
Chapter 2 Atomic Motion in an Optical Standing Wave
... where the tildes indicate operators after transformation. This Hamiltonian is then in the Schrödinger picture with respect to the field, where the field time dependence is generated by the presence of HF . In the classical limit, the average photon number N of the laser field is very large, and in a c ...
... where the tildes indicate operators after transformation. This Hamiltonian is then in the Schrödinger picture with respect to the field, where the field time dependence is generated by the presence of HF . In the classical limit, the average photon number N of the laser field is very large, and in a c ...
"Particles or waves"()
... even though they were aimed and fired in exactly the same way. The pattern that builds up reveals the wave nature of the particles as more and more photons hit the film. It is impossible to predict where any particular photon will turn up on the film, yet the overall pattern that eventually builds u ...
... even though they were aimed and fired in exactly the same way. The pattern that builds up reveals the wave nature of the particles as more and more photons hit the film. It is impossible to predict where any particular photon will turn up on the film, yet the overall pattern that eventually builds u ...
Chapter 8 - Lecture 3
... However, the positive and negative regions of Ψ1 can constructively/destructively interfere with the regions of Ψ2. ...
... However, the positive and negative regions of Ψ1 can constructively/destructively interfere with the regions of Ψ2. ...
CHAPTER 9: Statistical Physics
... energy and jump to a higher state. Therefore the fraction of electrons capable of participating in this thermal process is on the order of kT / EF. ...
... energy and jump to a higher state. Therefore the fraction of electrons capable of participating in this thermal process is on the order of kT / EF. ...
PPT
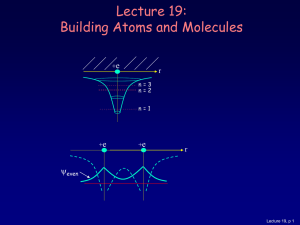
... As you learned in chemistry, the various behaviors of all the elements (and all the molecules made up from them) is all due to the way the electrons organize themselves, according to quantum mechanics. Lecture 19, p 16 ...
... As you learned in chemistry, the various behaviors of all the elements (and all the molecules made up from them) is all due to the way the electrons organize themselves, according to quantum mechanics. Lecture 19, p 16 ...
Fermions
... For fermions we must impose anti-commutations as the equal-time, canonical commutation relations. This will ensure the correct statistics and ensure consistency with microcausality with respect to commutations of operators o n {ψa (x), ψb (y)} = ψa† (x), ψb† (y) = 0 , n o ψa (x), ψb† (y) = δab δ (3) ...
... For fermions we must impose anti-commutations as the equal-time, canonical commutation relations. This will ensure the correct statistics and ensure consistency with microcausality with respect to commutations of operators o n {ψa (x), ψb (y)} = ψa† (x), ψb† (y) = 0 , n o ψa (x), ψb† (y) = δab δ (3) ...
1.2.8. Additional solutions to Schrödinger`s equation
... 1.2.8. Additional solutions to Schrödinger’s equation This section is devoted to some specific quantum structures that are present in semiconductor devices. These are: 1) the finite quantum well, a more realistic version of the infinite well as found in quantum well laser diodes, 2) a triangular wel ...
... 1.2.8. Additional solutions to Schrödinger’s equation This section is devoted to some specific quantum structures that are present in semiconductor devices. These are: 1) the finite quantum well, a more realistic version of the infinite well as found in quantum well laser diodes, 2) a triangular wel ...
Lecture 5: Spectroscopy and Photochemistry I
... break more and stronger bonds. We will pay special attention to them. ...
... break more and stronger bonds. We will pay special attention to them. ...
INTRODUCTION TO QUANTUM FIELD THEORY OF POLARIZED
... is normally made in terms of time-independent eigenfunctions |ni, which are the solutions of the time-independent Schrödinger equation. In the general case when the Hamiltonian is time dependent (which happens when the atomic system interacts with an electromagnetic field), expansion (7.6) implies ...
... is normally made in terms of time-independent eigenfunctions |ni, which are the solutions of the time-independent Schrödinger equation. In the general case when the Hamiltonian is time dependent (which happens when the atomic system interacts with an electromagnetic field), expansion (7.6) implies ...




















![Physics 322 Final Exam Study Guide (2015) [Pages 4 Only]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007969504_1-e89a1630d6e27466a3e33b80f7e23b58-300x300.png)

