* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Speeding Around the Sun
Attitude control wikipedia , lookup
Orbital mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Non-rocket spacelaunch wikipedia , lookup
Tidal acceleration wikipedia , lookup
Flight dynamics (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Transit (satellite) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-satellite weapon wikipedia , lookup
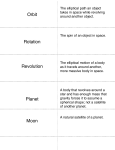
Speeding Around the Sun Forces acting on the stopper Tension of string Force from hand Direction of motion • Why did I need to continue to use a force on the stopper? • Gravity pulling down, friction… Reflection Questions • If string let go stopper would fly out like marble did with the tape • Yes stopper is accelerating changing directions! • Earth (stopper), Sun (straw-Mrs. O’s hand) gravity Direction of motion Direction planet would move without the sun’s gravitational pull. This motion is due to the planet’s inertia. Data Trend • Times increased as the length of string increased. Orbital speed should decrease as string length increased. • Reasons this might not have happened: –Timing and counting issues –Inconsistency of the force used when swinging the stopper –The string getting tangled with the straw and or finger Why did this happen? • Farther away from hand – less tension on the string (force) • Less force then less acceleration – changes directions slower – For planets – farther away from sun, less gravity – less acceleration Why did this happen continued… • Energy! • Farther from hand (the sun) the more potential energy the object has. • The more potential energy then less kinetic energy • Less kinetic energy, less speed! • Think of a roller coaster or the homework assignment on comets, orbit and energy Planet speed • Planets closest to sun are the fastest • Planets farthest from sun are the slowest What is a Satellite? • Satellite: an object that orbits another object in space • Natural: planets and moons • Artificial: Man made Why are satellites used? • • • • • Communication Military Weather To study and take pictures of the Earth GPS Launching a Satellite • Launched with a rocket, generally • satellite launch – videos from NASA • Orbits – Orbit demonstration Just in Case You Wanted to Know… • Rocket goes straight up with satellite and then tilts normally towards the East so Earth’s rotation can give it a boost • When satellite is horizontal the satellite is released from launch vehicle Satellite Earth Gravitational Force (the centripetal force) Inertia: Forward Motion Satellite is falling around the curved Earth Fuel • Satellites only need fuel in orbit to run instruments, overcome drag due to air resistance (friction), to reposition… • The higher the altitude the longer it can stay in orbit (less air resistance) • Types of fuels – solar panels, batteries, fuel cells, nuclear (for missions going to other planets), ion propulsion… Speed • If satellite is closer to Earth its orbital speed will be faster – just like planets that are closer to the sun Just in Case You Wanted to Know • If satellite is 150 miles high – 17,000 mph • If 22,223 miles high – 7,000 mph – this type of satellite revolve around the Earth once for every rotation of Earth – called Geosynchronous orbit – hover over 1 point of Earth To Leave Orbit • Satellite should speed up to escape Earth’s gravity (need to be going at least 25,000 mph!) • If satellites slow down they will eventually come back down to Earth (will crash or burn up) Orbiting Another Planet • If satellite goes by another planet at a close enough distance and a specific speed the satellite will be pulled in by the planet’s gravity and will begin to orbit that planet • Probably will be different speeds/distances then when orbiting Earth • Mars Orbiter – videos from NASA