PPT
... momentum of electron are gauge dependent and so their physical meaning is obscure. • The canonical photon spin and orbital angular momentum operators are also gauge dependent. Their physical meaning is obscure too. • Even it has been claimed in some textbooks that it is impossible to have photon spi ...
... momentum of electron are gauge dependent and so their physical meaning is obscure. • The canonical photon spin and orbital angular momentum operators are also gauge dependent. Their physical meaning is obscure too. • Even it has been claimed in some textbooks that it is impossible to have photon spi ...
Thermal Physics Concepts and Practice
... 4.1 Thermodynamic differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.1 Exact differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.2 Exactness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.3 Euler’s criterio ...
... 4.1 Thermodynamic differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.1 Exact differentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.2 Exactness . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4.1.3 Euler’s criterio ...
Optical properties of semiconductor quantum dots
... et al. 1998, Jacak et al. 1998). The extension and the shape of the dot confining potential varies, depending on the nanostructure fabrication technique: The dots that are studied most extensively by optical methods are induced by quantum well (QW) thickness fluctuations (Brunner et al. 1994, Flack ...
... et al. 1998, Jacak et al. 1998). The extension and the shape of the dot confining potential varies, depending on the nanostructure fabrication technique: The dots that are studied most extensively by optical methods are induced by quantum well (QW) thickness fluctuations (Brunner et al. 1994, Flack ...
Berry Phase Effects on Electronic Properties
... In 1984, Michael Berry wrote a paper that has generated immense interests throughout the different fields of physics including quantum chemistry (Berry, 1984). This is about the adiabatic evolution of an eigenenergy state when the external parameters of a quantum system change slowly and make up a l ...
... In 1984, Michael Berry wrote a paper that has generated immense interests throughout the different fields of physics including quantum chemistry (Berry, 1984). This is about the adiabatic evolution of an eigenenergy state when the external parameters of a quantum system change slowly and make up a l ...
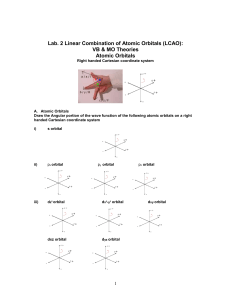
Lab
... It is the Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) in the valance of an atom: Individual wave functions (orbitals) combine to form hybrid atomic orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, sp3d2) Quantum mechanical approaches by combining the wave functions to give new wavefunctions are called hybridization o ...
... It is the Linear Combination of Atomic Orbitals (LCAO) in the valance of an atom: Individual wave functions (orbitals) combine to form hybrid atomic orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3, sp3d, sp3d2) Quantum mechanical approaches by combining the wave functions to give new wavefunctions are called hybridization o ...
Chapter 5 ANGULAR MOMENTUM AND ROTATIONS
... In classical mechanics the total angular momentum L ~ associated with such a …xed point is conserved. The existence of a conserved vector L system is itself a consequence of the fact that the associated Hamiltonian (or Lagrangian) is invariant under rotations, i.e., if the coordinates and momenta of ...
... In classical mechanics the total angular momentum L ~ associated with such a …xed point is conserved. The existence of a conserved vector L system is itself a consequence of the fact that the associated Hamiltonian (or Lagrangian) is invariant under rotations, i.e., if the coordinates and momenta of ...
Photodissociation of HBr. 1. Electronic Structure, Photodissociation
... There have been many previous theoretical studies of the ground state of HBr and its associated dipole moment.33-35 However, the number of calculations of the excited states is limited.14,36 Therefore, we have undertaken an ab initio investigation of the twelve electronic states, X1Σ+ (nondegenerate ...
... There have been many previous theoretical studies of the ground state of HBr and its associated dipole moment.33-35 However, the number of calculations of the excited states is limited.14,36 Therefore, we have undertaken an ab initio investigation of the twelve electronic states, X1Σ+ (nondegenerate ...
Probabilistic interpretation of resonant states
... The wave function of a resonant state has been discussed greatly since the early stage of quantum mechanics. As will be shown at the end of §3, it exponentially diverges in the distance from the scattering centre. Although this is an inevitable conclusion, the divergence has hindered the probabilist ...
... The wave function of a resonant state has been discussed greatly since the early stage of quantum mechanics. As will be shown at the end of §3, it exponentially diverges in the distance from the scattering centre. Although this is an inevitable conclusion, the divergence has hindered the probabilist ...
From Ultracold Atoms to Condensed Matter Physics
... harmonic confinement. On top of this harmonic trap, in analogy to the periodic potential felt by electrons in a solid, one can introduce a periodic potential using a combination of lasers. The lasers that create the lattice are detuned from an optical absorption line and generate an electric dipole ...
... harmonic confinement. On top of this harmonic trap, in analogy to the periodic potential felt by electrons in a solid, one can introduce a periodic potential using a combination of lasers. The lasers that create the lattice are detuned from an optical absorption line and generate an electric dipole ...
hidden symmetry and explicit spheroidal eigenfunctions of the
... where L (x) is an associated Laguerre polynomial. In the spherical case, for each 1, the Laguerre factor has n 1— 1 radial nodes, and the Gegenbauer factor has 1— m angular nodes. The total number of nodes thus is it m 1, inde pendent of the I value. In the parabolic case, s+ t= a= n—rn—I is again t ...
... where L (x) is an associated Laguerre polynomial. In the spherical case, for each 1, the Laguerre factor has n 1— 1 radial nodes, and the Gegenbauer factor has 1— m angular nodes. The total number of nodes thus is it m 1, inde pendent of the I value. In the parabolic case, s+ t= a= n—rn—I is again t ...
by Chao Shen - Deep Blue
... publications; Hong-Chen Jiang shared with me his extensive experience in tensor networks and DMRG during one summer; Guin-Dar Lin, who recently became an assistant professor at National Taiwan University, familiarized me with trapped ion quantum simulation and computation; YangHao Chan shared with m ...
... publications; Hong-Chen Jiang shared with me his extensive experience in tensor networks and DMRG during one summer; Guin-Dar Lin, who recently became an assistant professor at National Taiwan University, familiarized me with trapped ion quantum simulation and computation; YangHao Chan shared with m ...
Some insights on theoretical reaction dynamics: Use
... physics, where atoms of Ne are introduced into H2 plasma to act as a cooling H}quenching system. Two outstanding features make this reaction worth studying. These are the significant reactivity enhancement caused by vibrational excitation and, mainly, the structured shape of the reaction probability ...
... physics, where atoms of Ne are introduced into H2 plasma to act as a cooling H}quenching system. Two outstanding features make this reaction worth studying. These are the significant reactivity enhancement caused by vibrational excitation and, mainly, the structured shape of the reaction probability ...