Departament de Física Grup de Física Teòrica processes beyond the Standard Model
... large radiative corrections related with the supersymmetric strong and supersymmetric or 2HDM Yukawa sectors. To this end, we will, rst, brie y review the renormalization framework needed to carry out 1-loop calculations in the MSSM in chapter 3. All our 1-loop analyses will be made in a physically ...
... large radiative corrections related with the supersymmetric strong and supersymmetric or 2HDM Yukawa sectors. To this end, we will, rst, brie y review the renormalization framework needed to carry out 1-loop calculations in the MSSM in chapter 3. All our 1-loop analyses will be made in a physically ...
1 - VideoLectures.NET
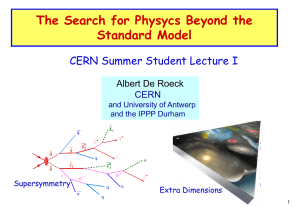
... anticipated in the TeV range (but not guaranteed) • The LHC will enter a new region: the TeV Scale • If either low mass Supersymmetry or Extra Dimensions in the TeV range exist the LHC can make an early discovery (first year to first few years) • To understand WHAT exactly we will have discovered wi ...
... anticipated in the TeV range (but not guaranteed) • The LHC will enter a new region: the TeV Scale • If either low mass Supersymmetry or Extra Dimensions in the TeV range exist the LHC can make an early discovery (first year to first few years) • To understand WHAT exactly we will have discovered wi ...
Lectures on Quantum Chromodynamics
... grade = 0.8 · (exam) + 0.2 · ∑ (homework)i /10 N i=1 where (exam) is the grade of the final exam that ranges from 0 to 100, (homework)i is the grade of each individual hand-in exercise attempt which also ranges from 0 to 100, and N is the number of lectures. Please note that no matter if you handed ...
... grade = 0.8 · (exam) + 0.2 · ∑ (homework)i /10 N i=1 where (exam) is the grade of the final exam that ranges from 0 to 100, (homework)i is the grade of each individual hand-in exercise attempt which also ranges from 0 to 100, and N is the number of lectures. Please note that no matter if you handed ...
God, Belief and Explanation
... some sense, see tables and chairs in a good light possessing normal eyesight and so on. Even if we don’t actually see them, ie, they are not actually being observed, nevertheless they are observable in the sense that it is possible to see them. Some philosophers of science, and indeed historically m ...
... some sense, see tables and chairs in a good light possessing normal eyesight and so on. Even if we don’t actually see them, ie, they are not actually being observed, nevertheless they are observable in the sense that it is possible to see them. Some philosophers of science, and indeed historically m ...
Verbparticles: active verbs
... the order between partic les and pronouns seems to be rigid throughout Sweden. We also do not have any evidenc e that the distinc tion predic ative nonpredic ative has any effec t on partic le plac ement. Sandøy (1976) reports that there is a distinc tion between direc tional a ...
... the order between partic les and pronouns seems to be rigid throughout Sweden. We also do not have any evidenc e that the distinc tion predic ative nonpredic ative has any effec t on partic le plac ement. Sandøy (1976) reports that there is a distinc tion between direc tional a ...