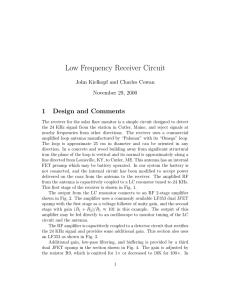
Low Frequency Receiver Circuit
... the 24 KHz signal from the station in Cutler, Maine, and reject signals at nearby frequencies from other directions. The receiver uses a commercial amplified loop antenna manufactured by “Palomar” with its “Omega” loop. The loop is approximate 25 cm in diameter and can be oriented in any direction. ...
... the 24 KHz signal from the station in Cutler, Maine, and reject signals at nearby frequencies from other directions. The receiver uses a commercial amplified loop antenna manufactured by “Palomar” with its “Omega” loop. The loop is approximate 25 cm in diameter and can be oriented in any direction. ...
INTELLIGENT TRAIN ENGINES
... transmitting signals only when the red light is on. If there is green light no transmission. The engine has a receiver which catches these transmitted signals and takes desire actions. Both the transmitter and receiver are of RF type with minimum range of 2KM, so that train can get enough time to de ...
... transmitting signals only when the red light is on. If there is green light no transmission. The engine has a receiver which catches these transmitted signals and takes desire actions. Both the transmitter and receiver are of RF type with minimum range of 2KM, so that train can get enough time to de ...
Chapter 4 - William Stallings, Data and Computer
... electric pulses. Ravens also are very expressive. By a combination voice, patterns of feather erection and body posture ravens communicate so clearly that an experienced observer can identify anger, affection, hunger, curiosity, playfulness, fright, boldness, and depression. —Mind of the Raven, Bern ...
... electric pulses. Ravens also are very expressive. By a combination voice, patterns of feather erection and body posture ravens communicate so clearly that an experienced observer can identify anger, affection, hunger, curiosity, playfulness, fright, boldness, and depression. —Mind of the Raven, Bern ...
Fourier Transforms - Leiden Observatory
... the density of sampling points (pushes the FT tiles farther apart), but both fixes cost computing time ...
... the density of sampling points (pushes the FT tiles farther apart), but both fixes cost computing time ...
Introduction - Eastern Illinois University
... Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that starts at 50 watts and experiences a 10-watt loss over a given section of cable ? Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that loses half its power during the course of transmission ? Q: Do Week 6 Exercise available in the Notes section of the course webs ...
... Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that starts at 50 watts and experiences a 10-watt loss over a given section of cable ? Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that loses half its power during the course of transmission ? Q: Do Week 6 Exercise available in the Notes section of the course webs ...
Introduction - Eastern Illinois University
... Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that starts at 50 watts and experiences a 10-watt loss over a given section of cable ? Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that loses half its power during the course of transmission ? Q: Do Week 6 Exercise available in the Notes section of the course webs ...
... Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that starts at 50 watts and experiences a 10-watt loss over a given section of cable ? Q: What is the decibel loss of a signal that loses half its power during the course of transmission ? Q: Do Week 6 Exercise available in the Notes section of the course webs ...
ITS_7_Signal loss
... It is not possible to avoid all noise, although it is important to keep the signal as high as possible, and to keep the noise as low as possible. This is called the signal to noise ratio. If there is too much noise then the receiving device will not be able to decode the signals correctly. ...
... It is not possible to avoid all noise, although it is important to keep the signal as high as possible, and to keep the noise as low as possible. This is called the signal to noise ratio. If there is too much noise then the receiving device will not be able to decode the signals correctly. ...
Higher HW “Wave Properties”
... lightning storm. She counts the time between the sound of thunder and the lightning flash as 5 seconds. Using an appropriate estimation for the speed of sound, calculate how far away the storm is. b/ Three minutes later she counts again and the time difference between the thunder and lightning is re ...
... lightning storm. She counts the time between the sound of thunder and the lightning flash as 5 seconds. Using an appropriate estimation for the speed of sound, calculate how far away the storm is. b/ Three minutes later she counts again and the time difference between the thunder and lightning is re ...
( )
... (d) The pan will be at its maximum speed at the equilibrium point which is the position where the system was at rest before the clay fell and hit the pan. Therefore, the is stretched a distance, D, form its initial unstretched length when the speed of the pan is a maximum. (e) ...
... (d) The pan will be at its maximum speed at the equilibrium point which is the position where the system was at rest before the clay fell and hit the pan. Therefore, the is stretched a distance, D, form its initial unstretched length when the speed of the pan is a maximum. (e) ...
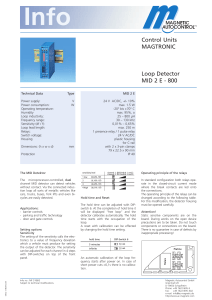
Control Units MAGTRONIC Loop Detector MID 2 E - 800
... The hold time can be adjusted with DIPswitch 6. At the completion of hold time it will be displayed "free loop" and the detector calibrates automatically. The hold time starts with the occupation of the loop. A reset with calibration can be effected by changing the hold time setting. ...
... The hold time can be adjusted with DIPswitch 6. At the completion of hold time it will be displayed "free loop" and the detector calibrates automatically. The hold time starts with the occupation of the loop. A reset with calibration can be effected by changing the hold time setting. ...
Exam-Prep Jepperdee
... What device is often used to match the xmtr output to other than 50 ohms? ...
... What device is often used to match the xmtr output to other than 50 ohms? ...
How To Solve R/L/C Circuits
... element), and the idea is to use the Loop Rule to get a differential equation whose solution is what you need. Please see the Kirchoff Howto for more details for some of the steps. 1. Identify loop or loops in the circuit where you want to find Q(t) and/or I(t). Draw and name currents, and label the ...
... element), and the idea is to use the Loop Rule to get a differential equation whose solution is what you need. Please see the Kirchoff Howto for more details for some of the steps. 1. Identify loop or loops in the circuit where you want to find Q(t) and/or I(t). Draw and name currents, and label the ...
THE INVENTION
... The maximum Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of wireless transmitters is a measure used by regulatory authorities to limit emissions. Prior to this innovation, licence exempt and low cost point to point wireless (such as Bluetooth and Wireless Local Area Networks WLANs which operate world-w ...
... The maximum Effective Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of wireless transmitters is a measure used by regulatory authorities to limit emissions. Prior to this innovation, licence exempt and low cost point to point wireless (such as Bluetooth and Wireless Local Area Networks WLANs which operate world-w ...
Electronic Music
... FM signals are not affected by static. With an FM broadcast, slight changes in amplitude don't matter -- since the audio signal is conveyed through changes in frequency, the FM receiver can just ignore changes in amplitude. AM carrier waves have much longer wavelengths than FM carrier waves, and as ...
... FM signals are not affected by static. With an FM broadcast, slight changes in amplitude don't matter -- since the audio signal is conveyed through changes in frequency, the FM receiver can just ignore changes in amplitude. AM carrier waves have much longer wavelengths than FM carrier waves, and as ...
Processor, Bus Driver, and Latches
... SCAN: Continuous Scan Control bit: (0) not used MULT: Multiple-Channel Control bit: (0) single channel used ...
... SCAN: Continuous Scan Control bit: (0) not used MULT: Multiple-Channel Control bit: (0) single channel used ...
Problem Set
... 7. A radio signal moves from air to glass. The angle of incidence is 200. Calculate the angle of refraction. The relative permittivity of glass is 7.8. Ans: 7.0340 8. If the critical frequency is 10 MHz, what is the OWF at an angle of 600? Ans: 9.81 MHz 9. At a certain time, the MUF for transmission ...
... 7. A radio signal moves from air to glass. The angle of incidence is 200. Calculate the angle of refraction. The relative permittivity of glass is 7.8. Ans: 7.0340 8. If the critical frequency is 10 MHz, what is the OWF at an angle of 600? Ans: 9.81 MHz 9. At a certain time, the MUF for transmission ...
Radio Communications Principles
... direction by a perfect isotropic omnidirectional antenna • If an antenna has a gain of 3dB, that antenna improves on the isotropic antenna in that direction by 3dB, or a factor of 2 (100.3) • The increased power radiated in a given direction is at the expense of other directions ...
... direction by a perfect isotropic omnidirectional antenna • If an antenna has a gain of 3dB, that antenna improves on the isotropic antenna in that direction by 3dB, or a factor of 2 (100.3) • The increased power radiated in a given direction is at the expense of other directions ...
File
... 5. In the figure below, line q in the standard (x,y) coordinate plane has equation 2x y = 1 and intersects line r, which is distinct from line q, at a point on the x-axis. The angles, a and b, formed by these lines and the x-axis are congruent. What is the slope of line r ? F. 2 G. H. ...
... 5. In the figure below, line q in the standard (x,y) coordinate plane has equation 2x y = 1 and intersects line r, which is distinct from line q, at a point on the x-axis. The angles, a and b, formed by these lines and the x-axis are congruent. What is the slope of line r ? F. 2 G. H. ...
Lecture 1 - Rabie Ramadan
... • That electronic circuits process signals, and thus understanding electrical signals is essential • The Thevenin and Norton representations of signal sources. • The representation of a signal as the sum of sine waves. • The analog and digital representations of a signal. • The most basic and pervas ...
... • That electronic circuits process signals, and thus understanding electrical signals is essential • The Thevenin and Norton representations of signal sources. • The representation of a signal as the sum of sine waves. • The analog and digital representations of a signal. • The most basic and pervas ...
continuous-time signal
... • QQQQ data is the historical data for an index fund, whose value tracks the stock price of 100 companies. • Go to http://finance.yahoo.com • Near the top of the page enter QQQQ and click “GO”. • In the left hand column click on “historical prices”. • Click on “Download to Spreadsheet”. • Example 1. ...
... • QQQQ data is the historical data for an index fund, whose value tracks the stock price of 100 companies. • Go to http://finance.yahoo.com • Near the top of the page enter QQQQ and click “GO”. • In the left hand column click on “historical prices”. • Click on “Download to Spreadsheet”. • Example 1. ...
Classifications of CT signals
... physical variable, eg: voltage, current etc. A signal is defined as a function of one or more independent variables. ...
... physical variable, eg: voltage, current etc. A signal is defined as a function of one or more independent variables. ...
Review for Exam 2
... 1) What are magnetic field lines? What are their directions for a permanent magnet? What are the units for magnetic fields? 2) What requirements does a charged particle in a magnetic field have to meet so that a magnetic force acts on it? 3) What is the magnetic force on a charged particle? What is its ...
... 1) What are magnetic field lines? What are their directions for a permanent magnet? What are the units for magnetic fields? 2) What requirements does a charged particle in a magnetic field have to meet so that a magnetic force acts on it? 3) What is the magnetic force on a charged particle? What is its ...
Radio direction finder

A radio direction finder (RDF) is a device for finding the direction, or bearing, to a radio source. The act of measuring the direction is known as radio direction finding or sometimes simply direction finding (DF). Using two or more measurements from different locations, the location of an unknown transmitter can be determined; alternately, using two or more measurements of known transmitters, the location of a vehicle can be determined. RDF is widely used as a radio navigation system, especially with boats and aircraft.RDF systems can be used with any radio source, although the size of the receiver antennas are a function of the wavelength of the signal; very long wavelengths (low frequencies) require very large antennas, and are generally used only on ground-based systems. These wavelengths are nevertheless very useful for marine navigation as they can travel very long distances and ""over the horizon"", which is valuable for ships when the line-of-sight may be only a few tens of kilometres. For aerial use, where the horizon may extend to hundreds of kilometres, higher frequencies can be used, allowing the use of much smaller antennas. An automatic direction finder, often tuned to commercial AM radio broadcasters, is a feature of almost all modern aircraft.For the military, RDF systems are a key component of signals intelligence systems and methodologies. The ability to locate the position of an enemy broadcaster has been invaluable since World War I, and play a key role in World War II's Battle of the Atlantic. It is estimated that the UK's advanced ""huff-duff"" systems were directly or indirectly responsible for 24% of all U-Boats sunk during the war. Modern systems often used phased array antennas to allow rapid beam forming for highly accurate results. These are generally integrated into a wider electronic warfare suite.Several distinct generations of RDF systems have been used over time, following the development of new electronics. Early systems used mechanically rotated antennas that compared signal strengths in different directions, and several electronic versions of the same concept followed. Modern systems use the comparison of phase or doppler techniques which are generally simpler to automate. Modern pseudo-Doppler direction finder systems consist of a number of small antennas fixed to a circular card, with all of the processing occurring in software.Early British radar sets were also referred to as RDF, which was a deception tactic. However, the terminology was not inaccurate; the Chain Home systems used separate omni-directional broadcasters and large RDF receivers to determine the location of the targets.