Exponential Carrier Wave Modulation
... – cancel out DSB modulation x(t) in the driving signal – synchronize the output frequency to the center frequency of the DSB spectra (the suppressed carrier) – to detect the DSB signal ...
... – cancel out DSB modulation x(t) in the driving signal – synchronize the output frequency to the center frequency of the DSB spectra (the suppressed carrier) – to detect the DSB signal ...
Chapter 10 - Electrical, Antenna and RF Safety
... • Confine antenna radiation to the radiating elements. Provide a single, good station ground, and eliminate radiation from transmission lines. Use good coaxial cable, not open-wire lines or end-fed antennas that come directly into the transmitter area. • No person should near any transmitting antenn ...
... • Confine antenna radiation to the radiating elements. Provide a single, good station ground, and eliminate radiation from transmission lines. Use good coaxial cable, not open-wire lines or end-fed antennas that come directly into the transmitter area. • No person should near any transmitting antenn ...
Chapter-1 Intro
... system helps to recuperate by reducing speed, and correcting wheels direction step-by-step. The reaction time of such electronic systems (much shorter than human reaction) has been proven to prevent a significant number of accidents. (D) Ultrasound medical instrument ...
... system helps to recuperate by reducing speed, and correcting wheels direction step-by-step. The reaction time of such electronic systems (much shorter than human reaction) has been proven to prevent a significant number of accidents. (D) Ultrasound medical instrument ...
k18v2. fm transmitter
... load (antenna) will change the operating frequency. This is normal. If the antenna load is heavy then the transmitter could be moved off frequency by 1MHz, or perhaps even more. The tuned coil, L1, has two output tappings for the antenna connection, marked "A" and "B". These are both low-level outpu ...
... load (antenna) will change the operating frequency. This is normal. If the antenna load is heavy then the transmitter could be moved off frequency by 1MHz, or perhaps even more. The tuned coil, L1, has two output tappings for the antenna connection, marked "A" and "B". These are both low-level outpu ...
Communications
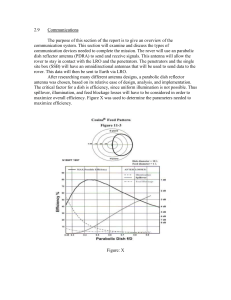
... Since the antenna has a high directive gain, it will need to be pointed as close to the LRO as possible to obtain a successful transmission. Thus, a gimble system will be needed to point the antenna at the LRO as well as a method to determine the relay satellite’s current position. The conical scann ...
... Since the antenna has a high directive gain, it will need to be pointed as close to the LRO as possible to obtain a successful transmission. Thus, a gimble system will be needed to point the antenna at the LRO as well as a method to determine the relay satellite’s current position. The conical scann ...
ECE 4117 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation ECE 4117
... The signal is shifted to its broadcast frequency, where it completes the modulated transmission signal. The signal would be ready to be broadcast over the air to the receiver. This step is usually handled in the USRP, so this signal is not necessary in a transmit layout. It is shown here as an examp ...
... The signal is shifted to its broadcast frequency, where it completes the modulated transmission signal. The signal would be ready to be broadcast over the air to the receiver. This step is usually handled in the USRP, so this signal is not necessary in a transmit layout. It is shown here as an examp ...
ch2-stallings
... Phase () - measure of the relative position in time within a single period of a signal Wavelength () - distance occupied by a single cycle of the signal ...
... Phase () - measure of the relative position in time within a single period of a signal Wavelength () - distance occupied by a single cycle of the signal ...
Document
... Phase () - measure of the relative position in time within a single period of a signal Wavelength () - distance occupied by a single cycle of the signal ...
... Phase () - measure of the relative position in time within a single period of a signal Wavelength () - distance occupied by a single cycle of the signal ...
Tech License Study Guide PowerPoint
... • Now that we know where we are in the RF spectrum and are sending a radio wave into space. • When we imprint some information on the radio wave, we modulate the wave. – Turn the wave on and off – Voice AM and FM ...
... • Now that we know where we are in the RF spectrum and are sending a radio wave into space. • When we imprint some information on the radio wave, we modulate the wave. – Turn the wave on and off – Voice AM and FM ...
Understand Waveguides
... impractical. Lines small enough in cross-sectional dimension to maintain TEM mode signal propagation for microwave signals tend to have low voltage ratings, and suffer from large, parasitic power losses due to conductor "skin" and dielectric effects. Fortunately, though, at these short wavelengths t ...
... impractical. Lines small enough in cross-sectional dimension to maintain TEM mode signal propagation for microwave signals tend to have low voltage ratings, and suffer from large, parasitic power losses due to conductor "skin" and dielectric effects. Fortunately, though, at these short wavelengths t ...
Lab 1: AMPLITUDE MODULATION
... 3.4 AM Modulation and Demodulation of Speech Signals Generate an AM signal using the speech signal available from the Trunks Panel as your message. Observe the time domain waveform. The frequency spectrum will extend for about 3 kHz either side of the carrier. Since this is a stochastic (random) si ...
... 3.4 AM Modulation and Demodulation of Speech Signals Generate an AM signal using the speech signal available from the Trunks Panel as your message. Observe the time domain waveform. The frequency spectrum will extend for about 3 kHz either side of the carrier. Since this is a stochastic (random) si ...
35. An electric current passing through a wire will produce
... A. Bring in the said equipment without notifying Royal Brunei Custom and Excise official B. Declare the equipment to the Royal Brunei Custom and Excise officials C. Pay import tax for the equipment D. Bring the equipment directly to AITI officials 20. What should be done when installing an antenna o ...
... A. Bring in the said equipment without notifying Royal Brunei Custom and Excise official B. Declare the equipment to the Royal Brunei Custom and Excise officials C. Pay import tax for the equipment D. Bring the equipment directly to AITI officials 20. What should be done when installing an antenna o ...
TenTec Orion
... on AGC, background noise clips. Signals clip too! • AGC is fully programmable on the Orion in addition to having conventional settings. Attack, hang, threshold can all be adjusted to operator taste, and threshold can be set to just before noise clips. • No weak ones will be clipped by AGC! • Uniform ...
... on AGC, background noise clips. Signals clip too! • AGC is fully programmable on the Orion in addition to having conventional settings. Attack, hang, threshold can all be adjusted to operator taste, and threshold can be set to just before noise clips. • No weak ones will be clipped by AGC! • Uniform ...
radio communications: am and fm
... The noise added to the FM signal by the receiver will also be occupying the same band as the FM signal itself. Such bandpass noise will corrupt the instantaneous value of the FM signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated s ...
... The noise added to the FM signal by the receiver will also be occupying the same band as the FM signal itself. Such bandpass noise will corrupt the instantaneous value of the FM signal, and thus corrupt the zero-crossings. It is the corruption of the zero-crossings that will affect the demodulated s ...
Communication Channels and Noise
... microwave systems carry large quantities of information. It is highly directional so it follow line-of-sight (LOS) propagation. The required antenna is smaller due to shorter wavelength (due to higher frequencies). Take note that the size of the antenna required to transmit a signal is proportional ...
... microwave systems carry large quantities of information. It is highly directional so it follow line-of-sight (LOS) propagation. The required antenna is smaller due to shorter wavelength (due to higher frequencies). Take note that the size of the antenna required to transmit a signal is proportional ...
mobile sniffer – concept
... There is RF radiations in the atmosphere due the operation of many electronic devices, Radio and Telecommunication devices. The RF level may change if a communication system generates very high frequency RF signals during its operation. The circuit can compare the normal RF in the room as well as th ...
... There is RF radiations in the atmosphere due the operation of many electronic devices, Radio and Telecommunication devices. The RF level may change if a communication system generates very high frequency RF signals during its operation. The circuit can compare the normal RF in the room as well as th ...
ELEC 477/677L Topics in Wireless System Design Spring 2006
... 50- resistors. Hence, a band-pass/low-pass/high-pass filter combination is required (band-pass for the IF; low-pass or high-pass for everything else). In a direct conversion receiver a lowpass/high-pass combination is all that is required. Figure 1 might help to clarify this. The output of a mixer ...
... 50- resistors. Hence, a band-pass/low-pass/high-pass filter combination is required (band-pass for the IF; low-pass or high-pass for everything else). In a direct conversion receiver a lowpass/high-pass combination is all that is required. Figure 1 might help to clarify this. The output of a mixer ...
AM Radio - s3.amazonaws.com
... of several EE subdisciplines: – Communications/signal processing (frequency domain analysis) – Electromagnetics (antennas, high-frequency circuits) – Power (batteries, power supplies) – Solid state (miniaturization, low-power electronics) Lecture 27 ...
... of several EE subdisciplines: – Communications/signal processing (frequency domain analysis) – Electromagnetics (antennas, high-frequency circuits) – Power (batteries, power supplies) – Solid state (miniaturization, low-power electronics) Lecture 27 ...
Data and Computer Communications
... •sufficiently higher than noise to be received without error ...
... •sufficiently higher than noise to be received without error ...
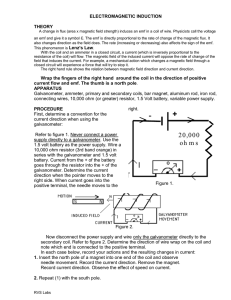
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION THEORY
... With the coil and an ammeter in a closed circuit, a current (which is inversely proportional to the resistance of the coil) will flow. The magnetic field of the induced current will oppose the rate of change of the field that induces the current. For example, a mechanical action which changes a magn ...
... With the coil and an ammeter in a closed circuit, a current (which is inversely proportional to the resistance of the coil) will flow. The magnetic field of the induced current will oppose the rate of change of the field that induces the current. For example, a mechanical action which changes a magn ...
The magnetic compass
... • The compass works because Earth is like a huge magnet. • In a two-minute or standard-rate turn, the aircraft turns through 360° in two minutes, or 3°/sec. By dividing by three the number of degrees in the planned turn, the pilot may determine the number of seconds required in a standard-rate turn ...
... • The compass works because Earth is like a huge magnet. • In a two-minute or standard-rate turn, the aircraft turns through 360° in two minutes, or 3°/sec. By dividing by three the number of degrees in the planned turn, the pilot may determine the number of seconds required in a standard-rate turn ...
Kirchoff Law Problem Solving
... Assign variables to the currents in each branch of the circuit(I1,I2,...)and choose directions for each current. Draw the circ uit with the current directions indicated by arrows. It does not matter whether or not you choose the correct direction. ...
... Assign variables to the currents in each branch of the circuit(I1,I2,...)and choose directions for each current. Draw the circ uit with the current directions indicated by arrows. It does not matter whether or not you choose the correct direction. ...
Radio direction finder

A radio direction finder (RDF) is a device for finding the direction, or bearing, to a radio source. The act of measuring the direction is known as radio direction finding or sometimes simply direction finding (DF). Using two or more measurements from different locations, the location of an unknown transmitter can be determined; alternately, using two or more measurements of known transmitters, the location of a vehicle can be determined. RDF is widely used as a radio navigation system, especially with boats and aircraft.RDF systems can be used with any radio source, although the size of the receiver antennas are a function of the wavelength of the signal; very long wavelengths (low frequencies) require very large antennas, and are generally used only on ground-based systems. These wavelengths are nevertheless very useful for marine navigation as they can travel very long distances and ""over the horizon"", which is valuable for ships when the line-of-sight may be only a few tens of kilometres. For aerial use, where the horizon may extend to hundreds of kilometres, higher frequencies can be used, allowing the use of much smaller antennas. An automatic direction finder, often tuned to commercial AM radio broadcasters, is a feature of almost all modern aircraft.For the military, RDF systems are a key component of signals intelligence systems and methodologies. The ability to locate the position of an enemy broadcaster has been invaluable since World War I, and play a key role in World War II's Battle of the Atlantic. It is estimated that the UK's advanced ""huff-duff"" systems were directly or indirectly responsible for 24% of all U-Boats sunk during the war. Modern systems often used phased array antennas to allow rapid beam forming for highly accurate results. These are generally integrated into a wider electronic warfare suite.Several distinct generations of RDF systems have been used over time, following the development of new electronics. Early systems used mechanically rotated antennas that compared signal strengths in different directions, and several electronic versions of the same concept followed. Modern systems use the comparison of phase or doppler techniques which are generally simpler to automate. Modern pseudo-Doppler direction finder systems consist of a number of small antennas fixed to a circular card, with all of the processing occurring in software.Early British radar sets were also referred to as RDF, which was a deception tactic. However, the terminology was not inaccurate; the Chain Home systems used separate omni-directional broadcasters and large RDF receivers to determine the location of the targets.