Introduction to Fundamental Crystal Oscillators
... kHz difference between the parallel resonant and series resonant conditions, the series resonant condition being lower in frequency. If parallel resonance is required, it is necessary to specify a load capacitance for the Crystal. This capacitance is not related to any capacitance present in the cry ...
... kHz difference between the parallel resonant and series resonant conditions, the series resonant condition being lower in frequency. If parallel resonance is required, it is necessary to specify a load capacitance for the Crystal. This capacitance is not related to any capacitance present in the cry ...
CHAPTE 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction I have performed
... project and studies, the solutions of the project related, overview on different approaches made by previous researchers and make a comparison between my final year project and those similar projects. ...
... project and studies, the solutions of the project related, overview on different approaches made by previous researchers and make a comparison between my final year project and those similar projects. ...
COILS
... Coil is designed to give output of 20,000volts at the sparkplug. In the compression chamber 14,000volts are needed to give adequate spark to ignite mixture. Starter motor takes massive current from battery to turn engine This leaves reduced voltage for coil. Say, if a coil is designed to take 10volt ...
... Coil is designed to give output of 20,000volts at the sparkplug. In the compression chamber 14,000volts are needed to give adequate spark to ignite mixture. Starter motor takes massive current from battery to turn engine This leaves reduced voltage for coil. Say, if a coil is designed to take 10volt ...
10 mst perpendicular to a magnetic field of induction 1 Wb na2
... A jet plane is travelling towards west at a speed of 1800 km/h. What is the voltage difference developed between the ends of the wing having a span of 25 m, if the Earth’s magnetic field at the location has a magnitude of 5 × 10–4 T and the dip angle is 30°. [3.1 V] A wire 88 cm long bent into a cir ...
... A jet plane is travelling towards west at a speed of 1800 km/h. What is the voltage difference developed between the ends of the wing having a span of 25 m, if the Earth’s magnetic field at the location has a magnitude of 5 × 10–4 T and the dip angle is 30°. [3.1 V] A wire 88 cm long bent into a cir ...
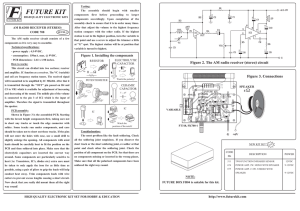
MK484 receiver
... 300 microampers ( 0,003 miliampers ), assures an extremely long life for this battery...if you consider that the set will function till its voltage drop to 1.1 volts. Other attractive characteristics are its 0.8 to 1.5 milivolts output voltage enough to drive an audio amplifier, and its frequency co ...
... 300 microampers ( 0,003 miliampers ), assures an extremely long life for this battery...if you consider that the set will function till its voltage drop to 1.1 volts. Other attractive characteristics are its 0.8 to 1.5 milivolts output voltage enough to drive an audio amplifier, and its frequency co ...
ECE 6130 Lab 4: Diode Detector
... a. Solder on the diode and capacitor using the surface-mount soldering equipment. b. Solder wires through the holes from ground to make necessary short circuits using regular solder equipment. Measurements / Week 2: 4. Test your circuit on the network analyzer. a. Measure S11 for the diode detector. ...
... a. Solder on the diode and capacitor using the surface-mount soldering equipment. b. Solder wires through the holes from ground to make necessary short circuits using regular solder equipment. Measurements / Week 2: 4. Test your circuit on the network analyzer. a. Measure S11 for the diode detector. ...
IC Crystal Oscillator Circuits
... specialised test equipment. One check for ‘goodness’ is to monitor the waveforms at the input and output of the inverting gate. This will require a high bandwidth oscilloscope and a specialised probe. The normal x10 oscilloscope probe will have an input impedance of ~10 MΩ in parallel with 10pF. The ...
... specialised test equipment. One check for ‘goodness’ is to monitor the waveforms at the input and output of the inverting gate. This will require a high bandwidth oscilloscope and a specialised probe. The normal x10 oscilloscope probe will have an input impedance of ~10 MΩ in parallel with 10pF. The ...
AC Circuits Tip Sheet - faculty at Chemeketa
... The key to creating an AC circuit is an AC power supply. An AC power supply has two parameters, a potential difference, E0, and a frequency or angular frequency, f or ω. An AC power supply can interact with resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other circuit elements just like a DC battery or power ...
... The key to creating an AC circuit is an AC power supply. An AC power supply has two parameters, a potential difference, E0, and a frequency or angular frequency, f or ω. An AC power supply can interact with resistors, capacitors, inductors, and other circuit elements just like a DC battery or power ...
Lab #1: Ohm`s Law (and not Ohm`s Law)
... goes on ground side of cap when measuring it • instrumentation amplifier: needed when measuring voltage across R • calculate RC from the values of the components • measure the RC time constant (t), which is the time to drop to 37% of maximum signal • compare ...
... goes on ground side of cap when measuring it • instrumentation amplifier: needed when measuring voltage across R • calculate RC from the values of the components • measure the RC time constant (t), which is the time to drop to 37% of maximum signal • compare ...
Simple Ways On How To Test A Crystal With Tester Or
... On Screen Display (OSD) to disappear from the screen. Some On Screen Display even missing half of the display and also erratic. Replacing only the crystal solve the OSD problem in Monitor. A loosen crystal connection in Computer Motherboard could cause the system to ‘hang’ after running for sometime ...
... On Screen Display (OSD) to disappear from the screen. Some On Screen Display even missing half of the display and also erratic. Replacing only the crystal solve the OSD problem in Monitor. A loosen crystal connection in Computer Motherboard could cause the system to ‘hang’ after running for sometime ...
Parallel circuits - Journal of Pyrotechnics
... elements are added to the circuit. As a result, the total amount of current flowing always decreases. • To maintain the same current as more elements are added, greater and greater voltage will be needed from the power source. • If the wire size is sufficient (or can be ignored) for a single element ...
... elements are added to the circuit. As a result, the total amount of current flowing always decreases. • To maintain the same current as more elements are added, greater and greater voltage will be needed from the power source. • If the wire size is sufficient (or can be ignored) for a single element ...
Crystal radio
A crystal radio receiver, also called a crystal set or cat's whisker receiver, is a very simple radio receiver, popular in the early days of radio. It needs no other power source but that received solely from the power of radio waves received by a wire antenna. It gets its name from its most important component, known as a crystal detector, originally made from a piece of crystalline mineral such as galena. This component is now called a diode.Crystal radios are the simplest type of radio receiver and can be made with a few inexpensive parts, such as a wire for an antenna, a coil of copper wire for adjustment, a capacitor, a crystal detector, and earphones. They are distinct from ordinary radios as they are passive receivers, while other radios use a separate source of electric power such as a battery or the mains power to amplify the weak radio signal so as to make it louder. Thus, crystal sets produce rather weak sound and must be listened to with sensitive earphones, and can only receive stations within a limited range.The rectifying property of crystals was discovered in 1874 by Karl Ferdinand Braun, and crystal detectors were developed and applied to radio receivers in 1904 by Jagadish Chandra Bose, G. W. Pickard and others.Crystal radios were the first widely used type of radio receiver, and the main type used during the wireless telegraphy era. Sold and homemade by the millions, the inexpensive and reliable crystal radio was a major driving force in the introduction of radio to the public, contributing to the development of radio as an entertainment medium around 1920.After about 1920, crystal sets were superseded by the first amplifying receivers, which used vacuum tubes (Audions), and became obsolete for commercial use. They, however, continued to be built by hobbyists, youth groups, and the Boy Scouts as a way of learning about the technology of radio. Today they are still sold as educational devices, and there are groups of enthusiasts devoted to their construction who hold competitions comparing the performance of their home-built designs.Crystal radios receive amplitude modulated (AM) signals, and can be designed to receive almost any radio frequency band, but most receive the AM broadcast band. A few receive shortwave bands, but strong signals are required. The first crystal sets received wireless telegraphy signals broadcast by spark-gap transmitters at frequencies as low as 20 kHz.