presentation
... solutions of equations using symbols instead of specific numbers, and arithmetic operations to establish procedures for manipulating these symbols • Modern Algebra - arose from classical algebra by increasing its attention to abstract mathematical structures. Mathematicians consider modern algebra a ...
... solutions of equations using symbols instead of specific numbers, and arithmetic operations to establish procedures for manipulating these symbols • Modern Algebra - arose from classical algebra by increasing its attention to abstract mathematical structures. Mathematicians consider modern algebra a ...
Equations in Quaternions
... The necessityof these conditionsis shown in ?6; the proofgives a slightly strongerresultthan stated in the theoremabove, since only those equations with coefficientsfrom C are used. The writeris indebted to Jacobson and Baer for permissionto give theirproofshere. Note that (1) is a special equation. ...
... The necessityof these conditionsis shown in ?6; the proofgives a slightly strongerresultthan stated in the theoremabove, since only those equations with coefficientsfrom C are used. The writeris indebted to Jacobson and Baer for permissionto give theirproofshere. Note that (1) is a special equation. ...
Algebra 2
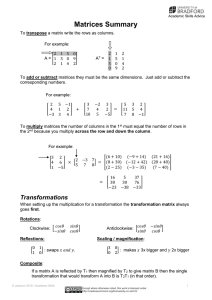
... CMF: Factor out what is common among terms. DOTS: a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a - b) SOTC: a3 + b3 = (a + b)( - + ) DOTC: a3 – b3 = (a - b)( + + ) Easy T (factors of last term that add up to middle term) Perfect Square T: (x – 3)2 or (x + 5)2 not the same as (x2 + 52) Hard T (guess and check, or grouping) C ...
... CMF: Factor out what is common among terms. DOTS: a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a - b) SOTC: a3 + b3 = (a + b)( - + ) DOTC: a3 – b3 = (a - b)( + + ) Easy T (factors of last term that add up to middle term) Perfect Square T: (x – 3)2 or (x + 5)2 not the same as (x2 + 52) Hard T (guess and check, or grouping) C ...
Solving linear equations
... beam model. They will need to code the model in an appropriate way. Refer to the diagram for a balance beam approach. Discuss their solution methods. ...
... beam model. They will need to code the model in an appropriate way. Refer to the diagram for a balance beam approach. Discuss their solution methods. ...
Document
... Which of the following is true for the line x = 2? a.)It is a vertical line. b.)It is a horizontal line. c.)It has a slope of zero. d.)It has a y-intercept of 2. ...
... Which of the following is true for the line x = 2? a.)It is a vertical line. b.)It is a horizontal line. c.)It has a slope of zero. d.)It has a y-intercept of 2. ...
3.1 Solving One-Step Equations
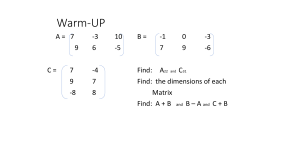
... Flip-flop each side of the equation If a = b then b = a TO SOLVE EVERY EQUATION:(with one variable) Ask Yourself this EVERY time you solve an equation 1. Do Distributive Property. 2. Combine Like Terms. 3. Move all variables to one side. 4. Add/subtract on both sides. 5. Multiply/divide on both si ...
... Flip-flop each side of the equation If a = b then b = a TO SOLVE EVERY EQUATION:(with one variable) Ask Yourself this EVERY time you solve an equation 1. Do Distributive Property. 2. Combine Like Terms. 3. Move all variables to one side. 4. Add/subtract on both sides. 5. Multiply/divide on both si ...