DSP_Test1_2006
... discrete-time signals. Their z-transforms are as follows: X(z) = … + z3x[3] + z2x[2] + zx[1] + x[0] + z1x[1] + z2x[2] + z3x[3] + … Y(z) = … + z3y[3] + z2y[2] + zy[1] + y[0] + z1y[1] + z2y[2] + z3y[3] + … The multiplication of X(z) and Y(z) results in a new polynomial W(z) = X(z)Y(z). Let ...
... discrete-time signals. Their z-transforms are as follows: X(z) = … + z3x[3] + z2x[2] + zx[1] + x[0] + z1x[1] + z2x[2] + z3x[3] + … Y(z) = … + z3y[3] + z2y[2] + zy[1] + y[0] + z1y[1] + z2y[2] + z3y[3] + … The multiplication of X(z) and Y(z) results in a new polynomial W(z) = X(z)Y(z). Let ...
Math 310, Lesieutre Problem set #7 October 14, 2015 Problems for
... which isn’t in V because 12 + 12 = 2 > 1. This means that V isn’t a subspace. 4.1.5 Let P2 be the vector space of polynomials of degree at most 2. Is the set of polynomials of the form at2 a subset of P2 (where a is a scalar?) It is a subspace. We have (at2 ) + (bt2 ) = (a + b)t2 , which is also of ...
... which isn’t in V because 12 + 12 = 2 > 1. This means that V isn’t a subspace. 4.1.5 Let P2 be the vector space of polynomials of degree at most 2. Is the set of polynomials of the form at2 a subset of P2 (where a is a scalar?) It is a subspace. We have (at2 ) + (bt2 ) = (a + b)t2 , which is also of ...
Math A2 Regents
... 13) The graph of the equation x2 + y2 = 4 can be described as a a) Line passing through points (0, 2) and (2, 0) b) Parabola with its vertex at (0 2) c) Circle with its center at the origin and a radius of 2 d) Circle with its center at the origin and a radius of 4 ...
... 13) The graph of the equation x2 + y2 = 4 can be described as a a) Line passing through points (0, 2) and (2, 0) b) Parabola with its vertex at (0 2) c) Circle with its center at the origin and a radius of 2 d) Circle with its center at the origin and a radius of 4 ...
AR6 Unit 8 REVIEW Understanding and Solving Equations
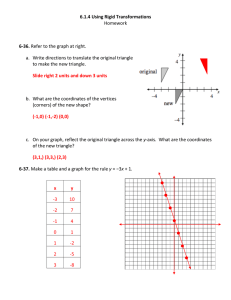
... Create a table of values for x and y using the slope-intercept form equation, y = mx + b. - for the value of m, choose an integer > 2 - for the value of b, choose and integer > 3 - your table should include 4 values each for x and y ...
... Create a table of values for x and y using the slope-intercept form equation, y = mx + b. - for the value of m, choose an integer > 2 - for the value of b, choose and integer > 3 - your table should include 4 values each for x and y ...
1/16/15
... Proposition 0.3. Suppose that {vi }i∈I is a set of eigenvectors of T with associated eigenvalues {λi }i∈I . If λi 6= λj whenever i 6= j then the set {vi }i∈I is linearly independent. Proof. We will prove that for all n less than or equal to the cardinality of I (which may be all n, if I is infinite) ...
... Proposition 0.3. Suppose that {vi }i∈I is a set of eigenvectors of T with associated eigenvalues {λi }i∈I . If λi 6= λj whenever i 6= j then the set {vi }i∈I is linearly independent. Proof. We will prove that for all n less than or equal to the cardinality of I (which may be all n, if I is infinite) ...
file
... change the subject of a formula, where the subject appears on one or both sides of the formula ...
... change the subject of a formula, where the subject appears on one or both sides of the formula ...