Genetics Practice Test (H)
... C) A strand of mRNA dictates the amino acids that will be incorporated into protein. D) The mRNA has codons which form base pairs with the anticodons on the tRNA. ...
... C) A strand of mRNA dictates the amino acids that will be incorporated into protein. D) The mRNA has codons which form base pairs with the anticodons on the tRNA. ...
Gene Cloning 2
... • One goal may be to produce a protein product for use. • A second goal may be to prepare many copies of the gene itself. – This may enable scientists to determine the gene’s nucleotide sequence or provide an organism with a new metabolic capability by transferring a gene from another organism. ...
... • One goal may be to produce a protein product for use. • A second goal may be to prepare many copies of the gene itself. – This may enable scientists to determine the gene’s nucleotide sequence or provide an organism with a new metabolic capability by transferring a gene from another organism. ...
word - marric.us
... previous experience necessary. Must be able to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. Accuracy and Speed vital for this job in the field of translation. Applicants must demonstrate skills in transporting and positioning amino acids. Salary commensurate with experience. Executive Position availabl ...
... previous experience necessary. Must be able to transcribe code in a nuclear environment. Accuracy and Speed vital for this job in the field of translation. Applicants must demonstrate skills in transporting and positioning amino acids. Salary commensurate with experience. Executive Position availabl ...
8.7 Mutations
... 2. Translocation results from the exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes. 3. Chromosomal mutations tend to have a bigger affect on the individual. ...
... 2. Translocation results from the exchange of DNA segments between nonhomologous chromosomes. 3. Chromosomal mutations tend to have a bigger affect on the individual. ...
DNA
... found to exist then the original peppered type • Having black wings found to be advantageous because of industry producing soot that was black during this time ...
... found to exist then the original peppered type • Having black wings found to be advantageous because of industry producing soot that was black during this time ...
1. Changes to the number of chromosomes
... These changes affect whole regions of a chromosome and will involve many genes. (There are 30,000 genes in humans shared between the 23 chromosomes which form one chromosome set. Remember we have 2 chromosome sets in all our diploid cells and get one copy of each gene from Mum and one copy from Dad. ...
... These changes affect whole regions of a chromosome and will involve many genes. (There are 30,000 genes in humans shared between the 23 chromosomes which form one chromosome set. Remember we have 2 chromosome sets in all our diploid cells and get one copy of each gene from Mum and one copy from Dad. ...
mutated
... Damage may occur at any time in any cell. Errors during chromosome replication happen only about once in 100,000 bases. Given that the human genome has about 6 billion bases, this means each replication cycle will have 60,000 errors associated with it. Cells contain several complex systems to fix da ...
... Damage may occur at any time in any cell. Errors during chromosome replication happen only about once in 100,000 bases. Given that the human genome has about 6 billion bases, this means each replication cycle will have 60,000 errors associated with it. Cells contain several complex systems to fix da ...
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells
... Transposon is cut out of its location by an enzyme Transposase is encoded within the transposon ...
... Transposon is cut out of its location by an enzyme Transposase is encoded within the transposon ...
DNA and Mutations article
... A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another (i.e., a change in a single "chemical letter" such as switching an A to a G). Such a substitution could: 1. Change a codon to one that encodes a different amino acid and cause a small change in the protein produced. For example, sickle ...
... A substitution is a mutation that exchanges one base for another (i.e., a change in a single "chemical letter" such as switching an A to a G). Such a substitution could: 1. Change a codon to one that encodes a different amino acid and cause a small change in the protein produced. For example, sickle ...
Pre-exam 2
... amino acids, and the ribosome. (You may also use the magnets on the white board for this purpose.) What sequence of amino acids corresponds to the gene? (Use the dictionary of the genetic code in ...
... amino acids, and the ribosome. (You may also use the magnets on the white board for this purpose.) What sequence of amino acids corresponds to the gene? (Use the dictionary of the genetic code in ...
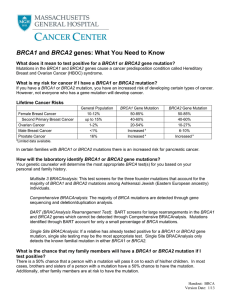
Investigating cancer presentation notes(, 2.2
... It may be worth highlighting the incidence of malignant melanoma, a form of skin cancer associated with UV damage. This is the most common cancer in young adults aged 15 – 34 years old years old. You can at this point encourage the class to think about why certain cancers are more common and ...
... It may be worth highlighting the incidence of malignant melanoma, a form of skin cancer associated with UV damage. This is the most common cancer in young adults aged 15 – 34 years old years old. You can at this point encourage the class to think about why certain cancers are more common and ...
Unit 3 – Heredity Genetics and Evolution – Quiz 2 Name: :______ 1
... 13. The diagram shows two paired homologous chromosomes. What do R and r represent? A. two different forms of a gene C. two identical genes B. two gametes that can form a zygote D. two chromosomes in a hybrid pea plant ...
... 13. The diagram shows two paired homologous chromosomes. What do R and r represent? A. two different forms of a gene C. two identical genes B. two gametes that can form a zygote D. two chromosomes in a hybrid pea plant ...
Answers-pg-294 - WordPress.com
... presumably the longer the organisms are involved in thesuffering most basic of DNA coiling, Istarts would that histone reproduce without anystructure effects. The real problem as expect the organism defects could have serious consequences. undergoes continued reproduction. Eventually there will be n ...
... presumably the longer the organisms are involved in thesuffering most basic of DNA coiling, Istarts would that histone reproduce without anystructure effects. The real problem as expect the organism defects could have serious consequences. undergoes continued reproduction. Eventually there will be n ...
Unit VII: Genetics
... F1 = first filial generation = offspring of the original plants F2 = second filial generation = offspring of F1 d) Crosses – for each trait Mendel crosses true breeding plants and makes observations of the offspring ex: P Tall Pea Plant x Short Pea Plant F1 All tall pea plants ...
... F1 = first filial generation = offspring of the original plants F2 = second filial generation = offspring of F1 d) Crosses – for each trait Mendel crosses true breeding plants and makes observations of the offspring ex: P Tall Pea Plant x Short Pea Plant F1 All tall pea plants ...
made from DNA aptamers核酸适配体, which are short
... Researchers have found that O- linked β- N –acetyl-Dglucosamine ( O-GlcNAc) discourages memory formation when it’s attached to the transcription factor CREB and that memory improves when the sugar is removed or absent. The finding reveals a previously unknown sugar-based mechanism for regulating控制 g ...
... Researchers have found that O- linked β- N –acetyl-Dglucosamine ( O-GlcNAc) discourages memory formation when it’s attached to the transcription factor CREB and that memory improves when the sugar is removed or absent. The finding reveals a previously unknown sugar-based mechanism for regulating控制 g ...
Genetics
... • Transposons are small pieces of DNA that move readily from one site on bacterial chromosome to another or from bacterial chromosome to plasmid. • They carry antibiotic resistance genes. • Transfer of transposons on plasmids to other bacteria by conjugation contributes to antibiotic resistance. ...
... • Transposons are small pieces of DNA that move readily from one site on bacterial chromosome to another or from bacterial chromosome to plasmid. • They carry antibiotic resistance genes. • Transfer of transposons on plasmids to other bacteria by conjugation contributes to antibiotic resistance. ...
DNA/RNA
... Recombinant DNA- Genetically engineered DNA prepared by splicing genes from one species into the cells of a different species. Such DNA becomes part of the host's genetic makeup and is ...
... Recombinant DNA- Genetically engineered DNA prepared by splicing genes from one species into the cells of a different species. Such DNA becomes part of the host's genetic makeup and is ...
IB Biology Topic 4: Genetics (15 hours)
... 4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology 1. Outline the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA. a. DNA is _________________________ b. Primers are annealed to the start end of the required section of DNA c. DNA _____________________ uses complementary ba ...
... 4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology 1. Outline the use of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to copy and amplify minute quantities of DNA. a. DNA is _________________________ b. Primers are annealed to the start end of the required section of DNA c. DNA _____________________ uses complementary ba ...
File
... Steps to DNA Replication 1. In the nucleus, _______hydrogen bonds break between the nitrogen bases of DNA (A, T, G, C). 2. This causes the DNA to unzip like a zipper. 3. Enzymes in the nucleus called _DNA polymerase directs free floating nucleotides in the nucleus to attach to each strand following ...
... Steps to DNA Replication 1. In the nucleus, _______hydrogen bonds break between the nitrogen bases of DNA (A, T, G, C). 2. This causes the DNA to unzip like a zipper. 3. Enzymes in the nucleus called _DNA polymerase directs free floating nucleotides in the nucleus to attach to each strand following ...
Exam 2
... ____31. When a typical restriction enzyme cuts a DNA molecule, the cuts are staggered so that the DNA fragments have singlestranded ends. This is important in recombinant DNA work because _____. A. it allows a cell to recognize fragments produced by the enzyme B. the single-stranded ends serve as st ...
... ____31. When a typical restriction enzyme cuts a DNA molecule, the cuts are staggered so that the DNA fragments have singlestranded ends. This is important in recombinant DNA work because _____. A. it allows a cell to recognize fragments produced by the enzyme B. the single-stranded ends serve as st ...
BIO 304 Genetics
... 1. genome______ A complete set of the DNA of an organism. 2. phosphodiester Nucleotides are linked together in a single strand of DNA by this bond. 3. thymine______ In DNA, the complementary pairing partner of adenine is this base. 4. introns_______ In eukaryotes, these segments of RNA primary trans ...
... 1. genome______ A complete set of the DNA of an organism. 2. phosphodiester Nucleotides are linked together in a single strand of DNA by this bond. 3. thymine______ In DNA, the complementary pairing partner of adenine is this base. 4. introns_______ In eukaryotes, these segments of RNA primary trans ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.