Earth Systems Standards Aligned to National Science Education
... isotopes present in rocks to measure the time since the rock was formed. ...
... isotopes present in rocks to measure the time since the rock was formed. ...
A Living Planet
... - lithosphere solid rock portion of earth; includes crust and upper mantle - hydrosphere bodies of water in the atmosphere as well as rain and precipitation - biosphere where plants and animals live ...
... - lithosphere solid rock portion of earth; includes crust and upper mantle - hydrosphere bodies of water in the atmosphere as well as rain and precipitation - biosphere where plants and animals live ...
Vocabulary for Earth`s Structure and Note Cards Crust – the
... Outer core – liquid part of the core, made of molten iron and nickel Inner core – solid part of the core, mostly made of solid iron and nickel Asthenosphere – a plastic layer of the mantle on which pieces of the lithosphere move Lithosphere – the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle Seismic ...
... Outer core – liquid part of the core, made of molten iron and nickel Inner core – solid part of the core, mostly made of solid iron and nickel Asthenosphere – a plastic layer of the mantle on which pieces of the lithosphere move Lithosphere – the crust and the rigid upper part of the mantle Seismic ...
Earth`s Interior and Geophysical Properties
... * forces increase with an increase in mass of either. * forces decreases with distance apart. Gravity Meter - measures the gravitational attraction between the Earth and a mass within the instrument. *Used to explore local variations in rock density (or anything else that is down there) mass = d x v ...
... * forces increase with an increase in mass of either. * forces decreases with distance apart. Gravity Meter - measures the gravitational attraction between the Earth and a mass within the instrument. *Used to explore local variations in rock density (or anything else that is down there) mass = d x v ...
Chapter 2 Section 1 Notes
... b. Earth was stationary in the center of the celestial sphere 2. Greeks believed Earth was at the center of the revolving planets; this explanation was named a geocentric system. B. Ptolemy came up with a very different theory about the motion of the planets. 1. He believed that Earth was at the cen ...
... b. Earth was stationary in the center of the celestial sphere 2. Greeks believed Earth was at the center of the revolving planets; this explanation was named a geocentric system. B. Ptolemy came up with a very different theory about the motion of the planets. 1. He believed that Earth was at the cen ...
Use the diagram below to fill in the appropriate part of the earth.
... Section III: Traveling through the earth’s layers. (12 points) Scenario: This weekend I was at a garage sale and I bought a machine that would travel through the earth’s layers. So I decided to take a field trip and go to the core of the earth. But before I go, I decided to ask you about the densit ...
... Section III: Traveling through the earth’s layers. (12 points) Scenario: This weekend I was at a garage sale and I bought a machine that would travel through the earth’s layers. So I decided to take a field trip and go to the core of the earth. But before I go, I decided to ask you about the densit ...
Jianna Tameta October 30, 2014 The Earth`s Layers There are four
... There are four layers of the Earth. They are the crust, mantle, outer core, and the inner core. Scientists study earthquakes to find out what the inside of the Earth looks like. Scientists use a tool called a seismograph to study earthquakes. The first outer most layer is the crust, it’s Earth’s thi ...
... There are four layers of the Earth. They are the crust, mantle, outer core, and the inner core. Scientists study earthquakes to find out what the inside of the Earth looks like. Scientists use a tool called a seismograph to study earthquakes. The first outer most layer is the crust, it’s Earth’s thi ...
1 - JustAnswer
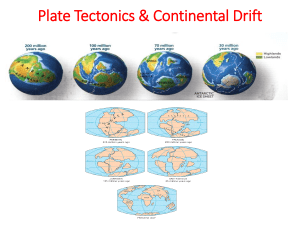
... three rock groups are related and how each group can be converted into a different rock group? I do not know this one, 1. What evidence convinced Wegener and others that continents must have moved in the past and at one time formed a supercontinent? First they had the shape of the continents, the wa ...
... three rock groups are related and how each group can be converted into a different rock group? I do not know this one, 1. What evidence convinced Wegener and others that continents must have moved in the past and at one time formed a supercontinent? First they had the shape of the continents, the wa ...
Earth`s Interior Worksheet A Journey to the Center of the Earth (p. 9
... 6. Name the two types of Earth’s crust. 7. Why do you think the ocean crust contains rocks that are more dense than the rocks found on land? Mantle (p. 10 - 11) 8. What does the layer of mantle consist of? 9. What makes up the lithosphere? 10. Right below the lithosphere is a layer of mantle that is ...
... 6. Name the two types of Earth’s crust. 7. Why do you think the ocean crust contains rocks that are more dense than the rocks found on land? Mantle (p. 10 - 11) 8. What does the layer of mantle consist of? 9. What makes up the lithosphere? 10. Right below the lithosphere is a layer of mantle that is ...
Measurement of charge to mass ratio on an electron
... The charge to mass ratio of an electron was studied using an electron beam tube and two Helmholtz coils. The set up of the apparatus is included with this report. This is the same experiment that was conducted by J.J. Thompson to measure the charge to mass ratio in the early 20th century. A beam of ...
... The charge to mass ratio of an electron was studied using an electron beam tube and two Helmholtz coils. The set up of the apparatus is included with this report. This is the same experiment that was conducted by J.J. Thompson to measure the charge to mass ratio in the early 20th century. A beam of ...
Meteorite - Otterbein University
... • Two high and two low tides per day • A result of the difference in gravitational pull from one side of the Earth to the other – F = G M m / R2 ...
... • Two high and two low tides per day • A result of the difference in gravitational pull from one side of the Earth to the other – F = G M m / R2 ...
Schiehallion experiment

The Schiehallion experiment was an 18th-century experiment to determine the mean density of the Earth. Funded by a grant from the Royal Society, it was conducted in the summer of 1774 around the Scottish mountain of Schiehallion, Perthshire. The experiment involved measuring the tiny deflection of a pendulum due to the gravitational attraction of a nearby mountain. Schiehallion was considered the ideal location after a search for candidate mountains, thanks to its isolation and almost symmetrical shape. One of the triggers for the experiment were anomalies noted during the survey of the Mason–Dixon Line.The experiment had previously been considered, but rejected, by Isaac Newton as a practical demonstration of his theory of gravitation. However, a team of scientists, notably Nevil Maskelyne, the Astronomer Royal, were convinced that the effect would be detectable and undertook to conduct the experiment. The deflection angle depended on the relative densities and volumes of the Earth and the mountain: if the density and volume of Schiehallion could be ascertained, then so could the density of the Earth. Once this was known, then this would in turn yield approximate values for those of the other planets, their moons, and the Sun, previously known only in terms of their relative ratios. As an additional benefit, the concept of contour lines, devised to simplify the process of surveying the mountain, later became a standard technique in cartography.