B - Uplift Education
... A sediments are deposited where the floor spreads, causing volcanoes B as the plates pull apart, magma moves to the surface, building ridges C ocean water erodes the weak spots on tectonic plates, building ridges D cold ocean water causes fissures that weaken the rocks, causing ...
... A sediments are deposited where the floor spreads, causing volcanoes B as the plates pull apart, magma moves to the surface, building ridges C ocean water erodes the weak spots on tectonic plates, building ridges D cold ocean water causes fissures that weaken the rocks, causing ...
The Earth`s Crust
... meet. When they meet they do not dip under one another. Instead they fold up into mountains such as the Himalayas and the Pyrenees. ...
... meet. When they meet they do not dip under one another. Instead they fold up into mountains such as the Himalayas and the Pyrenees. ...
faults_heating
... Off the coast of South America along the Peru-Chile trench, the oceanic Nazca Plate is pushing into and being subducted under the continental part of the South American Plate. The South American Plate is being lifted up, creating the towering Andes mountains. Strong, destructive earthquakes and the ...
... Off the coast of South America along the Peru-Chile trench, the oceanic Nazca Plate is pushing into and being subducted under the continental part of the South American Plate. The South American Plate is being lifted up, creating the towering Andes mountains. Strong, destructive earthquakes and the ...
PowerPoint Review
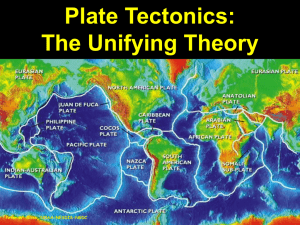
... The Earth’s crust is broken into plates that move & interact with each other. ...
... The Earth’s crust is broken into plates that move & interact with each other. ...
Test review Key File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 20. The deepest point in any ocean is in which ocean, and what is the name of the deepest point? Pacific Ocean, Mariana Trench. The deepest point is called Challenger Deep. 21. Kauai has moved 519 km from its original spot over the last 5,000,000 years. How fast did the Pacific plate move in order f ...
... 20. The deepest point in any ocean is in which ocean, and what is the name of the deepest point? Pacific Ocean, Mariana Trench. The deepest point is called Challenger Deep. 21. Kauai has moved 519 km from its original spot over the last 5,000,000 years. How fast did the Pacific plate move in order f ...
Chapter 4
... • Hot Spots - deep, long-lived, stationary mantle magma sources • Expressed at the surface by: – linear chain of volcanoes – aged with distance from hot spot • Over 100 identified • Used as fixed points against which plate motion is measured ...
... • Hot Spots - deep, long-lived, stationary mantle magma sources • Expressed at the surface by: – linear chain of volcanoes – aged with distance from hot spot • Over 100 identified • Used as fixed points against which plate motion is measured ...
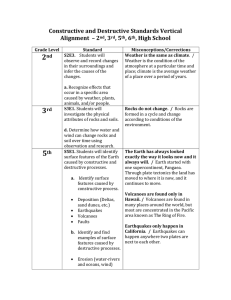
Constructive and Destructive Standards Vertical Alignment – 2 nd , 3
... many places around the world, but most are concentrated in the Pacific area known as The Ring of Fire. Earthquakes only happen in California. / Earthquakes can happen anywhere two plates are next to each other. ...
... many places around the world, but most are concentrated in the Pacific area known as The Ring of Fire. Earthquakes only happen in California. / Earthquakes can happen anywhere two plates are next to each other. ...
Outcome 7.4 Assessment Study Guide
... 3. Can you determine the age of fossils based on a column of rock? a. This would be similar to your How do You Stack Up? activity. 4. The five pieces of evidence Wegener used to support Continental Drift theory correct. 5. What is continental drift? 6. How are the mid-ocean ridges related to sea flo ...
... 3. Can you determine the age of fossils based on a column of rock? a. This would be similar to your How do You Stack Up? activity. 4. The five pieces of evidence Wegener used to support Continental Drift theory correct. 5. What is continental drift? 6. How are the mid-ocean ridges related to sea flo ...
Continental Drift
... Divergent boundaries most commonly occur along the crests of oceanic ridges such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge ...
... Divergent boundaries most commonly occur along the crests of oceanic ridges such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge ...
UCLA, ESS
... the process of subduction. In regions where plates converge, one lithospheric plate is forced down into the mantle beneath the other plate. These zones of subduction are visible on the seafloor as deep ocean trenches. They are seismically active areas characterized by shallow-, intermediate-, and de ...
... the process of subduction. In regions where plates converge, one lithospheric plate is forced down into the mantle beneath the other plate. These zones of subduction are visible on the seafloor as deep ocean trenches. They are seismically active areas characterized by shallow-, intermediate-, and de ...
Shaping Earths surface Ch 4 lesson 2
... The amount of energy released during an earthquake. Ranges from less than 1 to 9.9 The higher the number the stronger the earthquake. ...
... The amount of energy released during an earthquake. Ranges from less than 1 to 9.9 The higher the number the stronger the earthquake. ...
LAYERS OF THE EARTH
... is very thin compared to the other three layers. The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called plates. 5 to 25 miles thick and up to 1,600 F Two types of crust Oceanic and Continental ...
... is very thin compared to the other three layers. The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called plates. 5 to 25 miles thick and up to 1,600 F Two types of crust Oceanic and Continental ...
test - Scioly.org
... 47. What type of melting occurs at mid-ocean ridges due to a decrease in overlying pressure? 48. What type of melting occurs in subduction zones due to addition of volatiles such as water? ...
... 47. What type of melting occurs at mid-ocean ridges due to a decrease in overlying pressure? 48. What type of melting occurs in subduction zones due to addition of volatiles such as water? ...
Plate Tectonics Webquest
... where the ocean floor was being ripped in two lengthwise along the ridge crest. New magma from deep within the Earth rises easily through these weak zones and eventually erupts along the crest of the ridges to create new oceanic crust. This process, was later called _____________ _____________. 13. ...
... where the ocean floor was being ripped in two lengthwise along the ridge crest. New magma from deep within the Earth rises easily through these weak zones and eventually erupts along the crest of the ridges to create new oceanic crust. This process, was later called _____________ _____________. 13. ...
EarthLayersPlateTectonicsPP
... stripes in rocks in the ocean floor crust. 5. Satellite & Sonar data ...
... stripes in rocks in the ocean floor crust. 5. Satellite & Sonar data ...
Plate Tectonics and Plate Boundaries
... • When the sea floor spreads slowly the MidOcean ridge system is relatively narrow. • This displaces a relatively small amount of water, and exposes a large amount of marine limestone which, during the process of weathering decreases the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, and decreases the global ...
... • When the sea floor spreads slowly the MidOcean ridge system is relatively narrow. • This displaces a relatively small amount of water, and exposes a large amount of marine limestone which, during the process of weathering decreases the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere, and decreases the global ...
Notes!
... you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The asthenosphere is much hotter and has the ability to flow, like oobleck. The mesosphere is even hotter than the asthenosphere! Finally, the inner and outer core are extremely hot with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ba ...
... you live on, and it is the most widely studied and understood. The asthenosphere is much hotter and has the ability to flow, like oobleck. The mesosphere is even hotter than the asthenosphere! Finally, the inner and outer core are extremely hot with pressures so great you would be squeezed into a ba ...
Ocean Depth through Deep Time
... The Earth’s oceans have played an important role in the evolution of life and tectonics on Earth, and yet our understanding of basic connections between these remains limited. One of the central, and still unanswered questions, is whether Earth’s oceans have been present over all of Earth’s history, ...
... The Earth’s oceans have played an important role in the evolution of life and tectonics on Earth, and yet our understanding of basic connections between these remains limited. One of the central, and still unanswered questions, is whether Earth’s oceans have been present over all of Earth’s history, ...
Snack Tectonics Name ______________ Student Learning
... c. Notice how the frosting is exposed and pushed up where the plates are separated? This is analogous to how magma comes to the surface where real plates are moving apart at divergent plate boundaries. Most divergent plates boundaries are located within oceanic crust. When plates begin to pull apart ...
... c. Notice how the frosting is exposed and pushed up where the plates are separated? This is analogous to how magma comes to the surface where real plates are moving apart at divergent plate boundaries. Most divergent plates boundaries are located within oceanic crust. When plates begin to pull apart ...
Earthquakes PPT
... EITHER SIDE. When the MOVEMENT is SUDDEN, the ENERGY released causes an EARTHQUAKE. ...
... EITHER SIDE. When the MOVEMENT is SUDDEN, the ENERGY released causes an EARTHQUAKE. ...
Syllabus Danish International Geology 2014
... This theme covers these items, which you will study and explain by exercises and exams. 1. The Rock Cycle: Types of Rocks (igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks) and the minerals from which they form. 2. Plate Tectonics: The parts of the Earth - crust, mantle, inner and outer core, ...
... This theme covers these items, which you will study and explain by exercises and exams. 1. The Rock Cycle: Types of Rocks (igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks) and the minerals from which they form. 2. Plate Tectonics: The parts of the Earth - crust, mantle, inner and outer core, ...
Chapter 3 The Origin of Ocean Basins LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1
... d. Subduction is the process at a trench whereby one part of the sea floor plunges below another and down into the asthenosphere. a. As the rocks scrape past each other they generate earthquakes. b. In the asthenosphere the sea floor melts and the molten material rises, melting through the overlying ...
... d. Subduction is the process at a trench whereby one part of the sea floor plunges below another and down into the asthenosphere. a. As the rocks scrape past each other they generate earthquakes. b. In the asthenosphere the sea floor melts and the molten material rises, melting through the overlying ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.