* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet 9 - Midterm 1 Review Math 54, GSI
Vector space wikipedia , lookup
Linear least squares (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Covariance and contravariance of vectors wikipedia , lookup
Capelli's identity wikipedia , lookup
Rotation matrix wikipedia , lookup
Principal component analysis wikipedia , lookup
Jordan normal form wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Eigenvalues and eigenvectors wikipedia , lookup
Singular-value decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Non-negative matrix factorization wikipedia , lookup
Matrix (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Four-vector wikipedia , lookup
Perron–Frobenius theorem wikipedia , lookup
Determinant wikipedia , lookup
Gaussian elimination wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Orthogonal matrix wikipedia , lookup
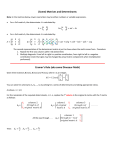
Worksheet 9 - Midterm 1 Review Math 54, GSI: Andrew Hanlon 1 Straightforward problems 1. Is the set of vectors below linearly independent? Do these vectors span all of R4 ? 1 1 10 0 2 6 , , −2 0 −14 0 3 9 2. For the matrix 1 −1 0 2 A = 2 4 8 0 , 0 3 9 1 find a basis for Null(A) and a basis for Col(A). 3. Consider the two matrices below. 1 2 A = 4 3 1 5 1 5 10 B= 2 4 8 Compute AB and BA. 4. Compute the determinant of the matrix below. 2 4 5 1 1 0 −1 1 A= −2 6 −3 3 2 −2 4 4 Is A invertible? 5. Solve the linear system 2 3 5 1 1 0 −1 x = 0 1 −2 1 0 using all three methods that we know (row reduction, finding the inverse matrix, and Cramer’s rule). 2 Intermediate problems 6. Compute the standard matrix of the linear map R2 → R2 that is defined by first rotating counterclockwise by 3π/2 then sending (1, 0) to (1, 1) while fixing (0, 1). 7. Show that there is no 2 × 4 matrix A that has x1 x 2 4 Null(A) = ∈ R : x1 = x2 = x3 = 0 x3 x4 8. Given that det(A) = 2, det(B) = 5, C is obtained by switching two rows of A and multiplying a column by 3, and all three matrices are 3 × 3. Compute the following or say if there is not enough information to uniquely determine the answer: det(AB), det(2A), det(A + B), and det(C). 9. True or false: The subset of n × n matrices consisting of matrices with determinant 1 is a subspace. Justify your answer. 10. True or false: Let Ao be a fixed n × n matrix. Then, the subset of n × n matrices consisting of matrices B that commute with Ao ( this means Ao B = BAo ) is a subspace of Mn×n . Justify your answer. 11. True or false: The determinant of AT A is never negative. Justify your answer. 3 Challenging problems 12. True or false: AT A = AAT for every n × n matrix A. Justify your answer. 13. True or false: Every subspace U ⊂ Rn is the null space (same as kernel) of a linear transformation T : Rn → Rk for some k. Justify your answer. 14. An n × n matrix is said to be symmetric if AT = A and anti-symmetric if AT = −A. Show that the sets of symmetric and anti-symmetric matrices are subspaces of Mn×n . Compute their dimensions and show that the span of vectors in their union is all of Mn×n . 15. Consider R 1the map I : C(R) → R where C(R) is the space of continuous functions on R given by I(f ) = 0 f (t) dt. Check that I is linear. Is I injective? Is I surjective? Find the dimensions of the kernel and range of I when it is restricted to the supspace of polynomials of degree ≤ n, Pn , of C(R). 16. For a vector space V , a linear transformation P : V → V is said to be a projection if P ◦ P = P . Show that P is the identity map on its range. Give an example of a projection.