Rocks in the Crust
... makes up only 5 percent of the crust. The distribution of rock types is a reflection of the rock cycle. Sedimentary rocks are most common at the surface because they are formed by processes that occur at the surface. Most igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks are formed by processes that occur deeper ...
... makes up only 5 percent of the crust. The distribution of rock types is a reflection of the rock cycle. Sedimentary rocks are most common at the surface because they are formed by processes that occur at the surface. Most igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks are formed by processes that occur deeper ...
Types of Rock - Leon County Schools
... A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter. ...
... A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals, or organic matter. ...
Chapter 4 Rocks
... 1. Igneous Rocks – “fire formed” 2. Sedimentary Rocks “sediment rocks” 3. Metamorphic Rocks “changed rock” ...
... 1. Igneous Rocks – “fire formed” 2. Sedimentary Rocks “sediment rocks” 3. Metamorphic Rocks “changed rock” ...
How Does Earth Work?
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely silica (45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, C ...
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely silica (45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, C ...
Rocks - Trimble County Schools
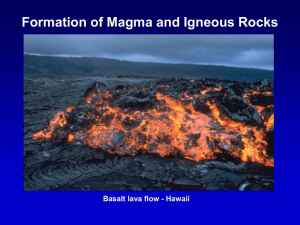
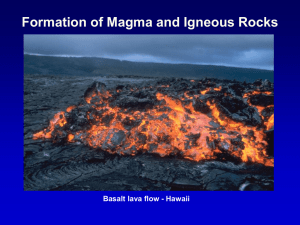
... lava cools. Igneous rock can form: – underground, where the magma (a hot liquid) cools slowly OR – above ground, where the magma cools quickly. ...
... lava cools. Igneous rock can form: – underground, where the magma (a hot liquid) cools slowly OR – above ground, where the magma cools quickly. ...
22.3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle
... 21.3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Rocks are classified into three major groups based on how they formed Igneous Rocks • Can be divided into two categories based on where they form ...
... 21.3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Rocks are classified into three major groups based on how they formed Igneous Rocks • Can be divided into two categories based on where they form ...
powerpoint science - Jordan Elementary School
... If scientists found fossils of an evergreen in an area. . . What would that tell you about the previous climate? ...
... If scientists found fossils of an evergreen in an area. . . What would that tell you about the previous climate? ...
File
... crystallization of magma. Sedimentary—formed from weathered material carried by water, wind, or ice. Metamorphic—formed from preexisting rocks transformed by high temperature, high pressure, or both—without melting. 12. What are the most common igneous rocks, and where do they generally occur? On th ...
... crystallization of magma. Sedimentary—formed from weathered material carried by water, wind, or ice. Metamorphic—formed from preexisting rocks transformed by high temperature, high pressure, or both—without melting. 12. What are the most common igneous rocks, and where do they generally occur? On th ...
Geology Trail
... Still looking through the window, notice the flat land in front of you which is the flood plain of the river. The River Severn system has probably existed for over 200,000 years and over that time it has experienced very cold periods when the ice sheets were only a few miles to the north. This is t ...
... Still looking through the window, notice the flat land in front of you which is the flood plain of the river. The River Severn system has probably existed for over 200,000 years and over that time it has experienced very cold periods when the ice sheets were only a few miles to the north. This is t ...
Formation of Magma and Igneous Rocks Basalt
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely SiO2 (~45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, Ca ...
... How do we classify igneous rocks into groups? • Composition – primary classification method • As magma cools, minerals will solidify at various temperatures. • Minerals that form depend on the chemical composition of the magma. • Most magma is largely SiO2 (~45 to 80%) with oxides of Al, Mg, Fe, Ca ...
EPSC2015-105
... 2. Texture classification Sedimentary rock types are assigned by measuring grains in the best available resolution image and classifying as conglomerate/breccia, (coarse, medium, or fine) sandstone, siltstone, or mudstone [4]. If grains are not resolvable in MAHLI images, grains in the rock are assu ...
... 2. Texture classification Sedimentary rock types are assigned by measuring grains in the best available resolution image and classifying as conglomerate/breccia, (coarse, medium, or fine) sandstone, siltstone, or mudstone [4]. If grains are not resolvable in MAHLI images, grains in the rock are assu ...
THIS ROCKS!
... formed either underground or above ground. • When the melted rock called magma cools slowly underground, it becomes igneous rocks. • Igneous rocks are also formed when volcanoes erupt, causing the magma to rise above the earth's surface. Magma above the earth is called lava. • Igneous rocks are form ...
... formed either underground or above ground. • When the melted rock called magma cools slowly underground, it becomes igneous rocks. • Igneous rocks are also formed when volcanoes erupt, causing the magma to rise above the earth's surface. Magma above the earth is called lava. • Igneous rocks are form ...
Types of Rock
... mineral crystals more time to grow. Fine-grained: cools quickly with little time for crystals to grow. ...
... mineral crystals more time to grow. Fine-grained: cools quickly with little time for crystals to grow. ...
study-guide-for-test-on-rocks
... ____________27. When high temperatures and pressure affect large regions of Earth’s crust. The result of this is changes in mineral and rock types, plus folding and deforming of the rock layers that make up the area. ____________28. When the rock minerals remain unchanged. The rock just breaks apart ...
... ____________27. When high temperatures and pressure affect large regions of Earth’s crust. The result of this is changes in mineral and rock types, plus folding and deforming of the rock layers that make up the area. ____________28. When the rock minerals remain unchanged. The rock just breaks apart ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
... arrangement of grains or other constituents within a rock • Texture of igneous rocks is primarily controlled by cooling rate • Extrusive igneous rocks cool quickly at or near Earth’s surface and are typically finegrained (most crystals <1 mm) • Intrusive igneous rocks cool slowly deep beneath Earth’ ...
... arrangement of grains or other constituents within a rock • Texture of igneous rocks is primarily controlled by cooling rate • Extrusive igneous rocks cool quickly at or near Earth’s surface and are typically finegrained (most crystals <1 mm) • Intrusive igneous rocks cool slowly deep beneath Earth’ ...
Rocks and Minerals Webquest
... Igneous Rocks http://www.minsocam.org/msa/collectors_corner/id/rock_key.ht m#Igneous ...
... Igneous Rocks http://www.minsocam.org/msa/collectors_corner/id/rock_key.ht m#Igneous ...
What are rocks? - The Geographer online
... Igneous rocks are formed from molten rock called magma. They are mostly crystalline (made up of interlocking crystals) and usually very hard to break. E.g. granite, basalt, andesite. ...
... Igneous rocks are formed from molten rock called magma. They are mostly crystalline (made up of interlocking crystals) and usually very hard to break. E.g. granite, basalt, andesite. ...
GEOLOGY 1.1.1. Common Properties. Igneous Rocks and Their
... extruded lavas may contain long hollow tubes or tunnels. ...
... extruded lavas may contain long hollow tubes or tunnels. ...
Rocks change as they move through the rock cycle.
... cementing it together. Some sedimentary rocks form in other ways, as when water evaporates, leaving behind minerals that were dissolved in it. Metamorphic rock (MEHT-uh-MAWR-fihk) forms when heat or pressure causes older rocks to change into new types of rocks. For example, a rock can get buried dee ...
... cementing it together. Some sedimentary rocks form in other ways, as when water evaporates, leaving behind minerals that were dissolved in it. Metamorphic rock (MEHT-uh-MAWR-fihk) forms when heat or pressure causes older rocks to change into new types of rocks. For example, a rock can get buried dee ...
Introducing Igneous Rocks
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the water ...
... If lava cools very quickly there is not enough time for the crystals to form. Instead volcanic glass is created, this is called obsidian. Lava can be erupted under water – there are many volcanoes at the bottom of the ocean, following the ocean ridges. When the lava comes into contact with the water ...
Rocks!
... We sometimes call rocks pebbles, boulders, stones, crystals or gemstones. A boulder is a large rock A pebble is a small rock that has been rounded by wind or water. Stones are larger than pebbles. Crystals and gemstones are rocks made of just one mineral. E.g a diamond is made of carbon. ...
... We sometimes call rocks pebbles, boulders, stones, crystals or gemstones. A boulder is a large rock A pebble is a small rock that has been rounded by wind or water. Stones are larger than pebbles. Crystals and gemstones are rocks made of just one mineral. E.g a diamond is made of carbon. ...
Erth 16 Lecture 3: Grand Canyon - geologic history and canyon
... of the Grand Canyon Series (1.2 to 0.8 Ga so a big gap from 540 Ma) • Elsewhere beneath the Tapeats sandstone we find very different kinds of rocks o igneous rock = rock form by cooling and solidification of silicate melts (700-1200°C), resulting in texture of interlocking crystals extrusive - for ...
... of the Grand Canyon Series (1.2 to 0.8 Ga so a big gap from 540 Ma) • Elsewhere beneath the Tapeats sandstone we find very different kinds of rocks o igneous rock = rock form by cooling and solidification of silicate melts (700-1200°C), resulting in texture of interlocking crystals extrusive - for ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.