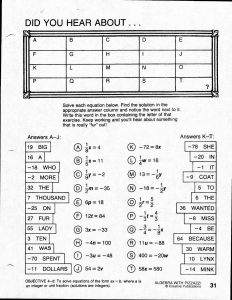
BLACKLINE MASTER 1-1
... equations can be represented by ordered pairs in the form (a, b). The largest value of b, to the nearest tenth, for the following system of equations is . x 2y 5 0 2x2 5x y 1 0 7. For the quadratic-quadratic system of equations shown, the value of k that would result in an infinite nu ...
... equations can be represented by ordered pairs in the form (a, b). The largest value of b, to the nearest tenth, for the following system of equations is . x 2y 5 0 2x2 5x y 1 0 7. For the quadratic-quadratic system of equations shown, the value of k that would result in an infinite nu ...
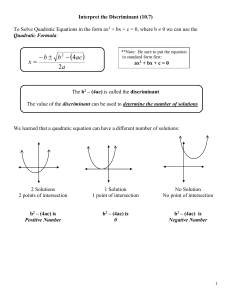
Interpret the Discriminant (10
... To Solve Quadratic Equations in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where b 0 we can use the Quadratic Formula: ...
... To Solve Quadratic Equations in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where b 0 we can use the Quadratic Formula: ...
Takayuki Ikkaku, Arisa Hosaka and Toshihiro Kawabata Objectives
... A quadratic equation can be written in the standard form; ...
... A quadratic equation can be written in the standard form; ...
answer all the questions (30 1 = 30)
... (a) consistent (b) inconsistent (c) consistent and the system reduces to two equations (d) consistent and the system reduces to a single equation In the system of 3 linear equations with three unknowns, if = 0 and all 2 2 minors of = 0 and atleast one 2 2 minor of x or y or z is non-zero ...
... (a) consistent (b) inconsistent (c) consistent and the system reduces to two equations (d) consistent and the system reduces to a single equation In the system of 3 linear equations with three unknowns, if = 0 and all 2 2 minors of = 0 and atleast one 2 2 minor of x or y or z is non-zero ...
Here
... Taking just the last two equations, we have a system with two variables. We can solve it for x and y, then use the first equation to get z. So start by solving the second equation for x: x = 2y − 4. Now substitute this into the third equation to eliminate x, and solve for y: −3x + y = 2 −3(2y − 4) + ...
... Taking just the last two equations, we have a system with two variables. We can solve it for x and y, then use the first equation to get z. So start by solving the second equation for x: x = 2y − 4. Now substitute this into the third equation to eliminate x, and solve for y: −3x + y = 2 −3(2y − 4) + ...
Notes
... Numbers If x + 9 = 12, then x + 9 – 9 = 12 – _____ . Algebra If x + a = b, then x + a – a = _____ – a. EXAMPLE 1 - Solving an Equation Using Subtraction Solution a) x + 7 = 13 ...
... Numbers If x + 9 = 12, then x + 9 – 9 = 12 – _____ . Algebra If x + a = b, then x + a – a = _____ – a. EXAMPLE 1 - Solving an Equation Using Subtraction Solution a) x + 7 = 13 ...
Linear Systems
... • For Am=y – GE reduces A to an upper triangular matrix – Perform “back substitution” using modified y – Modified y is equivalent to Ly • L is a lower triangular matrix • A=L*U ...
... • For Am=y – GE reduces A to an upper triangular matrix – Perform “back substitution” using modified y – Modified y is equivalent to Ly • L is a lower triangular matrix • A=L*U ...
6.3: Multivariable Linear Systems
... In fact, this method easily adapts to computer use for solving linear systems with dozens of variables. When elimination is used to solve a system of linear equations, the goal is to rewrite the system in a form to which back-substitution can be applied. ...
... In fact, this method easily adapts to computer use for solving linear systems with dozens of variables. When elimination is used to solve a system of linear equations, the goal is to rewrite the system in a form to which back-substitution can be applied. ...