Breast and Ovarian Cancer and Inherited Predisposition
... We all have two copies of a number of different genes that normally control orderly growth and division of our cells throughout life. These genes can therefore be thought of normally acting as ‘cancer protection’ genes. Variations to the information in one of these ‘cancer protection’ genes such as ...
... We all have two copies of a number of different genes that normally control orderly growth and division of our cells throughout life. These genes can therefore be thought of normally acting as ‘cancer protection’ genes. Variations to the information in one of these ‘cancer protection’ genes such as ...
Shotgun DNA sequencing using cloned DNase I
... as described i n Materials and Methods. Aliquots of these samples were electrophoresed on a 1.8?o agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. Included on the same gel were TaqI and EcoRI r e s t r i c t i o n fragments of pBR322 [26] as size markers. The amount of DNase I used for the digestion a ...
... as described i n Materials and Methods. Aliquots of these samples were electrophoresed on a 1.8?o agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. Included on the same gel were TaqI and EcoRI r e s t r i c t i o n fragments of pBR322 [26] as size markers. The amount of DNase I used for the digestion a ...
Question 2 (cont.) - Amazon Web Services
... managing systems involved in the Bill, the resources on these teams have supported SAPS systems over a number of years on Application Maintenance SLA (7 years on average). SITA is in the process to appoint technical resources to establish dedicated teams for the DNA Database and Labware configuratio ...
... managing systems involved in the Bill, the resources on these teams have supported SAPS systems over a number of years on Application Maintenance SLA (7 years on average). SITA is in the process to appoint technical resources to establish dedicated teams for the DNA Database and Labware configuratio ...
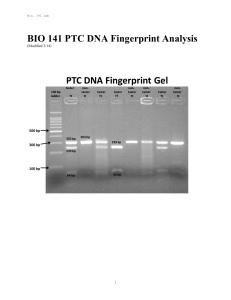
BIO 141 PTC DNA Fingerprint Analysis
... innocent people who are suspects in criminal cases. DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the bluep ...
... innocent people who are suspects in criminal cases. DNA’s structure resembles a twisted ladder called the double helix. DNA in all organisms consists of four bases called guanine, adenine, thymine, and cytosine. The unique order or sequence of these bases in an individual’s cells serves as the bluep ...
Transplantation Immunology pg. 1 Laura Rayne Today I`m going to
... You end up with the original DNA strand with a complementary synthesized strand attached to it. So you’ve doubled your DNA. Do this for thirty cycles, and you have a lot of DNA. It’s a cycle of denature and high temp, anneal and polymerize at low temp, back up to high temp, then low temp, etc. Gives ...
... You end up with the original DNA strand with a complementary synthesized strand attached to it. So you’ve doubled your DNA. Do this for thirty cycles, and you have a lot of DNA. It’s a cycle of denature and high temp, anneal and polymerize at low temp, back up to high temp, then low temp, etc. Gives ...
2007 - life.illinois.edu
... The indicator cells grown at 42° C were returned to 30°C and grown for several generations and checked again for plaquing by wt λ and λ imm434. They obtained the same results as with the cells grown at 42° and not shifted back to 30° (i.e. they still obtained clear plaques with wt λ and turbid plaq ...
... The indicator cells grown at 42° C were returned to 30°C and grown for several generations and checked again for plaquing by wt λ and λ imm434. They obtained the same results as with the cells grown at 42° and not shifted back to 30° (i.e. they still obtained clear plaques with wt λ and turbid plaq ...
The Structure of the Human AGT Protein Bound to DNA
... human protein (hAGT) bound to double-stranded DNA with a chemically modified cytosine base. The protein binds at two different sites: one at the modified base, and the other across a sticky-ended DNA junction. The protein molecule that binds the modified cytosine base flips the base and recognizes i ...
... human protein (hAGT) bound to double-stranded DNA with a chemically modified cytosine base. The protein binds at two different sites: one at the modified base, and the other across a sticky-ended DNA junction. The protein molecule that binds the modified cytosine base flips the base and recognizes i ...
Here - EdSpace
... The CRISPR/Cas9 system stands as one of the new developments in genetic engineering used to modify any genomic sequence with high levels of specificity. The system first found in bacteria allows these species to develop resistance to foreign genetic elements, providing an acquired immunity.1 More re ...
... The CRISPR/Cas9 system stands as one of the new developments in genetic engineering used to modify any genomic sequence with high levels of specificity. The system first found in bacteria allows these species to develop resistance to foreign genetic elements, providing an acquired immunity.1 More re ...
Lab 6: Electrophoresis
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
... helix at the same position on both strands to produce fragments with blunt ends (Figure 1). Other endonucleses cleave each strand off-center at specific nucleotides to produce fragments with “overhangs” or sticky ends. By using the same restriction enzyme to “cut” DNA from two different organisms, c ...
Sample Chapter - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... very so often, someone comes along who is able to push beyond our limits of understanding in science and change the way we view the natural world. Barbara McClintock was one of the most significant scientists in 20th-century biology because she caused a major shift in the way we view gene organizati ...
... very so often, someone comes along who is able to push beyond our limits of understanding in science and change the way we view the natural world. Barbara McClintock was one of the most significant scientists in 20th-century biology because she caused a major shift in the way we view gene organizati ...
Positive Darwinian Selection
... (1) The KA/KS test can only detect positive selection if the proportion of nonsynonymous substitutions that are adaptive is >70%. (2) The KA/KS test can only detect positive selection if it occurred recently. (3) The KA/KS test can only detect positive selection if there are few reversals (e.g., A t ...
... (1) The KA/KS test can only detect positive selection if the proportion of nonsynonymous substitutions that are adaptive is >70%. (2) The KA/KS test can only detect positive selection if it occurred recently. (3) The KA/KS test can only detect positive selection if there are few reversals (e.g., A t ...
figures - HAL
... This is the second report of human anophthalmia-associated mutations of the RAX homeobox gene (11). While the parents were not carefully examined, they did not complain of any visual impairment at the time their child was evaluated. The proband was demonstrated to bear composite heterozygous mutatio ...
... This is the second report of human anophthalmia-associated mutations of the RAX homeobox gene (11). While the parents were not carefully examined, they did not complain of any visual impairment at the time their child was evaluated. The proband was demonstrated to bear composite heterozygous mutatio ...
Dragon Meiosis
... simulate the process of crossing-over that occurs during prophase I. Select one sister chromatid from each of the homologous chromosomes in pair one and cut them in half. Now take each piece and tape it to the piece from the opposite chromatid. Reassemble the chromatids into the homologous chromosom ...
... simulate the process of crossing-over that occurs during prophase I. Select one sister chromatid from each of the homologous chromosomes in pair one and cut them in half. Now take each piece and tape it to the piece from the opposite chromatid. Reassemble the chromatids into the homologous chromosom ...
Trans-HHS Workshop: Diet, DNA Methylation
... (12,13). Vitamin D exerts an antioxidant activity, stabilizes chromosomal structure and prevents DNA double strandbreaks (14). Magnesium is an essential cofactor in DNA metabolism, and its role has been recognized in maintaining high fidelity in DNA transcription (15). Iron may cause DNA breaks (16) ...
... (12,13). Vitamin D exerts an antioxidant activity, stabilizes chromosomal structure and prevents DNA double strandbreaks (14). Magnesium is an essential cofactor in DNA metabolism, and its role has been recognized in maintaining high fidelity in DNA transcription (15). Iron may cause DNA breaks (16) ...
Test Information Sheet
... Genomic DNA from the submitted specimen was enriched for the complete coding region and splice site junctions of the genes on the panel using a proprietary targeted capture system developed by GeneDx. The products were sequenced on either an Illumina MiSeq or HiSeq instrument with 2x150 or 2x100 p ...
... Genomic DNA from the submitted specimen was enriched for the complete coding region and splice site junctions of the genes on the panel using a proprietary targeted capture system developed by GeneDx. The products were sequenced on either an Illumina MiSeq or HiSeq instrument with 2x150 or 2x100 p ...
Solid Tumour Section Nervous system: Medulloblastoma Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... breakpoint is in the proximal portion of p-arm at 17p11.2, so that the resultant structure is dicentric. In a few cases, partial or complete loss of 17p occurs through interstitial deletion, unbalanced translocation or monosomy 17. Chromosome 1 is also involved in medulloblastomas. The most frequent ...
... breakpoint is in the proximal portion of p-arm at 17p11.2, so that the resultant structure is dicentric. In a few cases, partial or complete loss of 17p occurs through interstitial deletion, unbalanced translocation or monosomy 17. Chromosome 1 is also involved in medulloblastomas. The most frequent ...
(GBA) and GTP Cyclohydrolase-1 (GCH1)
... Inheritance pattern (AD) not consistent with inheritance of two disease-causing alleles. No family history of Gaucher disease in 5’s family. (Conclusion consistent with Eblan et al. 2006, Gan-Or et al. 2009). ...
... Inheritance pattern (AD) not consistent with inheritance of two disease-causing alleles. No family history of Gaucher disease in 5’s family. (Conclusion consistent with Eblan et al. 2006, Gan-Or et al. 2009). ...
2) Chromatin = uncoiled DNA
... 3. When the 1st and 2nd amino acid is in place, the rRNA joins them by forming a____________________. As process continues, amino acid chain is formed until a stop codon. 4. The tRNA is ________________________ to find another of the same amino acid so the process can occur again and again. 5. The p ...
... 3. When the 1st and 2nd amino acid is in place, the rRNA joins them by forming a____________________. As process continues, amino acid chain is formed until a stop codon. 4. The tRNA is ________________________ to find another of the same amino acid so the process can occur again and again. 5. The p ...
Bowel Cancer and Inherited Predisposition
... genes in the cell of a tissue or organ must become faulty over time. ...
... genes in the cell of a tissue or organ must become faulty over time. ...
Inheritance and Adaptations
... nuh tipe). The phenotype of a trait is how the trait appears, or is expressed. Phenotypes result from the interaction of an organism’s genes and its environment. An organism’s environment changes all the time. Light, temperature, moisture, nutrients, and social factors are not constant. These factor ...
... nuh tipe). The phenotype of a trait is how the trait appears, or is expressed. Phenotypes result from the interaction of an organism’s genes and its environment. An organism’s environment changes all the time. Light, temperature, moisture, nutrients, and social factors are not constant. These factor ...
Genetics Test I Review - Daytona State College
... • Variable expressivity • The range of expression of a mutant phenotype. ...
... • Variable expressivity • The range of expression of a mutant phenotype. ...
Interpreting the prevalence of regulatory Snps in cancers and protein coding SNPs among non-cancer diseases using GWAS Association Studies
... environmental factors. To understand the biology behind complex disorders is very challenging, since the root cause for most of these disorders have not been identified so far. Genome Wide Association studies includes hundreds and thousands of SNPs which are tested concurrently in large number of ca ...
... environmental factors. To understand the biology behind complex disorders is very challenging, since the root cause for most of these disorders have not been identified so far. Genome Wide Association studies includes hundreds and thousands of SNPs which are tested concurrently in large number of ca ...
... This table was originally taken from the website: http://www.uea.ac.uk/~b270/repair.htm, which was last modified in 2005. This version is from Dec. 2012. Please feel free to send me any updates/corrections- highlighted so that I can find them. The references are not complete- to get current referenc ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.