State of Florida Well Completion Report Drill Cutting Description
... the base of plant root zone. Typically organic rich, brown or black sand and/or clay with plant fragments. • SAND — Sample is predominately non-cemented grains with a size range from 125 µm to 2 mm (see grain size chart). Quartz grains are most common. If grains are cemented together, it may be SAN ...
... the base of plant root zone. Typically organic rich, brown or black sand and/or clay with plant fragments. • SAND — Sample is predominately non-cemented grains with a size range from 125 µm to 2 mm (see grain size chart). Quartz grains are most common. If grains are cemented together, it may be SAN ...
Fossils USOE Text
... then you will love to learn about fossils. Fossils provide clues to Earth’s history. They provide important evidence that helps determine what happened and when it happened in prehistoric times. Fossils can be compared to one another and to organisms of today. This information can be used to make in ...
... then you will love to learn about fossils. Fossils provide clues to Earth’s history. They provide important evidence that helps determine what happened and when it happened in prehistoric times. Fossils can be compared to one another and to organisms of today. This information can be used to make in ...
Metamorphic Rocks, Part 1 LOWER
... become elongated and interlocking, but this can only be seen by microscopic examination of thin sections ...
... become elongated and interlocking, but this can only be seen by microscopic examination of thin sections ...
Metamorphic Rocks, Part 1 LOWER
... become elongated and interlocking, but this can only be seen by microscopic examination of thin sections ...
... become elongated and interlocking, but this can only be seen by microscopic examination of thin sections ...
Metamorphic Rocks, Part 1 LOWER
... become elongated and interlocking, but this can only be seen by microscopic examination of thin sections ...
... become elongated and interlocking, but this can only be seen by microscopic examination of thin sections ...
Help
... fire, Do you think that igneous rock is an appropriate name? Most sedimentary (sehd-ih-M~HN-tuh-ree) rocks are for~ned from particles that have been carried along and deposited by wind and water. These pardcles, or sediments (S~HD-ih-mehnts), include bits of rock in the form Of mud, sand, or pebbles ...
... fire, Do you think that igneous rock is an appropriate name? Most sedimentary (sehd-ih-M~HN-tuh-ree) rocks are for~ned from particles that have been carried along and deposited by wind and water. These pardcles, or sediments (S~HD-ih-mehnts), include bits of rock in the form Of mud, sand, or pebbles ...
Rocks, Fossils and Time: Making Sense of the Geologic Record
... but geologists also use them to ascertain environments of deposition Fossils provide some of the evidence for organic evolution and many fossils are of organisms now extinct ...
... but geologists also use them to ascertain environments of deposition Fossils provide some of the evidence for organic evolution and many fossils are of organisms now extinct ...
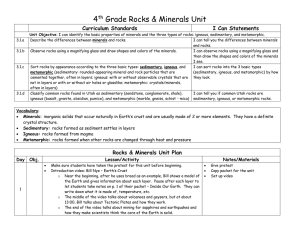
File - 4th Grade Standards
... metamorphic (sedimentary: rounded-appearing mineral and rock particles that are (sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic) by how cemented together, often in layers; igneous: with or without observable crystals that are they look. not in layers or with or without air holes or glasslike; metamorphic: cr ...
... metamorphic (sedimentary: rounded-appearing mineral and rock particles that are (sedimentary, igneous, and metamorphic) by how cemented together, often in layers; igneous: with or without observable crystals that are they look. not in layers or with or without air holes or glasslike; metamorphic: cr ...
Geologic Map of the Ranchos de Taos Quadrangle, Taos County
... Chama-El Rito Member of Tesuque Fm of Santa Fe Group (Middle Miocene)-In cross section only. Volcanic-rich, non-fossiliferous sandstone (50%) and conglomerate (42%), with minor mudrock interbeds (8%). Conglomerates are generally purplish to gray due to predominance of pebble-size Tertiary volcanic c ...
... Chama-El Rito Member of Tesuque Fm of Santa Fe Group (Middle Miocene)-In cross section only. Volcanic-rich, non-fossiliferous sandstone (50%) and conglomerate (42%), with minor mudrock interbeds (8%). Conglomerates are generally purplish to gray due to predominance of pebble-size Tertiary volcanic c ...
Weathering and Soils - exploreiowageology.org
... Products of weathering • Weathering of igneous and metamorphic rocks produces immature soils rich in unstable minerals. As the soil matures, it retains only the more resistant minerals. Clays, iron oxides or hydroxides, and aluminum hydroxides are present as secondary minerals • Weathering of silic ...
... Products of weathering • Weathering of igneous and metamorphic rocks produces immature soils rich in unstable minerals. As the soil matures, it retains only the more resistant minerals. Clays, iron oxides or hydroxides, and aluminum hydroxides are present as secondary minerals • Weathering of silic ...
Minerals (intro.)
... • If the water contains enough of the mineral, it will begin to crystallize in the water Rock Candy = water saturated with sugar + time ...
... • If the water contains enough of the mineral, it will begin to crystallize in the water Rock Candy = water saturated with sugar + time ...
Textures and Identification of Metamorphic Rocks
... the same size; fine grained marble often looks sugary. The physical properties (hardness, fizzing in acid) are those of calcite or dolomite. Quartzite is metamorphosed quartz sandstone or chert. It has a crystalline texture and can be distinguished from sandstone by its greater density and the inter ...
... the same size; fine grained marble often looks sugary. The physical properties (hardness, fizzing in acid) are those of calcite or dolomite. Quartzite is metamorphosed quartz sandstone or chert. It has a crystalline texture and can be distinguished from sandstone by its greater density and the inter ...
Name: India Coghlan. Visit this webpage… http://www.bbc.co.uk
... Igneous Rocks are formed from Molten rock. Molten rock is called Magma. When magma cools and solidifies, a type of rock called igneous rock forms. Igneous rocks contain crystals rather than grains. The size of the crystal depends on how fast the magma cools. If the magma cools slowly then the crysta ...
... Igneous Rocks are formed from Molten rock. Molten rock is called Magma. When magma cools and solidifies, a type of rock called igneous rock forms. Igneous rocks contain crystals rather than grains. The size of the crystal depends on how fast the magma cools. If the magma cools slowly then the crysta ...
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development
... Exposure - the more of the rock exposed to weathering agents, the faster the weathering rate. ...
... Exposure - the more of the rock exposed to weathering agents, the faster the weathering rate. ...
rock cycle
... when oceans, lakes, and rivers evaporate and leave behind sediment particles. They are sometimes called evaporites. Minerals dissolve and crystallize. ...
... when oceans, lakes, and rivers evaporate and leave behind sediment particles. They are sometimes called evaporites. Minerals dissolve and crystallize. ...
Metamorphic Rocks
... Heat and pressure generated by igneous intrusions Affects only a thin region of intruded rock. At shallow depths the mineral transformations generally associated with heat – pressure becomes important for intrusion at great depth A zone of alteration called an aureole forms in the rock surrounding t ...
... Heat and pressure generated by igneous intrusions Affects only a thin region of intruded rock. At shallow depths the mineral transformations generally associated with heat – pressure becomes important for intrusion at great depth A zone of alteration called an aureole forms in the rock surrounding t ...
Minerals - SchoolRack
... When magma cools slowly, crystals are large When magma cools quickly, crystals are small ...
... When magma cools slowly, crystals are large When magma cools quickly, crystals are small ...
Guide to rocks and minerals of Illinois
... student can see only those rocks and minerals that are to be found at or near the surface. For that reason the following paragraphs describing their geologic occurrence deal only with surface geology. The youngest of the major geologic divisions of our rocks is called the Pleistocene, which is the s ...
... student can see only those rocks and minerals that are to be found at or near the surface. For that reason the following paragraphs describing their geologic occurrence deal only with surface geology. The youngest of the major geologic divisions of our rocks is called the Pleistocene, which is the s ...
Ch 3
... 3. Limestone also can contain other minerals and sediments, but it must be at least 50 percent calcite. ...
... 3. Limestone also can contain other minerals and sediments, but it must be at least 50 percent calcite. ...
Name: India Coghlan. Visit this webpage… http://www.bbc.co.uk
... Igneous Rocks are formed from Molten rock. Molten rock is called Magma. When magma cools and solidifies, a type of rock called igneous rock forms. Igneous rocks contain crystals rather than grains. The size of the crystal depends on how fast the magma cools. If the magma cools slowly then the crysta ...
... Igneous Rocks are formed from Molten rock. Molten rock is called Magma. When magma cools and solidifies, a type of rock called igneous rock forms. Igneous rocks contain crystals rather than grains. The size of the crystal depends on how fast the magma cools. If the magma cools slowly then the crysta ...
What Is Weathering?
... What Is Mechanical Weathering? • Ice Wedging occurs when water seeps into cracks in rock & freezes…the rock expands and finally breaks • This type of weathering causes potholes in the road ...
... What Is Mechanical Weathering? • Ice Wedging occurs when water seeps into cracks in rock & freezes…the rock expands and finally breaks • This type of weathering causes potholes in the road ...
GEOLOGY 2020 Études de terrain I GEOLOGY 2020 Field studies I
... A. With the Devil’s Fence (Montana) map and using your B-B’ topographic profile, complete a geologic cross section to illustrate the subsurface geology B. With the maps attached, follow detailed instructions on geologic-topographic relationships Map 1. Examine the topographic model showing the surfa ...
... A. With the Devil’s Fence (Montana) map and using your B-B’ topographic profile, complete a geologic cross section to illustrate the subsurface geology B. With the maps attached, follow detailed instructions on geologic-topographic relationships Map 1. Examine the topographic model showing the surfa ...
The Rock Cycle
... gets all the way rocks to break into large to the ocean. and small pieces, called particles. Particles of broken rock called sediment are deposited as strata. Strata are layers of rock and soil in the earth. Sometimes, swiftly flowing water picks up these sediments and moves them to other places. Wh ...
... gets all the way rocks to break into large to the ocean. and small pieces, called particles. Particles of broken rock called sediment are deposited as strata. Strata are layers of rock and soil in the earth. Sometimes, swiftly flowing water picks up these sediments and moves them to other places. Wh ...
pdf
... particles with air in between the grains; the B horizon, which is nearly all inorganic particles with water in between the grains; and the bottom C horizon, which is the regolith with no organic materials, with bedrock below that. If you classify soils by their grain size distribution, then the tria ...
... particles with air in between the grains; the B horizon, which is nearly all inorganic particles with water in between the grains; and the bottom C horizon, which is the regolith with no organic materials, with bedrock below that. If you classify soils by their grain size distribution, then the tria ...
Mudrock

Mudrocks are a class of fine grained siliciclastic sedimentary rocks. The varying types of mudrocks include: siltstone, claystone, mudstone, slate, and shale. Most of the particles are less than 0.0625 mm (1/16th mm or 0.0025 inches) and are too small to study readily in the field. At first sight the rock types look quite similar; however, there are important differences in composition and nomenclature. There has been a great deal of disagreement involving the classification of mudrocks. There are a few important hurdles to classification, including:Mudrocks are the least understood, and one of the most understudied sedimentary rocks to dateIt is difficult to study mudrock constituents, due to their diminutive size and susceptibility to weathering on outcropsAnd most importantly, there is more than one classification scheme accepted by scientistsMudrocks make up fifty percent of the sedimentary rocks in the geologic record, and are easily the most widespread deposits on Earth. Fine sediment is the most abundant product of erosion, and these sediments contribute to the overall omnipresence of mudrocks. With increased pressure over time the platey clay minerals may become aligned, with the appearance of fissility or parallel layering. This finely bedded material that splits readily into thin layers is called shale, as distinct from mudstone. The lack of fissility or layering in mudstone may be due either to original texture or to the disruption of layering by burrowing organisms in the sediment prior to lithification. From the beginning of civilization, when pottery and mudbricks were made by hand, to now, mudrocks have been important. The first book on mudrocks, Geologie des Argils by Millot, was not published until 1964; however, scientists, engineers, and oil producers have understood the significance of mudrocks since the discovery of the Burgess Shale and the relatedness of mudrocks and oil. Literature on the elusive yet omnipresent rock-type has been increasing in recent years, and technology continues to allow for better analysis.