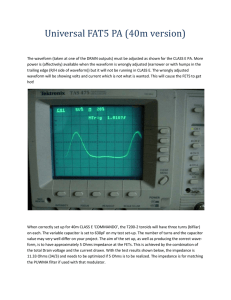
`Lithe Jim`
... made for listening to the then-new direct broadcasts of the 1938 tour of England by the Australian cricketers. The idea was to remove each of the headphones from the headband, and place one under each pillow so that two people could listen in bed. I suppose this wasn't necessary if 'mum' wasn't a cr ...
... made for listening to the then-new direct broadcasts of the 1938 tour of England by the Australian cricketers. The idea was to remove each of the headphones from the headband, and place one under each pillow so that two people could listen in bed. I suppose this wasn't necessary if 'mum' wasn't a cr ...
Word
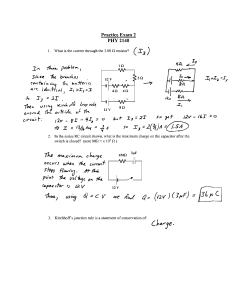
... 1. A variable capacitor, C, with a range from 10 pF to 365 pF is used in the tuning circuit of a car radio. The capacitor is part of a variable frequency LC circuit as shown opposite. a. What is the ratio of maximum to minimum frequencies that can be tuned with this capacitor? A second capacitor, C1 ...
... 1. A variable capacitor, C, with a range from 10 pF to 365 pF is used in the tuning circuit of a car radio. The capacitor is part of a variable frequency LC circuit as shown opposite. a. What is the ratio of maximum to minimum frequencies that can be tuned with this capacitor? A second capacitor, C1 ...
Quiz 6-2
... 3) A series RLC circuit has a 100-Ω resistor, a 0.100-µF capacitor and a 2.00-mH inductor connected across a 120V rms ac voltage source operating at (1000/π) Hz. What is the resonant frequency of this circuit? A) 70.7 kHz B) 22.5 kHz C) 35.3 kHz D) 11.3 kHz Answer: D 4) A series RLC circuit has a 10 ...
... 3) A series RLC circuit has a 100-Ω resistor, a 0.100-µF capacitor and a 2.00-mH inductor connected across a 120V rms ac voltage source operating at (1000/π) Hz. What is the resonant frequency of this circuit? A) 70.7 kHz B) 22.5 kHz C) 35.3 kHz D) 11.3 kHz Answer: D 4) A series RLC circuit has a 10 ...
Low Noise Infrared Detector
... • Goal: Detect and amplify small IR signal through background • Plan: Use chopper amplifier to minimize noise while providing high gain • What we did: • Built circuit with MRD3051 phototransistor • To do (before final): ...
... • Goal: Detect and amplify small IR signal through background • Plan: Use chopper amplifier to minimize noise while providing high gain • What we did: • Built circuit with MRD3051 phototransistor • To do (before final): ...
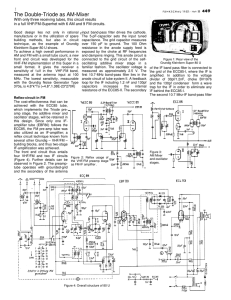
(Figure 1) display a varactor diode tunable
... frequency, respectively. If a current is applied at the Larmor frequency to a resonant circuit in series with a reference capacitor (Figure 3), the voltages across them will have a difference in phase of 90 degrees under tuned conditions. On resonance there is a DC null at the output of a multiplier ...
... frequency, respectively. If a current is applied at the Larmor frequency to a resonant circuit in series with a reference capacitor (Figure 3), the voltages across them will have a difference in phase of 90 degrees under tuned conditions. On resonance there is a DC null at the output of a multiplier ...
AC circuits ch 23 S2017
... fields and store magnetic energy, just like capacitors with electric fields. 2. Inductors & capacitors are used in tuning circuits in selecting signals. 3. Inductive-loops are used to detect vehicles at traffic lights. ...
... fields and store magnetic energy, just like capacitors with electric fields. 2. Inductors & capacitors are used in tuning circuits in selecting signals. 3. Inductive-loops are used to detect vehicles at traffic lights. ...
Session 25 Answers - Iowa State University
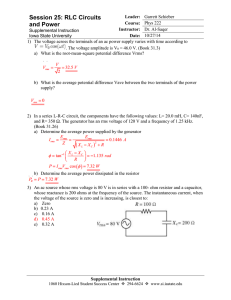
... 4) An R-L-C series circuit is constructed using a 175-ohm resistor, a 12.5-µF capacitor, and an 8.00-mH inductor, all connected across an ac source having a variable frequency and a voltage amplitude of 25.0 V. a) At what angular frequency will the impedance be smallest? ...
... 4) An R-L-C series circuit is constructed using a 175-ohm resistor, a 12.5-µF capacitor, and an 8.00-mH inductor, all connected across an ac source having a variable frequency and a voltage amplitude of 25.0 V. a) At what angular frequency will the impedance be smallest? ...
CR circuit - schoolphysics
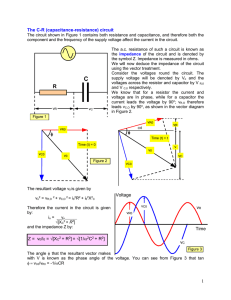
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
... The circuit shown in Figure 1 contains both resistance and capacitance, and therefore both the component and the frequency of the supply voltage affect the current in the circuit. The a.c. resistance of such a circuit is known as the impedance of the circuit and is denoted by the symbol Z. Impedance ...
electromagnetic induction and alternating current
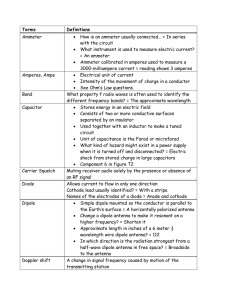
... 7. Write expression for the average value of the a.c voltage V = Vo sinωt over the time interval t =0 and t = π/ω. 8. An electrical element X, when connected to an alternating voltage source, has the current through it leading the voltage by π/2 rad. Identify X and write an expression for its reacta ...
... 7. Write expression for the average value of the a.c voltage V = Vo sinωt over the time interval t =0 and t = π/ω. 8. An electrical element X, when connected to an alternating voltage source, has the current through it leading the voltage by π/2 rad. Identify X and write an expression for its reacta ...
Exam-Prep Jepperdee: Technician Edition
... a Class C PA stage appropriate for a modulated signal? G7B11 ...
... a Class C PA stage appropriate for a modulated signal? G7B11 ...
Crystal radio
A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set or cat's whisker receiver, is a very simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It needs no other power source but that received solely from the power of radio waves received by a wire antenna. It gets its name from its most important component, known as a crystal detector, originally made from a piece of crystalline mineral such as galena. This component is now called a diode.Crystal radios are the simplest type of radio receiver and can be made with a few inexpensive parts, such as a wire for an antenna, a coil of copper wire for adjustment, a capacitor, a crystal detector, and earphones. They are distinct from ordinary radios as they are passive receivers, while other radios use a separate source of electric power such as a battery or the mains power to amplify the weak radio signal so as to make it louder. Thus, crystal sets produce rather weak sound and must be listened to with sensitive earphones, and can only receive stations within a limited range.The rectifying property of crystals was discovered in 1874 by Karl Ferdinand Braun, and crystal detectors were developed and applied to radio receivers in 1904 by Jagadish Chandra Bose, G. W. Pickard and others.Crystal radios were the first widely used type of radio receiver, and the main type used during the wireless telegraphy era. Sold and homemade by the millions, the inexpensive and reliable crystal radio was a major driving force in the introduction of radio to the public, contributing to the development of radio as an entertainment medium around 1920.After about 1920, crystal sets were superseded by the first amplifying receivers, which used vacuum tubes (Audions), and became obsolete for commercial use. They, however, continued to be built by hobbyists, youth groups, and the Boy Scouts as a way of learning about the technology of radio. Today they are still sold as educational devices, and there are groups of enthusiasts devoted to their construction who hold competitions comparing the performance of their home-built designs.Crystal radios receive amplitude modulated (AM) signals, and can be designed to receive almost any radio frequency band, but most receive the AM broadcast band. A few receive shortwave bands, but strong signals are required. The first crystal sets received wireless telegraphy signals broadcast by spark-gap transmitters at frequencies as low as 20 kHz.