Microsoft PowerPoint
... and phonons are particle like, or “real” waves (with zero static mass, reflecting the interaction between matters) can be particle like – Davison and Germer’s electron-Nickel crystal scattering experiment supported Bohr-de-Broglie’s theorem (1927), so electrons are wave like, or matters (with nonzer ...
... and phonons are particle like, or “real” waves (with zero static mass, reflecting the interaction between matters) can be particle like – Davison and Germer’s electron-Nickel crystal scattering experiment supported Bohr-de-Broglie’s theorem (1927), so electrons are wave like, or matters (with nonzer ...
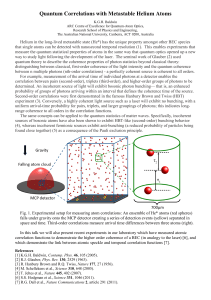
A boost for quantum reality
... experimenter’s ignorance about measurement outcomes, rather than the underlying physical reality, he says. The new theorem doesn’t rule that out. Still, Matt Leifer, a physicist at University College London who works on quantum information, says that the theorem tackles a big question in a simple an ...
... experimenter’s ignorance about measurement outcomes, rather than the underlying physical reality, he says. The new theorem doesn’t rule that out. Still, Matt Leifer, a physicist at University College London who works on quantum information, says that the theorem tackles a big question in a simple an ...
4_POSER_FAEN
... break a way from the surface with a kinetic energy that would depend on the intensity of the incident radiation. However, the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons was shown to be independent of the intensity of the radiation. Einstein (1905) resolved this paradox by proposing that the incident li ...
... break a way from the surface with a kinetic energy that would depend on the intensity of the incident radiation. However, the kinetic energy of the ejected electrons was shown to be independent of the intensity of the radiation. Einstein (1905) resolved this paradox by proposing that the incident li ...
Exact reduced dynamics and
... evolution, the concurrence of the reduced density matrix of the two coupled spins is also obtained exactly. It is shown that the dynamics of the entanglement depends on the initial state of the system and the coupling strength between the two coupled spins, the thermal temperature of the spin enviro ...
... evolution, the concurrence of the reduced density matrix of the two coupled spins is also obtained exactly. It is shown that the dynamics of the entanglement depends on the initial state of the system and the coupling strength between the two coupled spins, the thermal temperature of the spin enviro ...
Mott insulators, Noise correlations and Coherent Spin Dynamics in Optical Lattices
... quantum phases of strongly correlated systems have been proposed for ultracold gases in optical lattices, however it has been unclear how a large variety of such states could be efficiently detected. We show that Hanbury Brown-Twiss noise correlation measurements of ultracold quantum gases allow a d ...
... quantum phases of strongly correlated systems have been proposed for ultracold gases in optical lattices, however it has been unclear how a large variety of such states could be efficiently detected. We show that Hanbury Brown-Twiss noise correlation measurements of ultracold quantum gases allow a d ...
PPT - University of Washington
... Although |11> and |00> are unaffected by this perturbation, |10> and |01> are not eigenstates. These states are rotated. After a time pi*hbar/2*J, we have performed half of a swap operation. This is a known universal quantum gate ...
... Although |11> and |00> are unaffected by this perturbation, |10> and |01> are not eigenstates. These states are rotated. After a time pi*hbar/2*J, we have performed half of a swap operation. This is a known universal quantum gate ...
Lecture 4
... What does that mean? There might be a deeper „classical“ theory that allows to eliminate the probabilistic predictions of quantum mechanics by referring to „hidden parameters“ The state 1/21/2 (|00i+|11i) on two spatially separated qubits exhibits „spooky actions at a distance“: when measured it beh ...
... What does that mean? There might be a deeper „classical“ theory that allows to eliminate the probabilistic predictions of quantum mechanics by referring to „hidden parameters“ The state 1/21/2 (|00i+|11i) on two spatially separated qubits exhibits „spooky actions at a distance“: when measured it beh ...
Využití Kr laseru ve SLO UP a AVČR
... The measurement on the one of two correlated particles give us the power of prediction of the measurement results on the other one. Of course, one can never predict exactly the results of two complementary measurements at once. However, knowing what kind of measurement we want to predict on signal p ...
... The measurement on the one of two correlated particles give us the power of prediction of the measurement results on the other one. Of course, one can never predict exactly the results of two complementary measurements at once. However, knowing what kind of measurement we want to predict on signal p ...
Linear Circuit Analysis with Reactive Components
... Solving the Schrödinger Equation on a 2D Lattice in Quantum Wave Interference (QWI) PhET Sam Reid Quantum Wave Interference allows the user to visualize the propagation of a wavefunction in the presence of potential barriers and detectors. We implement a 2D Richardson algorithm[1], a local propagati ...
... Solving the Schrödinger Equation on a 2D Lattice in Quantum Wave Interference (QWI) PhET Sam Reid Quantum Wave Interference allows the user to visualize the propagation of a wavefunction in the presence of potential barriers and detectors. We implement a 2D Richardson algorithm[1], a local propagati ...
Quantum Mechanics
... The question of the distances between the planets used to be the biggest open problem in science. But we now know that it’s a complicated question that isn’t answered by the fundamental theory. ...
... The question of the distances between the planets used to be the biggest open problem in science. But we now know that it’s a complicated question that isn’t answered by the fundamental theory. ...
Bell`s Inequality - weylmann.com
... To rephrase Einstein’s original thought experiment, the EPR effect involves an unstable, spin-zero particle which spontaneously decays into two spin-1/2 particles that then fly away from each other. Quantum physics says that initially each daughter particle is in a superposition of spin eigenstates, ...
... To rephrase Einstein’s original thought experiment, the EPR effect involves an unstable, spin-zero particle which spontaneously decays into two spin-1/2 particles that then fly away from each other. Quantum physics says that initially each daughter particle is in a superposition of spin eigenstates, ...
Quantum Mechanics - Indico
... interpretation may have to be revised, not for philosophical reasons, but to enable us to construct more concise theories, recovering e.g. locality (which appears to have been lost in string theory). The “random numbers”, inherent in the usual statistical interpretation of the wave functions, may we ...
... interpretation may have to be revised, not for philosophical reasons, but to enable us to construct more concise theories, recovering e.g. locality (which appears to have been lost in string theory). The “random numbers”, inherent in the usual statistical interpretation of the wave functions, may we ...
Gerard `t Hooft
... Determinism at the Planck length (10 cm) Why not ? Simple-minded, “direct” approaches are doomed to fail. Problem that keeps coming up: why is energy always positive ? ...
... Determinism at the Planck length (10 cm) Why not ? Simple-minded, “direct” approaches are doomed to fail. Problem that keeps coming up: why is energy always positive ? ...
Bell's theorem
Bell's theorem is a ‘no-go theorem’ that draws an important distinction between quantum mechanics (QM) and the world as described by classical mechanics. This theorem is named after John Stewart Bell.In its simplest form, Bell's theorem states:Cornell solid-state physicist David Mermin has described the appraisals of the importance of Bell's theorem in the physics community as ranging from ""indifference"" to ""wild extravagance"". Lawrence Berkeley particle physicist Henry Stapp declared: ""Bell's theorem is the most profound discovery of science.""Bell's theorem rules out local hidden variables as a viable explanation of quantum mechanics (though it still leaves the door open for non-local hidden variables). Bell concluded:Bell summarized one of the least popular ways to address the theorem, superdeterminism, in a 1985 BBC Radio interview: