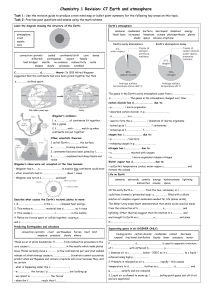
C7 Revision Earth and Atmosphere
... move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t be certain ...
... move. Plates normally move s………..….. (a few centimetres per year) but sudden release of strain energy causes e…………………………. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes and volcanic eruptions will occur because they can’t be certain ...
Plate Tectonics
... Rocks record the orientation of the magnetic field at the time of formation. Therefore, mid-ocean ridges are the locations where new sea floor is born and spreads outward (upwelling of hot mantle - decompression melting). Verified by comparison of anomalies to anomalies found in continental lava flo ...
... Rocks record the orientation of the magnetic field at the time of formation. Therefore, mid-ocean ridges are the locations where new sea floor is born and spreads outward (upwelling of hot mantle - decompression melting). Verified by comparison of anomalies to anomalies found in continental lava flo ...
journey 05 - Auburn High School
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
Who was the father of plate tectonics? Alfred Wegener Who was the
... 3. climatic (coal found in Antarctica, so continent must have once been closer to equator) (glacier deposits found in India & South America, so continents must have once been closer to south pole ...
... 3. climatic (coal found in Antarctica, so continent must have once been closer to equator) (glacier deposits found in India & South America, so continents must have once been closer to south pole ...
Year 8: Tectonics: Revision worksheet SS2017 1. Constructive plate
... melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock forms a volcano. 3. Collision plate margin Collision boundaries occur when two plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a ...
... melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock forms a volcano. 3. Collision plate margin Collision boundaries occur when two plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a ...
epicontinental seas
... Factors that influence isostasy are crust thickness, crust density, erosion rates, and glaciation rates. ...
... Factors that influence isostasy are crust thickness, crust density, erosion rates, and glaciation rates. ...
OUTDOOR SCIENCE SCHOOL VOC (#1 – Test)
... (c) farthest human have drilled into crust = 12 km or 7 miles 2. (Pg 7; 195) MANTLE – layer of the earth below the crust and above the core, made of molten and solid rock (a) lithosphere – solid-like, top portion of the upper mantle and the bottom most portion of the crust that floats above the asth ...
... (c) farthest human have drilled into crust = 12 km or 7 miles 2. (Pg 7; 195) MANTLE – layer of the earth below the crust and above the core, made of molten and solid rock (a) lithosphere – solid-like, top portion of the upper mantle and the bottom most portion of the crust that floats above the asth ...
When the Earth`s crust is under tension, what type
... Sea-floor spreading The process in which magma erupts at a spreading boundary along the ocean floor, resulting in new crust ...
... Sea-floor spreading The process in which magma erupts at a spreading boundary along the ocean floor, resulting in new crust ...
Rock Cycle Questions and Short Story
... down the side of a mountain and landed in a shallow ocean where they were buried for millions of years. 3. A river carried little sand grains and mud to the ocean where they were buried for millions of years. 4. A volcano erupted molten material across a rift valley. 5. Two tectonic plates converged ...
... down the side of a mountain and landed in a shallow ocean where they were buried for millions of years. 3. A river carried little sand grains and mud to the ocean where they were buried for millions of years. 4. A volcano erupted molten material across a rift valley. 5. Two tectonic plates converged ...
Untitled
... Collision boundaries occur when 2 plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a continental plate). This causes the material between them to buckle and rise up, forming fold mountains. The Himalayas are an example of a chain of fold mountains. They have been formed by the ...
... Collision boundaries occur when 2 plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a continental plate). This causes the material between them to buckle and rise up, forming fold mountains. The Himalayas are an example of a chain of fold mountains. They have been formed by the ...
plate tectonics
... the surface at the mid-ocean ridges • Then it flows sideways, carrying the seafloor away from the ridge. • As the new seafloor spreads apart, magma moves up and flows from the cracks, cools, and forms new seafloor. • Youngest rocks are located at the mid-ocean ridges and become increasingly older th ...
... the surface at the mid-ocean ridges • Then it flows sideways, carrying the seafloor away from the ridge. • As the new seafloor spreads apart, magma moves up and flows from the cracks, cools, and forms new seafloor. • Youngest rocks are located at the mid-ocean ridges and become increasingly older th ...
Tasty Plate Tectonics
... viscous layer on which Earth’s plates ride. The plates in this model are represented by fruit roll up (oceanic crust which is thin and dense) and graham crackers (continental crust which is thick but less dense). 5. Divergent plate boundary 1. Instruct students to place the two squares of fruit roll ...
... viscous layer on which Earth’s plates ride. The plates in this model are represented by fruit roll up (oceanic crust which is thin and dense) and graham crackers (continental crust which is thick but less dense). 5. Divergent plate boundary 1. Instruct students to place the two squares of fruit roll ...
The Theory of Continental Drift
... are broken into sections called plates • Plates move around on top of the ...
... are broken into sections called plates • Plates move around on top of the ...
Slide 1
... •Occurs mostly in the sea floor at the midocean ridge. •Another example is San Andreas fault. ...
... •Occurs mostly in the sea floor at the midocean ridge. •Another example is San Andreas fault. ...
Plate Tectonic is a theory in science!
... Boundaries? Plates grind past each other without the production or destruction of lithosphere move in opposite directions usually located in the ocaen Continental transform faults ...
... Boundaries? Plates grind past each other without the production or destruction of lithosphere move in opposite directions usually located in the ocaen Continental transform faults ...
Plate Boundaries $100
... Deep sea trenches and volcanoes often result at this specific type of plate boundary. ...
... Deep sea trenches and volcanoes often result at this specific type of plate boundary. ...
Puerto-Rico Trench
... with either continental or oceanic crust. • Ocean crust is dense enough and thin enough to be “dunked” back into the mantle where it collides with less dense crust. • This process of ocean crust being absorbed back into the mantle is called subduction. ...
... with either continental or oceanic crust. • Ocean crust is dense enough and thin enough to be “dunked” back into the mantle where it collides with less dense crust. • This process of ocean crust being absorbed back into the mantle is called subduction. ...
Tectonic Plate Boundaries
... collision of the Indian and Eurasian Plates. Its best known peaks, Mount Everest and K2, are among several mountains that measure over 8,000 meters high at their summits. Since the Indian Plate is continuing in its northward movement into Asia, the Himalayas continue to grow higher each year by smal ...
... collision of the Indian and Eurasian Plates. Its best known peaks, Mount Everest and K2, are among several mountains that measure over 8,000 meters high at their summits. Since the Indian Plate is continuing in its northward movement into Asia, the Himalayas continue to grow higher each year by smal ...
“Milk Chocolate Movement” worksheet
... intense heat from the Earth’s core. The crust then moves over the mantel and has fractured into seven major tectonic plates, which collide and grind past each other. Tectonic plates are responsible for the creation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. The oceanic plates are mostly made of dense ...
... intense heat from the Earth’s core. The crust then moves over the mantel and has fractured into seven major tectonic plates, which collide and grind past each other. Tectonic plates are responsible for the creation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes. The oceanic plates are mostly made of dense ...
Exam #2: study guide
... o The two most common elements in the Earth’s crust o Significance of eight most common elements in the Earth’s crust o Be able to define the properties that are used to identify minerals: luster; hardness; crystal habit; and cleavage o Understand how minerals are classified: silicates; oxides; sulf ...
... o The two most common elements in the Earth’s crust o Significance of eight most common elements in the Earth’s crust o Be able to define the properties that are used to identify minerals: luster; hardness; crystal habit; and cleavage o Understand how minerals are classified: silicates; oxides; sulf ...
Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the Late Latin tectonicus, from the Greek: τεκτονικός ""pertaining to building"") is a scientific theory that describes the large-scale motion of Earth's lithosphere. This theoretical model builds on the concept of continental drift which was developed during the first few decades of the 20th century. The geoscientific community accepted the theory after the concepts of seafloor spreading were later developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s.The lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of a planet (on Earth, the crust and upper mantle), is broken up into tectonic plates. On Earth, there are seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates. Where plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of boundary; convergent, divergent, or transform. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic trench formation occur along these plate boundaries. The lateral relative movement of the plates typically varies from zero to 100 mm annually.Tectonic plates are composed of oceanic lithosphere and thicker continental lithosphere, each topped by its own kind of crust. Along convergent boundaries, subduction carries plates into the mantle; the material lost is roughly balanced by the formation of new (oceanic) crust along divergent margins by seafloor spreading. In this way, the total surface of the globe remains the same. This prediction of plate tectonics is also referred to as the conveyor belt principle. Earlier theories (that still have some supporters) propose gradual shrinking (contraction) or gradual expansion of the globe.Tectonic plates are able to move because the Earth's lithosphere has greater strength than the underlying asthenosphere. Lateral density variations in the mantle result in convection. Plate movement is thought to be driven by a combination of the motion of the seafloor away from the spreading ridge (due to variations in topography and density of the crust, which result in differences in gravitational forces) and drag, with downward suction, at the subduction zones. Another explanation lies in the different forces generated by the rotation of the globe and the tidal forces of the Sun and Moon. The relative importance of each of these factors and their relationship to each other is unclear, and still the subject of much debate.























