What is Magnetism?
... Earth’s geographic north pole and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, so a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... Earth’s geographic north pole and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, so a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Book N Chapter 1 Study Guide 1. Magnet: Material with atomic
... North and South poles by curving around the magnetic object. 5. Magnetic Poles: The two ends of a magnet where the magnetic force is the strongest. All magnets have poles that are marked "north/south" or +/-. 6. Magnetic Domain: A group of atoms in a magnet that have electrons spinning in the same d ...
... North and South poles by curving around the magnetic object. 5. Magnetic Poles: The two ends of a magnet where the magnetic force is the strongest. All magnets have poles that are marked "north/south" or +/-. 6. Magnetic Domain: A group of atoms in a magnet that have electrons spinning in the same d ...
Magnetism
... Earth’s magnetic properties Gilbert was a scientist that showed that the Earth behaves as a magnet The Earth’s magnetic field is strongest at the poles The Earth’s magnetic field behaves as if there is a huge bar magnet in it’s centre. ...
... Earth’s magnetic properties Gilbert was a scientist that showed that the Earth behaves as a magnet The Earth’s magnetic field is strongest at the poles The Earth’s magnetic field behaves as if there is a huge bar magnet in it’s centre. ...
Understand Ohm`s law in both microscopic
... Biot Savart Law: be able to use to calculate the magnetic field from simple current elements, e.g. the magnetic field at the center of a circle of radius R carrying current I. Magnetic dipole moment: what is it, how is it directed, what is its magnitude? Torque on a magnetic dipole τ m B . What ...
... Biot Savart Law: be able to use to calculate the magnetic field from simple current elements, e.g. the magnetic field at the center of a circle of radius R carrying current I. Magnetic dipole moment: what is it, how is it directed, what is its magnitude? Torque on a magnetic dipole τ m B . What ...
15 HW 5.1 Magnetism.pub
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
... 10. Which describes magnetic declination? a. the angle between Earth's magnetic field and the Earth's surface b. the Earth's magnetic field strength at the equator c. the tendency for the Earth's magnetic field to reverse itself d. the angle between the geographic north and magnetic south poles ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... Earth, Locations on Earth, and Maps ______ 1. longitude a. any circle that runs east and west around the Earth ______ 2. legend b. semicircle that runs pole to pole ______ 3. parallel c. angular distance north or south of the equator ______ 4. meridian d. a list of map symbols and their meanings ___ ...
... Earth, Locations on Earth, and Maps ______ 1. longitude a. any circle that runs east and west around the Earth ______ 2. legend b. semicircle that runs pole to pole ______ 3. parallel c. angular distance north or south of the equator ______ 4. meridian d. a list of map symbols and their meanings ___ ...
Magnetism
... All atoms have magnetic fields because of the charged particles inside. Most atoms’ magnetic fields point in random directions, so they all cancel each other out. ...
... All atoms have magnetic fields because of the charged particles inside. Most atoms’ magnetic fields point in random directions, so they all cancel each other out. ...
What is Magnetism?
... exact same place, so a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... exact same place, so a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Student
... represented by ________________________. By convention, the lines are drawn ________________________ the north pole and ________________________ the south pole of a magnet. e) Electricity can be used to make magnets. The interaction between magnetism and electricity is called “______________________ ...
... represented by ________________________. By convention, the lines are drawn ________________________ the north pole and ________________________ the south pole of a magnet. e) Electricity can be used to make magnets. The interaction between magnetism and electricity is called “______________________ ...
Forces on Moving Charges in Magnetic Fields Standards
... Forces on Moving Charges in Magnetic Fields Standards Students should understand the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field, so they can: 1) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and B and explain why the magnetic force can perform no work. 2) Dedu ...
... Forces on Moving Charges in Magnetic Fields Standards Students should understand the force experienced by a charged particle in a magnetic field, so they can: 1) Calculate the magnitude and direction of the force in terms of q, v, and B and explain why the magnetic force can perform no work. 2) Dedu ...
magnets ch.18
... 2. p454 The parts of a magnet where the magnetic effects are strongest are called _______. 3. p454 The magnetic effects are strongest near the ______ of the bar magnet. 4. p 455 The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets is called the _____. 5. p 456 A ________ _________ exist ...
... 2. p454 The parts of a magnet where the magnetic effects are strongest are called _______. 3. p454 The magnetic effects are strongest near the ______ of the bar magnet. 4. p 455 The force of repulsion or attraction between the poles of magnets is called the _____. 5. p 456 A ________ _________ exist ...
Facts to Know This is the law of magnetic force: Unlike poles attract
... Magnets exert a force that cannot be seen. Magnets attract or repel things made out of iron, steel, nickel, or cobalt. Magnetism is a force that is all around us, and we use it every day. Some examples are: refrigerator doors, parts of computers, doorbells, televisions, electric can openers, junkyar ...
... Magnets exert a force that cannot be seen. Magnets attract or repel things made out of iron, steel, nickel, or cobalt. Magnetism is a force that is all around us, and we use it every day. Some examples are: refrigerator doors, parts of computers, doorbells, televisions, electric can openers, junkyar ...
Attract Repel To push away, as similar poles of two magnets push
... Long-distance: Something that is far away Magnet: An object that sticks to iron Magnetism: A property of certain kinds of materials that causes them to attract iron or steel Pole: Either of two opposing forces or parts, such as the poles of a magnet Prediction: An educated guess based on data or pre ...
... Long-distance: Something that is far away Magnet: An object that sticks to iron Magnetism: A property of certain kinds of materials that causes them to attract iron or steel Pole: Either of two opposing forces or parts, such as the poles of a magnet Prediction: An educated guess based on data or pre ...
L28
... field in the space around it, just like the Sun produces a gravitational field that holds the planets in their orbits • the magnetic field can be visualized with iron filings ...
... field in the space around it, just like the Sun produces a gravitational field that holds the planets in their orbits • the magnetic field can be visualized with iron filings ...
Magnetism Permanent magnetism Permanent magnets Homemade
... field of the coil aligns these little magnets giving a larger field than that of the coil alone. We say that the nail becomes “magnetized”, but the effect is not permanent. ...
... field of the coil aligns these little magnets giving a larger field than that of the coil alone. We say that the nail becomes “magnetized”, but the effect is not permanent. ...
Magnetism Summary - Don`t Trust Atoms
... magnets pole against a magnetic material in the same direction many times. The magnetic field is the area where a magnet exerts a magnetic force. The closer together the magnetic field lines, the stronger the magnetic force. ...
... magnets pole against a magnetic material in the same direction many times. The magnetic field is the area where a magnet exerts a magnetic force. The closer together the magnetic field lines, the stronger the magnetic force. ...
Magnetism
... The Earth behaves as if there is a huge bar magnet in its centre giving it a magnetic field. ...
... The Earth behaves as if there is a huge bar magnet in its centre giving it a magnetic field. ...
Paleomagnetism
... Detecting the Field • Earth’s magnetic field can’t be seen by the naked eye, and it also can’t be detected by a compass. • Instead, we use a device called a magnetometer which graphs out the changes in the magnetic field. • It is built into a ship or an airplane. ...
... Detecting the Field • Earth’s magnetic field can’t be seen by the naked eye, and it also can’t be detected by a compass. • Instead, we use a device called a magnetometer which graphs out the changes in the magnetic field. • It is built into a ship or an airplane. ...
∫
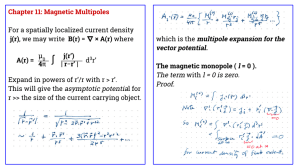
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
... Chapter 11: Magnetic Multipoles For a spatially localized current density j(r), we may write B(r) = ∇ × A(r) where A(r) = ...
Magnetism Review game Thursday
... Last One Standing Rules 1. Two teams: 2 front rows/2 back rows 2. Sit on the table in silence (If you talk you are OUT) 3. Each person receives a question, correct answers stay up, wrong answers sit down. 4. Team with most players still up at the end wins (3 Extra Credit points on the test) ...
... Last One Standing Rules 1. Two teams: 2 front rows/2 back rows 2. Sit on the table in silence (If you talk you are OUT) 3. Each person receives a question, correct answers stay up, wrong answers sit down. 4. Team with most players still up at the end wins (3 Extra Credit points on the test) ...
History of geomagnetism

The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applications to plate tectonics.Magnetism has been known since prehistory, but knowledge of the Earth's field developed slowly. The horizontal direction of the Earth's field was first measured in the fourth century BC but the vertical direction was not measured until 1544 AD and the intensity was first measured in 1791. At first, compasses were thought to point towards locations in the heavens, then towards magnetic mountains. A modern experimental approach to understanding the Earth's field began with de Magnete, a book published by William Gilbert in 1600. His experiments with a magnetic model of the Earth convinced him that the Earth itself is a large magnet.