24-1 Magnets: permanent & temporary
... two N poles repel as the two S poles N and S pole attract ...
... two N poles repel as the two S poles N and S pole attract ...
Fundamental nuclear symmetries meet classical electrodynamic
... History of magnetism • The magnetic force was known in antiquity – Magnetism more predominant in nature but more difficult to quantify: ...
... History of magnetism • The magnetic force was known in antiquity – Magnetism more predominant in nature but more difficult to quantify: ...
Lecture 9 Source of Magnetic field
... line integral of B ds around any closed path equals moI where I is the total steady current passing through any surface bounded by the closed path: ...
... line integral of B ds around any closed path equals moI where I is the total steady current passing through any surface bounded by the closed path: ...
Magnets - TeacherWeb
... • A material that has strong magnetic properties is called ferromagnetic (ferrum is a latin word for iron.) ...
... • A material that has strong magnetic properties is called ferromagnetic (ferrum is a latin word for iron.) ...
Magnetic field modelling Directional drilling Earth`s magnetic field
... field, generated by dynamo action deep in the molten iron outer core, that protects us from much of the Sun’s radiation. ...
... field, generated by dynamo action deep in the molten iron outer core, that protects us from much of the Sun’s radiation. ...
Guided Reading 15.1
... 4. Draw arrows to show the direction of the magnetic force for each type of interaction. In the box underneath each diagram, write “attract” or “repel” to describe the type of interaction. ...
... 4. Draw arrows to show the direction of the magnetic force for each type of interaction. In the box underneath each diagram, write “attract” or “repel” to describe the type of interaction. ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
Lesson 7 Magnets
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
... When a magnetic material is close to a magnet, it becomes a magnet itself magnet S ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
... groups of atoms are in tiny areas called domains. • The arrangement of domains in an object determines whether the object is magnetic. • When domains move the magnet is demagnetized or looses its magnetic properties. ...
... groups of atoms are in tiny areas called domains. • The arrangement of domains in an object determines whether the object is magnetic. • When domains move the magnet is demagnetized or looses its magnetic properties. ...
lab9 - phys2lab
... separate series would be record, current and α at 15 turns, 10 turns, and 5 turns. With these numbers we could make three graphs of current (I) vs. tanα and realize that they would plot a fairly straight line. To determine the slopes of each graph we would use linear regression. From these slopes we ...
... separate series would be record, current and α at 15 turns, 10 turns, and 5 turns. With these numbers we could make three graphs of current (I) vs. tanα and realize that they would plot a fairly straight line. To determine the slopes of each graph we would use linear regression. From these slopes we ...
A Late Paleozoic association of plants found only on the
... A Late Paleozoic association of plants found only on the Southern Hemisphere continents and India; named for its best‐known genus, Glossopteris. ...
... A Late Paleozoic association of plants found only on the Southern Hemisphere continents and India; named for its best‐known genus, Glossopteris. ...
Plate Tectonics - University of Hawaii at Hilo
... Plate Tectonics Continental drift-evidence for drifting continents Seafloor spreading-evidence for it: Sediment distribution, elevation, paleomagnetism What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic i ...
... Plate Tectonics Continental drift-evidence for drifting continents Seafloor spreading-evidence for it: Sediment distribution, elevation, paleomagnetism What causes the magnetic field of the earth? How is paleomagnetism useful for determining age of rocks. Magnetic field reversals. What is magnetic i ...
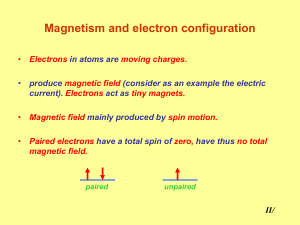
Magnetism and electron configuration
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
... Magnetism and electron configuration • Electrons in atoms are moving charges. • produce magnetic field (consider as an example the electric current). Electrons act as tiny magnets. ...
Magnetic field of the earth OBJEctiVE gEnEral
... geo-dynamo effect. Close to the surface of the earth, this field resembles that of a magnetic dipole with field lines emerging from the South Pole of the planet and circling back towards the North Pole. The angle between the actual magnetic field of the earth and the horizontal at a given point on t ...
... geo-dynamo effect. Close to the surface of the earth, this field resembles that of a magnetic dipole with field lines emerging from the South Pole of the planet and circling back towards the North Pole. The angle between the actual magnetic field of the earth and the horizontal at a given point on t ...
Instructions on how to use a Silva compass
... which ‘quadrant’ the magnetic bearing will be. STEP 2 Align the edge of the baseplate along the direction of travel. The "Direction of Travel" arrow (located on the baseplate) should point toward your destination and away from your starting point. STEP 3 Rotate the dial of the compass so the orienti ...
... which ‘quadrant’ the magnetic bearing will be. STEP 2 Align the edge of the baseplate along the direction of travel. The "Direction of Travel" arrow (located on the baseplate) should point toward your destination and away from your starting point. STEP 3 Rotate the dial of the compass so the orienti ...
Magnetic Earth - Earth Learning Idea
... Use a compass to show pupils that the Earth has a magnetic field which causes the magnetised needle in the compass to align itself north-south. TM Use the Magnaprobe (or a sewing needle that you have magnetised) to demonstrate that the Earth’s magnetic field is also three-dimensional. In TM the U.K. ...
... Use a compass to show pupils that the Earth has a magnetic field which causes the magnetised needle in the compass to align itself north-south. TM Use the Magnaprobe (or a sewing needle that you have magnetised) to demonstrate that the Earth’s magnetic field is also three-dimensional. In TM the U.K. ...
magnetic field - DiMaggio
... The word repel is used when 2 magnets push apart. o Like or same poles repel This attraction or repulsion between magnetic poles is called magnetic ...
... The word repel is used when 2 magnets push apart. o Like or same poles repel This attraction or repulsion between magnetic poles is called magnetic ...
18.1 - Pierce Public Schools
... o Magnetic field created by each iron atom exerting force on others atoms, causing groups of atoms to align to their magnetic poles so all alike poles facing same direction. This group of atoms called magnetic domain. Two types of magnets o Permanent magnets a magnet that’s magnetic domain fixed o ...
... o Magnetic field created by each iron atom exerting force on others atoms, causing groups of atoms to align to their magnetic poles so all alike poles facing same direction. This group of atoms called magnetic domain. Two types of magnets o Permanent magnets a magnet that’s magnetic domain fixed o ...
Magnetism
... (A) toward the right side of the screen (B) toward the top of the screen (C) into the screen (D) out of the screen ...
... (A) toward the right side of the screen (B) toward the top of the screen (C) into the screen (D) out of the screen ...
Forces Study Guide: Magnets
... a. Natural magnets – found in nature (magnetite). Originally discovered 2000 years ago in China and Greece. b. Electromagnets – strong magnets that are created by combining magnets and electricity. c. Permanent magnets – retain their magnetism (harder to make) d. Temporary magnets – lose their magne ...
... a. Natural magnets – found in nature (magnetite). Originally discovered 2000 years ago in China and Greece. b. Electromagnets – strong magnets that are created by combining magnets and electricity. c. Permanent magnets – retain their magnetism (harder to make) d. Temporary magnets – lose their magne ...
Fundamental nuclear symmetries meet classical electrodynamic
... History of magnetism • The magnetic force was known in antiquity – Magnetism more predominant in nature but more difficult to quantify: ...
... History of magnetism • The magnetic force was known in antiquity – Magnetism more predominant in nature but more difficult to quantify: ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.