
Data Transmission and Encoding
... representing more than one bit e.g. shifts of /2 (90o) Each element represents two bits Can use 8 phase angles and have more than one ...
... representing more than one bit e.g. shifts of /2 (90o) Each element represents two bits Can use 8 phase angles and have more than one ...
Integrated Design Techniques Ltd www .idtuk.com Communications
... As Suppliers therefore faced limited competition there was little incentive to start new development or to implement new technology. One consequence of this was that centrally-controlled Traffic Signal Controllers would only work with a specific communications circuit from BT. When BT announced the ...
... As Suppliers therefore faced limited competition there was little incentive to start new development or to implement new technology. One consequence of this was that centrally-controlled Traffic Signal Controllers would only work with a specific communications circuit from BT. When BT announced the ...
Bandwidth
... The signal undergoes some amount of degradation from noise, interference and distortion Receiver: The receiver’s function is to extract the desired signal from the received signal at the channel output and to convert it to a form suitable for the output transducer. Other functions performed by the r ...
... The signal undergoes some amount of degradation from noise, interference and distortion Receiver: The receiver’s function is to extract the desired signal from the received signal at the channel output and to convert it to a form suitable for the output transducer. Other functions performed by the r ...
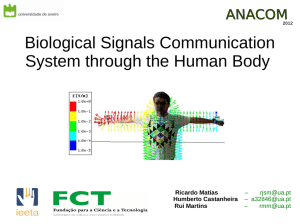
Biological Signals Communication System through the
... [7] Lin Zhong, Dania El-Daye et al., ”OsteoConduct: Wireless Body-Area Communication based on Bone Conduction”, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Dept. of Bioengineering of Rice University [8] Stefan Drude, ”Requirements and Application Scenarios for Body Area Networks”, NXP Semiconducto ...
... [7] Lin Zhong, Dania El-Daye et al., ”OsteoConduct: Wireless Body-Area Communication based on Bone Conduction”, Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Dept. of Bioengineering of Rice University [8] Stefan Drude, ”Requirements and Application Scenarios for Body Area Networks”, NXP Semiconducto ...
document
... logical connections to the media • Manage the flow and communication on the media • Embed the message onto the signal carried across the physical media ...
... logical connections to the media • Manage the flow and communication on the media • Embed the message onto the signal carried across the physical media ...
Blake`s Slides Chapter 7 File
... – Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM – Time-division multiplexing ...
... – Frequency-division multiplexing (FDM – Time-division multiplexing ...
receivers OF RADIO and TV broadcastING systems
... The general block diagram of radio channel of the broadcast and TV systems A sound or image, is transformed in voltage or current, modulates a high-frequency carrier. As a result the output radio signal (RS) of TX can be amplitude, phase or frequency modulated U t U t cos t t t t ...
... The general block diagram of radio channel of the broadcast and TV systems A sound or image, is transformed in voltage or current, modulates a high-frequency carrier. As a result the output radio signal (RS) of TX can be amplitude, phase or frequency modulated U t U t cos t t t t ...
module_30
... – Electric or electromagnetic or light representations of data. Means of propagating Data. Analog Signal Represent data with continuously varying sine wave. Continuously variable. Various media, e.g. wire, fiber optic, space Speech bandwidth 100Hz to 7kHz, Telephone bandwidth 300Hz to 3400Hz, ...
... – Electric or electromagnetic or light representations of data. Means of propagating Data. Analog Signal Represent data with continuously varying sine wave. Continuously variable. Various media, e.g. wire, fiber optic, space Speech bandwidth 100Hz to 7kHz, Telephone bandwidth 300Hz to 3400Hz, ...
Chapter 5: Telecommunications
... • All communications require three things: – Senders and receivers that have something to share • Coded by sender • Decoded by receiver ...
... • All communications require three things: – Senders and receivers that have something to share • Coded by sender • Decoded by receiver ...
FM Transmitter - IIT Hyderabad | Home
... jack or output port of a portable audio or video device, such as a CD player, portable media player, or satellite radio system. The sound is then broadcast through the transmitter, and plays through an FM broadcast band frequency. ...
... jack or output port of a portable audio or video device, such as a CD player, portable media player, or satellite radio system. The sound is then broadcast through the transmitter, and plays through an FM broadcast band frequency. ...
Computer Networks [Opens in New Window]
... This course is an introduction to Data communications and Networking hardware. The emphasis is on network hardware and topologies, physical interface standards, construction of transmission media, Local and Wide Area Network protocols as they relate to network hardware, hands-on Local Area Networks ...
... This course is an introduction to Data communications and Networking hardware. The emphasis is on network hardware and topologies, physical interface standards, construction of transmission media, Local and Wide Area Network protocols as they relate to network hardware, hands-on Local Area Networks ...
Chapter 3.
... 7. An AM radio transmitter operating on 3.9 MHz is modulated by frequencies up to 4 kHz. What are the maximum upper and lower side frequencies? What is the total bandwidth of the AM signal? 9. How much power appears in one sideband of an AM signal of a 5-kW transmitter modulated by 80%? 10. What is ...
... 7. An AM radio transmitter operating on 3.9 MHz is modulated by frequencies up to 4 kHz. What are the maximum upper and lower side frequencies? What is the total bandwidth of the AM signal? 9. How much power appears in one sideband of an AM signal of a 5-kW transmitter modulated by 80%? 10. What is ...
Data and Computer Communications
... •strong enough to be detected •sufficiently higher than noise to be received without error ...
... •strong enough to be detected •sufficiently higher than noise to be received without error ...
Data and Computer Communications
... attenuation across the band of frequencies used by using loading coils or amplifiers. ...
... attenuation across the band of frequencies used by using loading coils or amplifiers. ...
Introduction to Technologies
... brightness values, use address of the first to access the image data store a video sequence as series of images, add address of next and previous to each frame ...
... brightness values, use address of the first to access the image data store a video sequence as series of images, add address of next and previous to each frame ...
EEL 5718 Computer Communications
... • Modulation: maps blocks of bits to well-defined waveforms or symbols (a set of signals for better transmission), then shifts transmission to the carrier frequency band (the band you have right to transmit) • Demodulation: the inverse of modulation • Demodulation vs. Detection: Detection is to reco ...
... • Modulation: maps blocks of bits to well-defined waveforms or symbols (a set of signals for better transmission), then shifts transmission to the carrier frequency band (the band you have right to transmit) • Demodulation: the inverse of modulation • Demodulation vs. Detection: Detection is to reco ...
03-DataTransmission
... where signal strength falls off with distance depends on medium received signal strength must be: ...
... where signal strength falls off with distance depends on medium received signal strength must be: ...
DataTransmission
... • where signal strength falls off with distance • depends on medium • received signal strength must be: – strong enough to be detected – sufficiently higher than noise to receive without error ...
... • where signal strength falls off with distance • depends on medium • received signal strength must be: – strong enough to be detected – sufficiently higher than noise to receive without error ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1 - Eastern Washington University
... Optical Fiber Properties Advantages Very low attenuation Noise immunity Extremely high bandwidth Security: Very difficult to tap without breaking No corrosion More compact & lighter than copper wire ...
... Optical Fiber Properties Advantages Very low attenuation Noise immunity Extremely high bandwidth Security: Very difficult to tap without breaking No corrosion More compact & lighter than copper wire ...
Physical Layer
... • Modulation: maps blocks of bits to well-defined waveforms or symbols (a set of signals for better transmission), then shifts transmission to the carrier frequency band (the band you have right to transmit) • Demodulation: the inverse of modulation • Demodulation vs. Detection: Detection is to reco ...
... • Modulation: maps blocks of bits to well-defined waveforms or symbols (a set of signals for better transmission), then shifts transmission to the carrier frequency band (the band you have right to transmit) • Demodulation: the inverse of modulation • Demodulation vs. Detection: Detection is to reco ...
Chapter6 - UTK-EECS
... • Modulation: maps blocks of bits to well-defined waveforms or symbols (a set of signals for better transmission), then shifts transmission to the carrier frequency band (the band you have right to transmit) • Demodulation: the inverse of modulation • Demodulation vs. Detection: Detection is to reco ...
... • Modulation: maps blocks of bits to well-defined waveforms or symbols (a set of signals for better transmission), then shifts transmission to the carrier frequency band (the band you have right to transmit) • Demodulation: the inverse of modulation • Demodulation vs. Detection: Detection is to reco ...
Basic Communications Theory
... Any analogue signal is not formed by a single frequency if it is expanded in terms of Fourier series. The waveform such as voice produced by human being consists of waveforms of many different frequencies. Bandwidth = fh - fl ...
... Any analogue signal is not formed by a single frequency if it is expanded in terms of Fourier series. The waveform such as voice produced by human being consists of waveforms of many different frequencies. Bandwidth = fh - fl ...
Radio Merit Badge Req 8
... 8. Find out about three career opportunities in radio. Pick one and find out the education, training and experience required for this profession. Discuss this with your counselor, and explain why this profession might interest you. The US Department of Labor’s Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has an ...
... 8. Find out about three career opportunities in radio. Pick one and find out the education, training and experience required for this profession. Discuss this with your counselor, and explain why this profession might interest you. The US Department of Labor’s Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has an ...
Telecommunication

Telecommunication occurs when the exchange of information between two or more entities (communication) includes the use of technology. Communication technology uses channels to transmit information (as electrical signals), either over a physical medium (such as signal cables), or in the form of electromagnetic waves. The word is often used in its plural form, telecommunications, because it involves many different technologies.Early means of communicating over a distance included visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages such as coded drumbeats, lung-blown horns, and loud whistles. Modern technologies for long-distance communication usually involve electrical and electromagnetic technologies, such as telegraph, telephone, and teleprinter, networks, radio, microwave transmission, fiber optics, and communications satellites.A revolution in wireless communication began in the first decade of the 20th century with the pioneering developments in radio communications by Guglielmo Marconi, who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1909. Other highly notable pioneering inventors and developers in the field of electrical and electronic telecommunications include Charles Wheatstone and Samuel Morse (telegraph), Alexander Graham Bell (telephone), Edwin Armstrong, and Lee de Forest (radio), as well as John Logie Baird and Philo Farnsworth (television).








![Computer Networks [Opens in New Window]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001432217_1-c782ef807e718d5ed80f4e9484b1006a-300x300.png)












