The Rock Cycle
... The Rock Cycle shows how three basic rock types form Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic, and illustrates how geologic processes transform one rock type into another. ...
... The Rock Cycle shows how three basic rock types form Igneous, Sedimentary, Metamorphic, and illustrates how geologic processes transform one rock type into another. ...
Some Common Sedimentary Rocks
... Luster is the way a mineral shines or reflects light. The luster of a mineral is a clue to its identity. Minerals can be described as metallic, pearly, glassy, silky, greasy, brilliant, or dull. Silver has a very shiny luster. Fluorite has a very glassy luster. A mineral’s color depends ...
... Luster is the way a mineral shines or reflects light. The luster of a mineral is a clue to its identity. Minerals can be described as metallic, pearly, glassy, silky, greasy, brilliant, or dull. Silver has a very shiny luster. Fluorite has a very glassy luster. A mineral’s color depends ...
Ch 6-Rocks - USD305.com
... Chemical Stability ▪ Chemical compound maintains stability or breaks down to form different chemical ▪ Depends on chemical bonds between atoms in mineral ▪ More bonds between silicon and oxygen=more resistant Physical Stability ▪ Rocks have natural zones of weakness, determined where rocks form ...
... Chemical Stability ▪ Chemical compound maintains stability or breaks down to form different chemical ▪ Depends on chemical bonds between atoms in mineral ▪ More bonds between silicon and oxygen=more resistant Physical Stability ▪ Rocks have natural zones of weakness, determined where rocks form ...
Rocks and Paleo study guide no answers
... Most fossils form from animals or plants that once lived in or near quiet water such as __________________, lakes, or ________________ seas where sediments build up. Fossils found in rock include petrified fossils, molds and casts, carbon films, and trace fossils or when the remains of organisms are ...
... Most fossils form from animals or plants that once lived in or near quiet water such as __________________, lakes, or ________________ seas where sediments build up. Fossils found in rock include petrified fossils, molds and casts, carbon films, and trace fossils or when the remains of organisms are ...
Rocks and Soils Worksheet 040 – Rock Fact file Rocks and Soils
... Rocks and Soils Worksheet 040 – Rock Fact file ...
... Rocks and Soils Worksheet 040 – Rock Fact file ...
MEET SOME ROCKS AND MINERALS
... similar to basalt, but gabbro has larger crystals because it is made by slower-cooling magma. Much of the oceanic crust is gabbro, formed at mid-ocean ridges. Black and white “salt and pepper”, large crystals, dense, no air spaces. Like gabbro, granite is formed from cooling magma, but the magma is ...
... similar to basalt, but gabbro has larger crystals because it is made by slower-cooling magma. Much of the oceanic crust is gabbro, formed at mid-ocean ridges. Black and white “salt and pepper”, large crystals, dense, no air spaces. Like gabbro, granite is formed from cooling magma, but the magma is ...
Volcano in the lab: a wax volcano in action: teacher`s notes
... It is a common misconception that there is a universal layer of molten rock lying just below the Earth’s crust. This imaginary layer is often erroneously equated with the mantle, which is, in fact solid. Localised heating, and / or reduction in pressure, lead to partial melting, but the magma chambe ...
... It is a common misconception that there is a universal layer of molten rock lying just below the Earth’s crust. This imaginary layer is often erroneously equated with the mantle, which is, in fact solid. Localised heating, and / or reduction in pressure, lead to partial melting, but the magma chambe ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Sedimentary Rocks • The process of compaction (pressing tightly together) and cementation (binding together) complete the process of turning sediments into rocks ...
... Sedimentary Rocks • The process of compaction (pressing tightly together) and cementation (binding together) complete the process of turning sediments into rocks ...
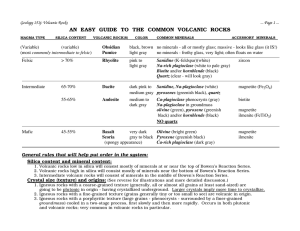
Volcanic Rock chart
... Crystal size (texture) and origins: (See reverse for illustrations and more detailed discussion.) 1. Igneous rocks with a coarse-grained texture (generally, all or almost all grains at least sand-sized) are going to be plutonic in origin - having crystallized underground. Larger crystals imply more ...
... Crystal size (texture) and origins: (See reverse for illustrations and more detailed discussion.) 1. Igneous rocks with a coarse-grained texture (generally, all or almost all grains at least sand-sized) are going to be plutonic in origin - having crystallized underground. Larger crystals imply more ...
Rocks, Part II: the rock "cycle"
... Metamorphic rocks: rocks so transformed by recrystallization caused by increased temperature and pressure that their original nature as an igneous or sedimentary rock can no longer be discerned ...
... Metamorphic rocks: rocks so transformed by recrystallization caused by increased temperature and pressure that their original nature as an igneous or sedimentary rock can no longer be discerned ...
Sedimentary rocks
... • These get deposited, compacted, and cemented just like rock sediments. • Coal and limestone are two examples. • Sometimes limestone can have fossils in it. ...
... • These get deposited, compacted, and cemented just like rock sediments. • Coal and limestone are two examples. • Sometimes limestone can have fossils in it. ...
Earths History Presentation
... periods of time. • Index fossils are useful in correlating the sedimentary rocks in which they are found. ...
... periods of time. • Index fossils are useful in correlating the sedimentary rocks in which they are found. ...
Formation of Gems and Minerals
... – Minerals found in these rocks might include gems such as garnet and cordierite. • Regionally metamorphosed rocks: large volumes of rock that are buried and changed in response to increases in pressure and temperature • Contact metamorphism: This is the process by which the minerals in rocks change ...
... – Minerals found in these rocks might include gems such as garnet and cordierite. • Regionally metamorphosed rocks: large volumes of rock that are buried and changed in response to increases in pressure and temperature • Contact metamorphism: This is the process by which the minerals in rocks change ...
rock cycle vocabulary - Greenup County School
... 5. metamorphic rock – a rock that forms when heat, pressure, or fluids act on igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rock to change its form or composition, or both 6. igneous rock – rock formed when magma or lava cools and hardens 7. lava – molten rock that flows from volcanoes onto Earth’s sur ...
... 5. metamorphic rock – a rock that forms when heat, pressure, or fluids act on igneous, sedimentary, or other metamorphic rock to change its form or composition, or both 6. igneous rock – rock formed when magma or lava cools and hardens 7. lava – molten rock that flows from volcanoes onto Earth’s sur ...
Fossils Test Study Guide
... fossil- imprints, remains, or traces of once-living organisms that have been preserved; usually found in sedimentary rock conditions necessary for fossils to form- 1. must be a once-living organism 2. must be buried quickly 3. must be protected from scavengers or microorganisms 4. must have hard par ...
... fossil- imprints, remains, or traces of once-living organisms that have been preserved; usually found in sedimentary rock conditions necessary for fossils to form- 1. must be a once-living organism 2. must be buried quickly 3. must be protected from scavengers or microorganisms 4. must have hard par ...
A Trip Through Geologic Time Test Study Guide fossil
... fossil- imprints, remains, or traces of once-living organisms that have been preserved; usually found in sedimentary rock conditions necessary for fossils to form- 1. must be a once-living organism 2. must be buried quickly 3. must be protected from scavengers or microorganisms 4. must have hard par ...
... fossil- imprints, remains, or traces of once-living organisms that have been preserved; usually found in sedimentary rock conditions necessary for fossils to form- 1. must be a once-living organism 2. must be buried quickly 3. must be protected from scavengers or microorganisms 4. must have hard par ...
IGNOTES
... Clinopyroxene began to crystallize at 1185 C. This was joined by plagioclase at 1175 C, followed by opaque minerals (ilmenite and magnetite at 1070 C, apatite at 1030 C, with complete solidification by 1000 C (Fig 3-9 E&B) Thus we can see that the minerals precipitating from a melt do not all d ...
... Clinopyroxene began to crystallize at 1185 C. This was joined by plagioclase at 1175 C, followed by opaque minerals (ilmenite and magnetite at 1070 C, apatite at 1030 C, with complete solidification by 1000 C (Fig 3-9 E&B) Thus we can see that the minerals precipitating from a melt do not all d ...
Rocks and Minerals
... Igneous Rocks • Igneous rock forms when molten rock cools and solidifies. • Intrusive: cools within the earth. • Extrusive: cools on or above the earth’s surface. • Made of various mineral crystals. • The more quickly the rock cools, the less the crystals grow. ...
... Igneous Rocks • Igneous rock forms when molten rock cools and solidifies. • Intrusive: cools within the earth. • Extrusive: cools on or above the earth’s surface. • Made of various mineral crystals. • The more quickly the rock cools, the less the crystals grow. ...
the geosphere - Blinklearning
... They are natural, not made by humans. They have a definite chemical composition; they are composed of chemical elements that are always combined in the same proportion to create the same mineral. They have a crystalline structure. Their particles are arranged to form geometric structures such as cub ...
... They are natural, not made by humans. They have a definite chemical composition; they are composed of chemical elements that are always combined in the same proportion to create the same mineral. They have a crystalline structure. Their particles are arranged to form geometric structures such as cub ...
Geology 101 Homework 5
... Show me completed work for credit on or before _______________________ Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. Read Chap. 5 Chap. 8 and Interlude B (p. 234-239) Metamorphic rock, protolith Foliated, nonfoliated metamorphic rocks Slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss Marble, quartzite Metamorphic ...
... Show me completed work for credit on or before _______________________ Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. Read Chap. 5 Chap. 8 and Interlude B (p. 234-239) Metamorphic rock, protolith Foliated, nonfoliated metamorphic rocks Slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss Marble, quartzite Metamorphic ...
rock
... The Rock Cycle • Any of the three major types of rock can be changed into another of the three types. • Geologic forces and processes cause rock to change from one type to another. • The rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock forms, changes from one form to another, is destroyed, and f ...
... The Rock Cycle • Any of the three major types of rock can be changed into another of the three types. • Geologic forces and processes cause rock to change from one type to another. • The rock cycle is the series of processes in which rock forms, changes from one form to another, is destroyed, and f ...
Informational Text: Rocks
... The core of the earth is composed of a 3D-mile thick bed of rock. Whether on land or in the sea, the substratum is solid rock. Rocks surround us both above the surface and below. Thousands of years ago rocks were used to form primitive hunting implements, to club animals, to pound animal skins for c ...
... The core of the earth is composed of a 3D-mile thick bed of rock. Whether on land or in the sea, the substratum is solid rock. Rocks surround us both above the surface and below. Thousands of years ago rocks were used to form primitive hunting implements, to club animals, to pound animal skins for c ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.