reported lateral size of these WWFs is ≈ 5-10 nm. The height of the WWF is between one and two monolayers. Here, we approximate WWFs as disk-like structures wi ...
... experimental data in Refs.,?, ?, ?, ? we treat Inx Ga1−x N as a random alloy and include WWFs at the upper QW interface.? The experimentally reported lateral size of these WWFs is ≈ 5-10 nm. The height of the WWF is between one and two monolayers. Here, we approximate WWFs as disk-like structures wi ...
Bose-Glass Phases of Ultracold Atoms due to Cavity Backaction Hessam Habibian,
... sufficiently strong lasers quantum fluctuations can support the buildup of an intracavity field, which in turn amplifies quantum fluctuations. The dynamics is described by a Bose-Hubbard model where the coefficients due to the cavity field depend on the atomic density at all lattice sites. Quantum M ...
... sufficiently strong lasers quantum fluctuations can support the buildup of an intracavity field, which in turn amplifies quantum fluctuations. The dynamics is described by a Bose-Hubbard model where the coefficients due to the cavity field depend on the atomic density at all lattice sites. Quantum M ...
Hadron-Hadron Scattering at High Energies
... vacuum, it is natural to associate its exchange with the exchange of gluons. The understanding of the detailed nature of the gluon- eld processes behind this phenomenology is of course an important problem. It is now understood that many important features are due to non-perturbative QCD e ects. Sof ...
... vacuum, it is natural to associate its exchange with the exchange of gluons. The understanding of the detailed nature of the gluon- eld processes behind this phenomenology is of course an important problem. It is now understood that many important features are due to non-perturbative QCD e ects. Sof ...
Driven Bose-Hubbard model with a parametrically modulated
... with diverging position and momentum variances. The driven single-particle problem is still exactly solvable in terms of the Mathieu equation with its known stability diagram. For interacting particles, this is no longer possible. To elucidate the impact of quantum many-body interactions on the para ...
... with diverging position and momentum variances. The driven single-particle problem is still exactly solvable in terms of the Mathieu equation with its known stability diagram. For interacting particles, this is no longer possible. To elucidate the impact of quantum many-body interactions on the para ...
Scattering of Dirac Fermions in Barrier Geometries on the Surface of
... We next add a scalar potential localized on the edge of the material and see that, upon increasing its value, the edge states reconstruct as to avoid the region of high scalar potential, but still remain gapless. Finally, we add edge terms which break time-reversal symmetry and examine their effects ...
... We next add a scalar potential localized on the edge of the material and see that, upon increasing its value, the edge states reconstruct as to avoid the region of high scalar potential, but still remain gapless. Finally, we add edge terms which break time-reversal symmetry and examine their effects ...
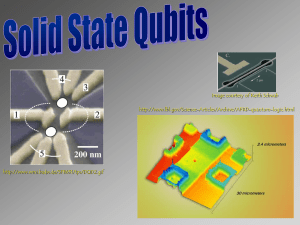
superconducting qubits solid state qubits
... microfabricated devices, just like the superconducting qubits are. Image courtesy of Charlie Marcus ...
... microfabricated devices, just like the superconducting qubits are. Image courtesy of Charlie Marcus ...
Chiral Prethermalization in Supersonically Split Condensates
... time scales. These developments, have, in turn, reinvigorated theoretical interest in the study of out-of-equilibrium dynamics of isolated quantum systems. Amidst such interest, one-dimensional (1D) systems have garnered particular attention because the nonequilibrium behavior in these systems is en ...
... time scales. These developments, have, in turn, reinvigorated theoretical interest in the study of out-of-equilibrium dynamics of isolated quantum systems. Amidst such interest, one-dimensional (1D) systems have garnered particular attention because the nonequilibrium behavior in these systems is en ...
1 Basics of Semiconductor and Spin Physics
... the lowest allowed bands are completely filled with electrons (according to the Pauli principle), while the higher bands are empty. In most cases only the upper filled band (valence band) and the first empty band (conduction band) are of interest. The conduction and valence bands are separated by a ...
... the lowest allowed bands are completely filled with electrons (according to the Pauli principle), while the higher bands are empty. In most cases only the upper filled band (valence band) and the first empty band (conduction band) are of interest. The conduction and valence bands are separated by a ...
QCD Matter Phase Diagram
... such as isolated quarks or gluons, are never observed. Suppose we have a system of two quarks with appropriate colors and we try to drag them appart as shown on the right side of figure 2. Since we know, that the strong potential increases with distance between two quarks, so at some point it become ...
... such as isolated quarks or gluons, are never observed. Suppose we have a system of two quarks with appropriate colors and we try to drag them appart as shown on the right side of figure 2. Since we know, that the strong potential increases with distance between two quarks, so at some point it become ...
Is there a stable hydrogen atom in higher dimensions?
... with the well-known paper of Ehrenfest5 and has inspired many additional interesting investigations. For reviews see Refs. 6 and 7, and for a recent paper on this problem see Ref. 8 where the dimensionality of space–time has been related to physical phenomena which are accessible to experiment. Acco ...
... with the well-known paper of Ehrenfest5 and has inspired many additional interesting investigations. For reviews see Refs. 6 and 7, and for a recent paper on this problem see Ref. 8 where the dimensionality of space–time has been related to physical phenomena which are accessible to experiment. Acco ...
A model of interacting partons for hadronic structure functions
... made of point-like constituents called partons. These were identified with the quarks which were until then, hypothetical particles. Structure functions can be expressed in terms of parton distribution functions. These describe the distribution of partons within the proton. Soon after, Quantum Chrom ...
... made of point-like constituents called partons. These were identified with the quarks which were until then, hypothetical particles. Structure functions can be expressed in terms of parton distribution functions. These describe the distribution of partons within the proton. Soon after, Quantum Chrom ...
Ground state and dynamic structure of quantum fluids
... He and 3 He, the former being a 99.99986% of the total population. The atomic structure of the He atom is very simple, having two electrons in the 1s orbital in a spin singlet state around a nucleus, composed of two protons and two neutrons in the case of the 4 He, and two protons and one neutron fo ...
... He and 3 He, the former being a 99.99986% of the total population. The atomic structure of the He atom is very simple, having two electrons in the 1s orbital in a spin singlet state around a nucleus, composed of two protons and two neutrons in the case of the 4 He, and two protons and one neutron fo ...
Quantized conductance in magnetic field: spin resolved plateaus
... QPCs is also recorded with an additional voltage amplifier. These four terminal measurement method allows precise measurement of the resistance of the QPC, without parazitic resistances of the cables, ohmics or circuitry. For DC bias measurements an external DC voltage was supplied to our voltage con ...
... QPCs is also recorded with an additional voltage amplifier. These four terminal measurement method allows precise measurement of the resistance of the QPC, without parazitic resistances of the cables, ohmics or circuitry. For DC bias measurements an external DC voltage was supplied to our voltage con ...
quantum transport phenomena of two
... 1.1 Two-dimensional electron gas in semiconductor heterostructures In this section we summarize some basic concepts related to two-dimensional electron gas systems. As an example, we discuss the gallium arsenide (GaAs) / aluminium gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) material system which provides a very high ...
... 1.1 Two-dimensional electron gas in semiconductor heterostructures In this section we summarize some basic concepts related to two-dimensional electron gas systems. As an example, we discuss the gallium arsenide (GaAs) / aluminium gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) material system which provides a very high ...