NASA Workshop on Scientific Requirements for Mitigation of
... objects by 2008. While no known asteroid is on collision course with Earth, ongoing detection should alert us to serious threats. Significant topics of discussion at the workshop included large uncertainties in the state of scientific knowledge of asteroid surfaces, despite great advances in recent ...
... objects by 2008. While no known asteroid is on collision course with Earth, ongoing detection should alert us to serious threats. Significant topics of discussion at the workshop included large uncertainties in the state of scientific knowledge of asteroid surfaces, despite great advances in recent ...
Attitude and Orbit Control for small satellites
... I would start to direct a warm thank you to the persons below, since this nal thesis work could not have been completed without their help and aid. Par Degerman { who helped me with the layout of the report as well as assisted me with the syntax LATEX, in which this nal thesis work is written. An ...
... I would start to direct a warm thank you to the persons below, since this nal thesis work could not have been completed without their help and aid. Par Degerman { who helped me with the layout of the report as well as assisted me with the syntax LATEX, in which this nal thesis work is written. An ...
The three toed sloth is the slowest moving land mamal on the
... 11) An astronaut is motionless in outer space and upon a command the propulsion unit on his back ejects some gas with a velocity of +14 ms-1. The astronaut (mass 160kg) recoils with a velocity of -0.5 ms-1. What was the mass of the gas ? 12) A two stage rocket moves in space with a constant velocity ...
... 11) An astronaut is motionless in outer space and upon a command the propulsion unit on his back ejects some gas with a velocity of +14 ms-1. The astronaut (mass 160kg) recoils with a velocity of -0.5 ms-1. What was the mass of the gas ? 12) A two stage rocket moves in space with a constant velocity ...
Lecture2
... Xenon Ion Propulsion System Thrusts are 60-200 milliNewtons Used for “station-keeping” and deepspace missions ...
... Xenon Ion Propulsion System Thrusts are 60-200 milliNewtons Used for “station-keeping” and deepspace missions ...
also available online
... For simplicity, this review will assume circular orbits. Tethers can be in an ellipse; those are just more complicated to discuss. The two connected objects will move at the orbital velocity of their center of mass. If they have unequal masses, the lighter end will be farther from that center of mas ...
... For simplicity, this review will assume circular orbits. Tethers can be in an ellipse; those are just more complicated to discuss. The two connected objects will move at the orbital velocity of their center of mass. If they have unequal masses, the lighter end will be farther from that center of mas ...
PowerPoint file: Higher Physics: Gravitation
... Kepler (1571–1630) developed three laws which predicted that the orbits of the planets are elliptical, with the Sun at the focus. What evidence is there to support this? © ESA ...
... Kepler (1571–1630) developed three laws which predicted that the orbits of the planets are elliptical, with the Sun at the focus. What evidence is there to support this? © ESA ...
Propulsion systems
... LEO and then boost with a final stage burn. To achieve a high, circular orbit at apogee, need a high thrust, short duration burn Usually provided by a solid propellant apogee ...
... LEO and then boost with a final stage burn. To achieve a high, circular orbit at apogee, need a high thrust, short duration burn Usually provided by a solid propellant apogee ...
Kepler, a Planet Hunting Mission
... Kepler's elliptical orbit law: The planets orbit the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus. Kepler's equal-area law: The line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal amounts of time. Kepler's law of periods: The time required for a planet to orbit the sun, called ...
... Kepler's elliptical orbit law: The planets orbit the sun in elliptical orbits with the sun at one focus. Kepler's equal-area law: The line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal amounts of time. Kepler's law of periods: The time required for a planet to orbit the sun, called ...
θ θ θ θ θ θ - Physicshelpline
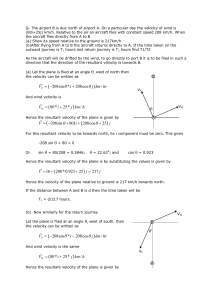
... (a) Show its speed relative to the ground is 217km/h (b)After flying from A to B the aircraft returns directly to A. If the time taken on the outward journey is T1 hours and return journey is T2 hours find T1/T2 As the aircraft will be drifted by the wind, to go directly to port B it is to be flied ...
... (a) Show its speed relative to the ground is 217km/h (b)After flying from A to B the aircraft returns directly to A. If the time taken on the outward journey is T1 hours and return journey is T2 hours find T1/T2 As the aircraft will be drifted by the wind, to go directly to port B it is to be flied ...
Mission to Mercury
... difficult for a spacecraft to travel there due to the extreme temperatures involved, but scientists are keen to send a probe there for the valuable clues that such a mission can provide in understanding both the planet itself and the formation of our solar system; clues which cannot be obtained with ...
... difficult for a spacecraft to travel there due to the extreme temperatures involved, but scientists are keen to send a probe there for the valuable clues that such a mission can provide in understanding both the planet itself and the formation of our solar system; clues which cannot be obtained with ...
Next Exit 0.5 Million Kilometers
... right) because the orbit always returns to the same spot with the same velocity. But if you have an orbit that is gradually spiraling inward (bottom left), the Poincaré cut will show a set of points trending to the left as the radius decreases, and up because objects in lower orbits move faster. Cou ...
... right) because the orbit always returns to the same spot with the same velocity. But if you have an orbit that is gradually spiraling inward (bottom left), the Poincaré cut will show a set of points trending to the left as the radius decreases, and up because objects in lower orbits move faster. Cou ...
Satellite Communication
... • The radius of the orbit is also the distance from the center of the earth. • For each orbit the amount of gravity available is therefore fixed • That in turn means that the speed at which the satellite travels is determined by the orbit ...
... • The radius of the orbit is also the distance from the center of the earth. • For each orbit the amount of gravity available is therefore fixed • That in turn means that the speed at which the satellite travels is determined by the orbit ...
Comparative Planetology
... captured into its retrograde orbit by Neptune. There are many more satellites with retrograde orbits. However, these are much smaller than Triton, objects in a size range of only a few hundred km. The rotation periods of the major satellites and of most satellites in general are equal to their orbit ...
... captured into its retrograde orbit by Neptune. There are many more satellites with retrograde orbits. However, these are much smaller than Triton, objects in a size range of only a few hundred km. The rotation periods of the major satellites and of most satellites in general are equal to their orbit ...
5050_Rsrch - Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research
... Another problem is that these orbits are extremely complicated and it is very difficult plot trajectories to them. According to Martin Lo, a mission designer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, "they look like a line drawn around the edge of a Pringle's potato chip," (Taubes ...
... Another problem is that these orbits are extremely complicated and it is very difficult plot trajectories to them. According to Martin Lo, a mission designer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, "they look like a line drawn around the edge of a Pringle's potato chip," (Taubes ...
HSC Physics – Core Module 1 – Space
... left to complete their unpowered flight. Throughout the flight the projectile is subject to only one force - the force of gravity and just one acceleration – acceleration due to gravity. This rate of acceleration applies to all objects large or small. The trajectory of a projectile is the path that ...
... left to complete their unpowered flight. Throughout the flight the projectile is subject to only one force - the force of gravity and just one acceleration – acceleration due to gravity. This rate of acceleration applies to all objects large or small. The trajectory of a projectile is the path that ...
Semi Plenary 2
... This impulse is often required to keep a safe distance from the planet. The angle a and the periapsis radius rp are related. ...
... This impulse is often required to keep a safe distance from the planet. The angle a and the periapsis radius rp are related. ...
Document
... Validity of the Patched Conic Method The Earth’s SOI is 145 Earth radii. This is extremely large compared to the size of the Earth: The velocity relative to the planet on an escape hyperbola is considered to be the hyperbolic excess velocity vector. ...
... Validity of the Patched Conic Method The Earth’s SOI is 145 Earth radii. This is extremely large compared to the size of the Earth: The velocity relative to the planet on an escape hyperbola is considered to be the hyperbolic excess velocity vector. ...
to see a sample homework problem set from Dynamics
... 12.112 It was observed that during its first flyby of the earth, the Galileo spacecraft had a velocity of 6.48 mi/s as it reached its minimum distance of 4560 mi from the center of the earth. Assuming that the trajectory of the spacecraft was parabolic, determine the time needed for the spacecraft t ...
... 12.112 It was observed that during its first flyby of the earth, the Galileo spacecraft had a velocity of 6.48 mi/s as it reached its minimum distance of 4560 mi from the center of the earth. Assuming that the trajectory of the spacecraft was parabolic, determine the time needed for the spacecraft t ...
Page 434
... What happened to him? Tried and put under house arrest; he said he was wrong under the threat of death Would you do what everyone else did and doubt him? Bacon/Descartes both tried to understand how truth is determined; searched for knowledge ...
... What happened to him? Tried and put under house arrest; he said he was wrong under the threat of death Would you do what everyone else did and doubt him? Bacon/Descartes both tried to understand how truth is determined; searched for knowledge ...
Constant 1g acceleration
... Space Travel Under Constant 1g Acceleration The basic principle behind every high-thrust interplanetary space probe is to accelerate briefly, and then coast, following an elliptical, parabolic, or mildly hyperbolic solar trajectory to your destination, using gravity assists whenever possible. But th ...
... Space Travel Under Constant 1g Acceleration The basic principle behind every high-thrust interplanetary space probe is to accelerate briefly, and then coast, following an elliptical, parabolic, or mildly hyperbolic solar trajectory to your destination, using gravity assists whenever possible. But th ...
ECE 6390: Satellite Communications and Navigation Systems TEST
... outer planets without using extraordinary amounts of fuel, cost, and propulsion complexity. Under most circumstances, the orbit of a satellite around the solar system is an ellipse with the massive sun at one of the focii. The sun provides the principle gravitational forces to maintain the orbit, un ...
... outer planets without using extraordinary amounts of fuel, cost, and propulsion complexity. Under most circumstances, the orbit of a satellite around the solar system is an ellipse with the massive sun at one of the focii. The sun provides the principle gravitational forces to maintain the orbit, un ...
presentation
... Gravity assists can also be used to slow down celestial objects, which would be useful for sending probes or stations to study inner Solar system phenomena like the presence of a weak electromagnetic field on Mercury. In this animation The shuttle follows a similar trajectory to the slingshot refue ...
... Gravity assists can also be used to slow down celestial objects, which would be useful for sending probes or stations to study inner Solar system phenomena like the presence of a weak electromagnetic field on Mercury. In this animation The shuttle follows a similar trajectory to the slingshot refue ...
Orbital mechanics

Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to the practical problems concerning the motion of rockets and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and Newton's law of universal gravitation. It is a core discipline within space mission design and control. Celestial mechanics treats more broadly the orbital dynamics of systems under the influence of gravity, including both spacecraft and natural astronomical bodies such as star systems, planets, moons, and comets. Orbital mechanics focuses on spacecraft trajectories, including orbital maneuvers, orbit plane changes, and interplanetary transfers, and is used by mission planners to predict the results of propulsive maneuvers. General relativity is a more exact theory than Newton's laws for calculating orbits, and is sometimes necessary for greater accuracy or in high-gravity situations (such as orbits close to the Sun).